-
 TCGA discovers potential therapeutic targets for lung squamous cell carcinoma
TCGA discovers potential therapeutic targets for lung squamous cell carcinoma
NCI Press Release
(Posted: 09/10/2012) - After sequencing the genomes of nearly 200 patients, researchers from The Cancer Genome Atlas initiative have identified potential therapeutic targets in lung squamous cell carcinoma, the second most common form of lung cancer. In the image above, squamous lung cancer subtypes are grouped into four columns. The horizontal rows depict genes identified by TCGA and how they differ by subtype.
-
 Gene identified that sensitizes cancer cells to chemotherapy drugs
Gene identified that sensitizes cancer cells to chemotherapy drugs
NCI News Note
(Posted: 08/27/2012) - NCI scientists have found that a gene, Schlafen-11 (SLFN11), sensitizes cells to substances known to cause irreparable damage to DNA. As part of their study, the researchers used a repository of 60 cell types to identify predictors of cancer cell response to classes of DNA damaging agents, widely used as chemotherapy treatments for many cancers.
-
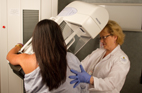 Breast cancer patients with high density mammograms do not have increased risk of death
Breast cancer patients with high density mammograms do not have increased risk of death
NCI Press Release
(Posted: 08/20/2012) - High mammographic breast density, which is a marker of increased risk of developing breast cancer, does not seem to increase the risk of death among breast cancer patients, according to a study led by Gretchen L. Gierach, Ph.D., NCI. In the image above, a physician examines a digital mammogram of a dense breast and points to a potential tumor.
-
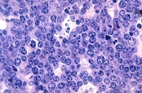 NIH study shows Burkitt lymphoma is molecularly distinct from other lymphomas
NIH study shows Burkitt lymphoma is molecularly distinct from other lymphomas
NCI Press Release
(Posted: 08/13/2012) - Scientists have uncovered a number of molecular signatures in Burkitt lymphoma, including unique genetic alterations that promote cell survival, that are not found in other lymphomas. These findings provide the first genetic evidence that Burkitt lymphoma is a cancer fundamentally distinct from other types of lymphoma.
-
 Study shows colon and rectal tumors constitute a single type of cancer; The Cancer Genome Atlas generates genomic data for colon and rectal cancers that point to potential targets for treatment
Study shows colon and rectal tumors constitute a single type of cancer; The Cancer Genome Atlas generates genomic data for colon and rectal cancers that point to potential targets for treatment
NCI Press Release
(Posted: 07/18/2012) - The pattern of genomic alterations in colon and rectal tissues is the same regardless of anatomic location or origin within the colon or the rectum, leading researchers to conclude that these two cancer types can be grouped as one, according to The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) project's large-scale study of colon and rectal cancer tissue specimens.
-
 NIH tools facilitate matching cancer drugs with gene targets
NIH tools facilitate matching cancer drugs with gene targets
NCI Press Release
(Posted: 07/16/2012) - A new study details how a suite of web-based tools provides the research community with greatly improved capacity to compare data derived from large collections of genomic information against thousands of drugs. By comparing drugs and genetic targets, researchers can more easily identify pharmaceuticals that could be effective against different forms of cancer.The newly updated software, called CellMiner, was built for use with the NCI-60, one of the most widely utilized collections of cancer cell samples employed in the testing of potential anti-cancer drugs
-
 NCI scientists image proteins displayed on HIV surface
NCI scientists image proteins displayed on HIV surface
NCI News Note
(Posted: 07/12/2012) - Using a technique called cryo-electron microscopy, researchers NCI have been able to detect shape changes in a protein called Env that is part of HIV (the human immunodeficiency virus). HIV infection is initiated when Env binds to receptors on host cells.
-
 NCI and the Republic of Peru Sign Statement of Intent
NCI and the Republic of Peru Sign Statement of Intent
NCI News Note
(Posted: 06/21/2012) - The U.S. National Cancer Institute and the Republic of Peru signed a statement of intent to share an interest in fostering collaborative biomedical research in oncology and a common goal in educating and training the next generation of cancer research scientists and clinicians.

-
 Cancer survivorship conference highlights research for survivor care: Biennial conference aims to improve quality and length of life for cancer survivors
Cancer survivorship conference highlights research for survivor care: Biennial conference aims to improve quality and length of life for cancer survivors
NCI Press Release
(Posted: 06/14/2012) - More than 400 leading experts in cancer survivorship convened today for a conference, Cancer Survivorship Research: Translating Science to Care, to focus on such current concerns as how obesity might not have the same effects on all cancer survivors, and the substantial and increasing economic burden of cancer survivorship in the United States. The conference is jointly sponsored by the American Cancer Society’s Behavioral Research Center, the National Cancer Institute’s Office of Cancer Survivorship, the Lance Armstrong Foundation, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
-
 NIH Human Microbiome Project defines normal bacterial makeup of the body; Genome sequencing creates first reference data for microbes living with healthy adults
NIH Human Microbiome Project defines normal bacterial makeup of the body; Genome sequencing creates first reference data for microbes living with healthy adults
NIH Press Release
(Posted: 06/13/2012) - Microbes inhabit just about every part of the human body, living on the skin, in the gut, and up the nose. Sometimes they cause sickness, but most of the time, microorganisms live in harmony with their human hosts, providing vital functions essential for human survival. For the first time, a consortium of researchers organized by the National Institutes of Health has mapped the normal microbial make-up of healthy humans, producing numerous insights and even a few surprises.
News from NCI


