North American Catfishes (Ictaluridae)
With their barbels and scaleless bodies, ictalurids are among the most distinctive North American fishes. Some might also be surprised to learn that Ictaluridae is the largest family of fishes indigenous to North America (Burr and Mayden 1992). Most of this diversity is found in the genus Noturus, a taxon of small, cryptic catfishes, commonly known as madtoms.
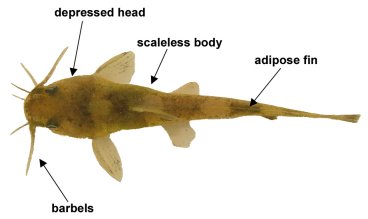
Figure 1. Family level identifiers. Brindled Madtom (Noturus miurus).
Family Level Identifiers (see Fig. 1):
- Head either depressed or moderately depressed
- Scaleless.
- Dorsal fin short and usually with 1 spine.
- Mouth with 8 barbels.
- Adipose fin present.
- More - tips about genus identification
Habitat:
Catfish occupy a variety of freshwater habitats, from wetlands and lakes to rivers and small streams. Most of the physically larger species occupy medium to large river habitats, in addition to lakes and reservoirs. The smaller species (Noturus genus) vary to such a degree that it is difficult to make general statements regrading habitat preference.
Pollution Tolerance:
Generally, catfishes of the Ameirus, Ictalurus and Pylodictis genera are "intermediate species" in terms of pollution tolerance. The pollution intolerant ictalurids are primarily from the Noturus genus (madtoms). The madtoms also account for the majority of the imperiled catfish species, which Etnier (1997) attributes to pollution, altered stream flows, and small ranges. Of the 26 described madtom species, five are federally listed as endangered or threatened (Burr and Stockel, 1999).
Use in IBI:
While there is not a specific metric for ictalurids, there are circumstances when they are used in conjunction with other benthic species. The genus Noturus (madtoms), for example, might be used in conjunction with darters or other benthic insectivores in Metric 2: Number and Identity of Darter Species. Many madtoms are also considered intolerant species, and therefore would be used in Metric 5: Number and Identity of Intolerant Species.
It should also be noted that were alternative insectivore metrics are used, madtoms might also be included in this grouping, as many smaller species feed primarily on mayflies, caddisflies, stoneflies, blackflies and midges.
| Species Name | Common Name | Pollution Tolerance | Habitat Disturbance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ameiurus catus | White Catfish | M | NR |
| Ameiurus melas | Black Bullhead | M | T |
| Ameiurus natalis | Yellow Bullhead | T | MT |
| Ameiurus nebulosus | Brown Bullhead | T | MI |
| Ictalurus furcatus | Blue Catfish | M | MT |
| Ictalurus punctatus | Channel Catfish | M | MT |
| Noturus eleutherus | Mountain Madtom | I | I |
| Noturus exilis | Slender Madtom | I | I |
| Noturus flavus | Stonecat Madtom | I | I |
| Noturus gyrinus | Tadpole Madtom | M | I |
| Noturus insignis | Margined Madtom | M | NR |
| Noturus miurus | Brindled Madtom | I | I |
| Noturus nocturnus | Freckled Madtom | M | MI |
| Noturus stigmosus | Northern Madtom | I | NR |
| Noturus trautmani | Scioto Madtom | I | NR |
| Pylodictis olivaris | Flathead Catfish | M | MT |
| Pollution Tolerance | Habitat Disturbance |
|---|---|
| T = Tolerant | T = Tolerant |
| M = Intermediate | MT = Moderately Tolerant |
| I = Intolerant | MI = Moderately Intolerant |
| NR = No ranking | I = Intolerant |
| NR = No ranking |
![[logo] US EPA](https://cybercemetery.unt.edu/archive/nbii/20120113022229im_/http://www.epa.gov/epafiles/images/logo_epaseal.gif)