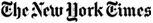This article is by Edmund L. Andrews, Andrew Ross Sorkin and Mary Williams Walsh.
The government faced mounting pressure on Monday to put billions more in some of the nation’s biggest banks, two of the biggest automakers and the biggest insurance company, despite the billions it has already committed to rescuing them.
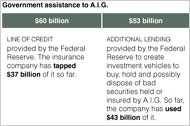
The government’s boldest rescue to date, its $150 billion commitment for the insurance giant American International Group, is foundering. A.I.G. indicated on Monday it was now negotiating for tens of billions of dollars in additional assistance as losses have mounted.
Separately, the Obama administration confirmed it was in discussions to aid Citigroup, the recipient of $45 billion so far, that could raise the government’s stake in the banking company to as much as 40 percent.
The Treasury Department named a special adviser to work with General Motors and Chrysler, two of Detroit’s biggest automakers, which are seeking $22 billion on top of the $17 billion already granted to them.
All these companies’ mushrooming needs reflect just how hard it is to stanch the flow of losses as the economy deteriorates. Even though the government’s finances are being stretched — and still more aid might be needed in the future — it is being forced to fill the growing holes in the finances of these companies out of fear that the demise of an important company could set off a chain reaction.
The deepening global downturn is dragging down all kinds of businesses, and, with no bottom to the recession in sight, investors sent the the Dow industrials down 250.89 points, or 3.7 percent, to 7,114.78, a 3.7 percent drop for the day and a loss of about 50 percent from their peak in the fall of 2007. Asian markets followed suit on Tuesday by flirting with the lows they hit last October, with stocks in Hong Kong dropping more than 3 percent, and Japan's Nikkei 225 index dropping more than 2 percent before rebounding slightly.
In an unexpectedly assertive joint statement after two weeks of bank stock declines, the Treasury Department, the Federal Reserve and federal bank regulatory agencies announced that the government might demand a direct ownership stake in major banks that do not have enough capital to weather a deeper downturn. The government will begin conducting a test of the banks’ financial health this week.
Administration officials emphasized that nationalizing any of the major banks was their least favorite solution to the banking crisis, but they acknowledged that some banks might be both too big to fail and too fragile to endure another round of shocks without substantial help.
Banks that fail the test will have to raise additional capital. If they are unable to raise capital in the private market, they would have to take money from the government in exchange for preferred stock that would be convertible into common shares, thus giving the government a bigger stake.
The administration is debating how big a role to play in the auto businesses, what concessions the companies should make in return for aid and whether bankruptcy should be considered, though it prefers a private sector solution.
On Monday, Steven Rattner, co-founder of a private equity firm, the Quadrangle Group, was named an adviser to the Treasury on the auto industry.
As the administration takes bigger stakes in companies, the value held by existing shareholders is being diluted, which could make it even harder to attract private money in the future.
Timothy F. Geithner, the secretary of the Treasury, recently outlined a bank recovery plan that included a program to attract a combination of public and private money to buy troubled mortgages and other assets.
A.I.G. serves as a cautionary note about the difficulty of luring private investors when the size of the losses is unknown. In the months since the government initially stepped in last fall to take an 80 percent stake in the insurer, the company has suffered deepening losses and has been forced to post more collateral with its trading partners.
The company, according to a person close to the negotiations, is discussing the prospect of converting the government’s $40 billion in preferred shares into common equity.
The prototype could turn out to be Citigroup, which is negotiating with regulators to replace the government’s nonvoting preferred shares with shares that are convertible into common stock.
“We absolutely believe that our private banking system is best off being in private hands and we are trying our best to keep it that way,” said one senior administration official, who spoke on condition of anonymity. But, he continued, the government is already deeply involved in propping up the banking system and may have no choice.
Officials said they were bracing for the possibility of new problems that might indeed require the government to take a more aggressive stance.
“Given our involvement at this particular stage, there is an element, a possibility over time, that we will end up with some ownership of these institutions,” the official said. “This is really about aggressive anticipatory action. It is an acceptance that the future is uncertain, but that we can plan on a certain basis for it.”
Acquiring common stock would give the government more control, but expose it to more risk. Armed with voting shares, government officials would have more power to replace management and change company strategy. But the Treasury would lose its claim to dividend payments, which in Citigroup’s case amount to more than $2.25 billion a year.
A.I.G. declined to provide details of its new financial problems, citing the “quiet period” just before it issues fourth-quarter results. But some people familiar with A.I.G.’s negotiations said it was on the brink of reporting one of the biggest year-end losses in American history.
Such losses lead to a bigger problem. A further credit rating downgrade would force the company to raise more capital, according to a person involved in the negotiations. The losses appeared to be across the board, unlike the insurer’s losses of last September, which were confined mostly to derivative contracts called credit-default swaps.
A.I.G. has not been writing new credit-default swap contracts, and had tried to put the swaps disaster behind it. In November the company worked out a relief package with the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, in which the most toxic of its swap contracts were put into a kind of quarantine, so they could no longer hurt its balance sheet. But A.I.G. had written several other classes of credit-default swaps, which it kept on its books.
If the latest round of losses severely weaken A.I.G.’s capital and its creditworthiness, then its swap counterparties may be entitled to demand that A.I.G. come up with a large amount of cash for collateral — precisely the problem that brought the company to its knees last September.
“They stand, unfortunately, to bring others down with them if they go down,” said Donn Vickrey of Gradient Analytics, an independent research firm.
The difficulty of shoring up A.I.G. must weigh on the administration at this moment. The administration’s banking statement amounted to a plan of action demonstrating a way to demand a major and possibly a controlling stake in systemically important banks like Citigroup and Bank of America.
“They are desperate to not nationalize the banks,” said Robert J. Barbera, chief economist at ITG. “They know what happened when they took Iraq and they would just as soon not take over the banks, because if you own it, you gotta fix it.”