NOAA Restricts Commercial Mackerel, Cod Fishing in Western Aleutians to Protect Western Steller Sea Lions
But finds Eastern Stellers may have recovered enough to be removed from endangered list
December 8, 2010
NOAA’s Fisheries Service today issued its final interim rule to reduce commercial fishing for groundfish stocks in the Aleutian Islands in an effort to provide more food for the endangered western Steller sea lion.
The rule, which would prohibit fishing for Atka mackerel and Pacific cod, the main source of food for the animal, in an area off the western Aleutian Islands, goes into effect Jan. 1, 2011.
Fishing for these species will be prohibited in area 543 of the Aleutian Islands subarea, at the western tip of the Aleutian archipelago (see map below). The rule also further restricts fishing in the remainder of the Aleutian Islands subarea (areas 542 and 541 on map). These protective measures include establishing a three nautical mile buffer around a newly established rookery, new fishing closures for Atka mackerel and Pacific cod in important Steller sea lion critical habitat foraging zones, reductions in Atka mackerel harvest amounts, and varying seasonal closures for various areas targeting Pacific cod.
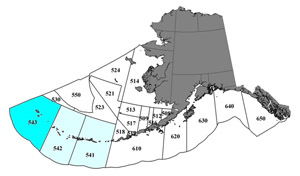
Jan. 1, 2011, fisheries closure map for Atka mackerel and Pacific cod. Fishing for these species will be prohibited in area 543 of the Aleutian Islands subarea, at the western tip of the Aleutian archipelago (see map above). The rule also further restricts fishing in the remainder of the Aleutian Islands subarea (areas 542 and 541 on map).
Download here (Credit: NOAA)
Under the Endangered Species Act, NOAA’s Fisheries Service must ensure that agency actions to allow fisheries do not jeopardize the continued existence of endangered species such as the western Steller sea lion.
The final Alaska groundfish biological opinion, also issued today by NOAA’s Fisheries Service, found that continuing with the current fishing levels and practices is likely to jeopardize the continued existence of the western distinct population segment of Steller sea lions and adversely affect their critical habitat.
The western Steller sea lion is either failing to recover or is declining in the western and central Aleutian Islands sub-regions, with the most serious decline in the westernmost sub-population corresponding to fishing area 543. The animals in the area experienced a 45-percent decline between 2000 and 2008, and according to NOAA scientists, one of the major factors responsible for this decline may be lack of food.
In developing the final biological opinion and the final interim rule, NOAA’s Fisheries Service took into account the proposal recommended by the North Pacific Fishery Management Council at its August meeting, as well as all public comments. The final documents incorporate some elements of the council’s proposal.
Concurrent with the regulatory actions, NOAA’s Fisheries Service continues to investigate Steller sea lion population dynamics, foraging ecology, physiology and biology, as well as effects on sea lions from killer whales, climate change, fisheries, diseases and various pollutants.
NOAA’s Fisheries Service plans to have the Center for Independent Experts review the final biological opinion in spring 2011. The center is a non-governmental organization that provides independent peer review of federal agency science, including NOAA’s Fisheries Service science, to ensure scientific integrity when it is used to make policy decisions.
For more information on the western Steller sea lion and the Alaska Groundfish Biological Opinion and to comment on the final interim rule, please visit http://alaskafisheries.noaa.gov.
While the western Steller sea lion population continues to struggle, NOAA is currently evaluating the status of the eastern Steller sea lion population, which lives east of 144 degree west longitude and may be recovered enough to be removed from the list of endangered and threatened wildlife.
The eastern population, which is listed as threatened under the Endangered Species Act, includes sea lions living in southeast Alaska, British Columbia, California, and Oregon.
NOAA’s Fisheries Service began its status review of the eastern Steller sea lion June 29 to determine whether or not it should be removed from the list of threatened and endangered species (delisted), or reclassified.
On August 30, the states of Washington and Oregon submitted a petition asking that the eastern population be delisted. The state of Alaska submitted a similar petition a day later, September 1.
NOAA’s Fisheries Service today announced its finding on its review of those two petitions that there is now substantial information indicating the species’ recovery, and that delisting may be warranted. NOAA’s Fisheries Service must complete the status review of the eastern Steller sea lion and issue its finding by August 30, 2011, within 12 months of receipt of the first petition.
To ensure a comprehensive review, NOAA’s Fisheries Service will have a 60-day public comment period regarding the status of the eastern Steller sea lion.
Comments should be addressed to:
Assistant Regional Administrator
Protected Resources Division
NOAA Fisheries Alaska Regional Office
Attn: Ellen Sebastian
Comments may be submitted by the following methods:
- Electronically via the Federal eRulemaking Portal, http://www.regulations.gov
- By mail to:
P.O. Box 21668
Juneau, AK 99802-1668
- Hand delivered to:
Juneau Federal Building
709 West 9th Street
Room 420A
Juneau, Alaska
- By fax: 907-586-7557
For more information on the Notice of Finding on the petitions to delist the eastern Steller sea lion, go to http://alaskafisheries.noaa.gov.
NOAA’s mission is to understand and predict changes in the Earth's environment, from the depths of the ocean to the surface of the sun, and to conserve and manage our coastal and marine resources. Visit us on Facebook at http://www.facebook.com/usnoaagov.




