Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles
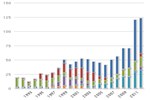
Fuel cell vehicles, powered by hydrogen, have the potential to revolutionize our transportation system. They are more efficient than conventional internal combustion engine vehicles and produce no harmful tailpipe exhaust—their only emission is water. Fuel cell vehicles and the hydrogen infrastructure to fuel them are in an early stage of development. The U.S. Department of Energy is leading government and industry efforts to make hydrogen-powered vehicles an affordable, environmentally friendly, and safe transportation option. Hydrogen is considered an alternative fuel under the Energy Policy Act of 1992 and qualifies for alternative fuel vehicle tax credits.
What is a fuel cell vehicle?
Fuel cell vehicles use a completely different propulsion system than conventional vehicles, which can be two to three times more efficient. Unlike conventional vehicles, they produce no harmful exhaust emissions. Other benefits include increasing U.S. energy security and strengthening the economy.
Fuel cell vehicles can be fueled with pure hydrogen gas stored directly on the vehicle or extracted from a secondary fuel—such as methanol, ethanol, or natural gas—that carries hydrogen. These secondary fuels must first be converted into hydrogen gas by an onboard device called a reformer. Fuel cell vehicles fueled with pure hydrogen emit no pollutants, only water and heat. Vehicles that use secondary fuels and a reformer produce only small amounts of air pollutants.
Fuel cell vehicles can be equipped with other advanced technologies to increase efficiency, such as regenerative braking systems, which capture the energy lost during braking and store it in a large battery. These vehicles are still at an early stage of development. Research and development efforts are bringing them closer to commercialization.
How Fuel Cell Vehicles Work
Like all-electric vehicles, fuel cell vehicles use electricity to power motors located near the vehicle's wheels. In contrast to electric vehicles, fuel cell vehicles produce their primary electricity using a fuel cell powered by hydrogen.
The most common type of fuel cell for vehicle applications is the polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) fuel cell. In a PEM fuel cell, an electrolyte membrane is sandwiched between a positive electrode (cathode) and a negative electrode (anode). Hydrogen is introduced to the anode and oxygen to the cathode. The hydrogen molecules travel through the membrane to the cathode but not before the membrane strips the electrons off the hydrogen molecules.
The electrons are forced to travel through an external circuit to recombine with the hydrogen ions on the cathode side, where the hydrogen ions, electrons, and oxygen molecules combine to form water. The flow of electrons through the external circuit forms the electrical current needed to power a vehicle. See the fuel cell animation to learn more about the process.