Some Screens Miss Spread of Breast Cancer: Study
Bone scans, liver ultrasounds and chest X-rays only caught small number of cases.
By Amanda Gardner
HealthDay Reporter
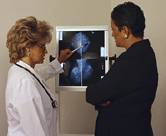
TUESDAY, Sept. 11 (HealthDay News) -- In a new study, three types of screening methods used to determine whether breast cancer has spread to other parts of the body only spotted a small portion of tumors that had done so.
This may mean that bone scans, liver ultrasounds and chest X-rays may not have a significant role to play in tracking the stage a breast cancer is at, particularly for tumors that are diagnosed earlier, the researchers added.
"Very low detection rates, particularly for stage I and II breast cancer, really question the utility of these three [techniques]," said study author Stuart-Allison Moffat Staley, a medical student at the University of North Carolina School of Medicine in Chapel Hill.
Moffat Staley presented her findings Tuesday in San Francisco at the 2012 Breast Cancer Symposium, sponsored by the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
Extravagant ordering of tests can also result in unnecessary biopsies and anxiety, sometimes resulting in more harm than good, added Dr. Andrew Seidman, a medical oncologist at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City.
Both Moffat Staley and Seidman, who is also an ASCO official, spoke at a Tuesday news conference.
When it spreads, breast cancer often travels to the bone, liver and lung, hence the use of these particular scans to assess metastases, Moffat Staley explained. These three techniques are significantly less expensive than two other options that are available, CT scans and MRIs, he noted.
Of course, when used in thousands of breast cancer patients (some of whom undergo all three scans) the practice becomes costly, not only to the health care system but also to individual patients, she added.
In the research, Moffat Staley combined data from eight studies and found detection rates of only 0.51 percent, 0.82 percent, 2.43 percent for chest X-ray, liver ultrasound and bone scans, respectively.
Detection rates were higher for Stage III cancers: about 4.6 percent, 4.2 percent and 12.5 percent, respectively.
At some point, screening will be needed to make sure there's no metastases, as this will determine what kind of treatment a woman will get, noted Dr. Stephanie Bernik, chief of surgical oncology at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York City. She was not involved in the study.
Bone scans, liver ultrasounds and chest X-rays are not necessarily the tests of choice for many doctors. CT scans and PET scans are also often used, Bernik noted.
Moffat Staley stressed that more studies need to be done on this issue, specifically research that compares these three screenings against CT scans, MRIs and PET scans.
Research presented at medical meetings should be considered preliminary because it hasn't undergone the scrutiny of studies published in peer-reviewed journals.
More information
The U.S. National Cancer Institute has more on breast cancer.
(SOURCES: Stephanie Bernik, M.D., chief, surgical oncology, Lenox Hill Hospital, New York City; Sept. 11, 2012, news conference with: Stuart-Allison Moffat Staley, MPH, medical student, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, and Andrew Seidman, M.D., medical oncologist, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York City)
Copyright © 2012 HealthDay. All rights reserved.
HealthDay news articles are derived from various sources and do not reflect federal policy. Womenshealth.gov does not endorse opinions, products, or services that may appear in news stories.
womenshealth.gov
A federal government website managed by the Office on Women's Health in the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health at the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
200 Independence Avenue, S.W. • Washington, DC 20201


 Text size
Text size Email
Email