Translational Hepatology Unit Current Project Images
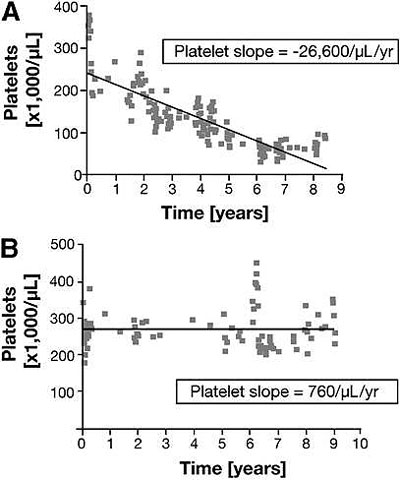
Platelet slopes from representative patients in a CGD cohort who a) died and b) survived to end of follow-up in a cohort of CGD patients. Hepatic involvement and portal hypertension predict mortality in chronic granulomatous disease. Feld JJ, Hussain N, Wright EC, Kleiner DE, Hoofnagle JH, Ahlawat S, Anderson V, Hilligoss D, Gallin JI, Liang TJ, Malech HL, Holland SM, Heller T. Gastroenterology. 2008 Jun;134(7):1917-26.
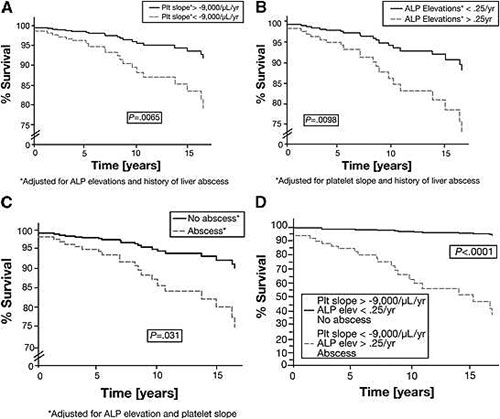
Estimate of the survival function in a cohort of CGD patients for each of the determinants of mortality based on the Cox proportional hazards model. The curves compare the survival estimates for patients with and without a) declining platelet slope b) ALP elevations and c) a history of liver abscess. Each curve is adjusted for all factors in the multivariable Cox model. d) This figure compares the survival function for patients with all three determinants of mortality with that for patients with none of these factors. Hepatic involvement and portal hypertension predict mortality in chronic granulomatous disease. Feld JJ, Hussain N, Wright EC, Kleiner DE, Hoofnagle JH, Ahlawat S, Anderson V, Hilligoss D, Gallin JI, Liang TJ, Malech HL, Holland SM, Heller T. Gastroenterology. 2008 Jun;134(7):1917-26.
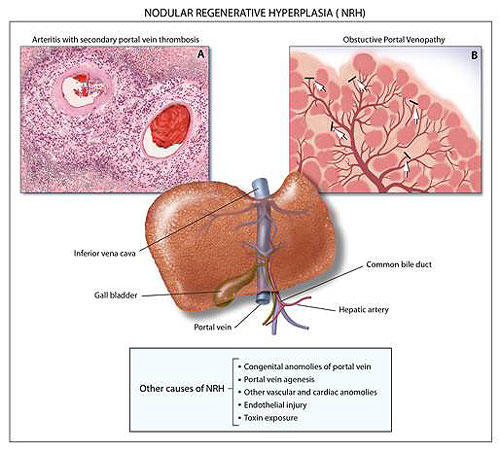
Venopathy as a potential cause of Nodular Regenerative Hyperplasia. Nodular regenerative hyperplasia: not all nodules are created equal. Reshamwala PA, Kleiner DE, Heller T. Hepatology. 2006 Jul;44(1):7-14.
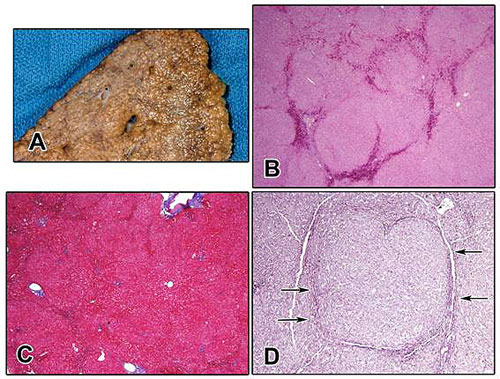
(A) Gross photograph of a resected specimen showing NRH. The liver parenchyma is diffusely transformed into nodules approximately 1 mm in size. There is a superficial resemblance to cirrhosis; however, the nodules are not separated by fibrosis. (B) Low magnification examination shows vague nodularity on routine staining, here enhanced by congestion in areas of atrophy between the nodules (hematoxylin-eosin; original magnification ×4). (C) Staining for collagen with a Masson trichrome shows that there is no significant fibrosis present. (Masson trichrome; original magnification ×4). (D) The diagnosis is most easily made using a reticulin stain, which demonstrates nodules with expanded liver cell plates surrounded by zones of reticulin compression (arrows), where the liver cells are small, atrophic, and pressed together (reticulin; original magnification ×10). Nodular regenerative hyperplasia: not all nodules are created equal. Reshamwala PA, Kleiner DE, Heller T. Hepatology. 2006 Jul;44(1):7-14.
Page last updated: January 24, 2012