Permanent Certification Program
Overview
The Permanent Certification Program (PCP) is the second part of ONC’s two-part approach to establish a transparent and objective certification process, following the Temporary Certification Program (TCP).
The TCP was established to ensure that Certified EHR Technology (CEHRT) be available for adoption by health care providers who seek to qualify for the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) EHR incentive payments beginning in 2011.
The PCP will replace the TCP in summer 2012, and ONC will continue to manage the overall program.
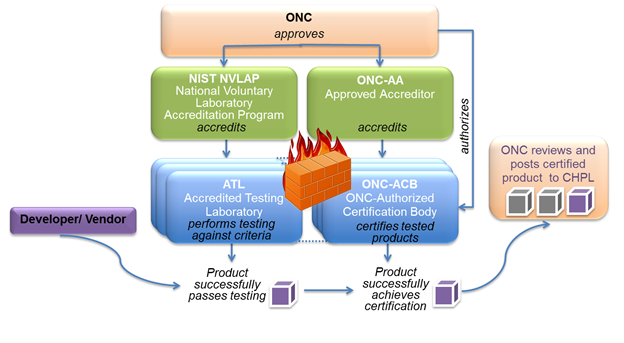
Once the PCP becomes operational, testing and certification activities will be performed by separate entities. Testing will be performed by Accredited Testing Laboratories (ATLs) and certification will be completed by ONC-Authorized Certification Bodies (ONC-ACBs). Developers and Vendors will first test their product with an ATL, and if their product meets the requirements, they will work with an ONC-ACB to certify the product. Once the product is certified, it is submitted to ONC and ONC will post the product on the Certified Health IT Product List (CHPL).
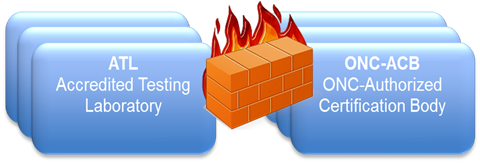
It is possible for a single organization to serve as both an ONC-ACB and an ATL, as long as a firewall is established between testing and certification activities.
Firewall between the ATL and ONC-ACB
Proposed Program Name Change
The name of the Permanent Certification Program has been proposed to change to the ONC HIT Certification Program.
More information is available in the Health Information Technology: Standards, Implementation Specifications, and Certification Criteria for Electronic Health Record Technology, 2014 Edition; Revisions to the Permanent Certification Program for Health Information Technology, Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM).
Background
In January 2011, ONC issued the Final Rule to establish the Permanent Certification Program for Health Information Technology.
In June 2011, ONC approved the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) as the ONC-Approved Accreditor (ONC- AA) for the PCP. The ONC-AA will accredit organizations to certify EHR technology under the PCP. Once these organizations are certified by the ONC-AA, they will apply to ONC for authorization to certify EHR products. Upon authorization, these organizations will become ONC-Authorized Certification Bodies (ONC-ACBs). The National Voluntary Laboratory Accreditation Program (NVLAP) accredits testing laboratories, designating them as Accredited Testing Laboratories (ATLs) in the PCP.
More information about the PCP is available in Final Rule: Establishment of the Permanent Certification Program for Health Information Technology [PDF - 413 KB].
Differences from the Temporary Certification Program
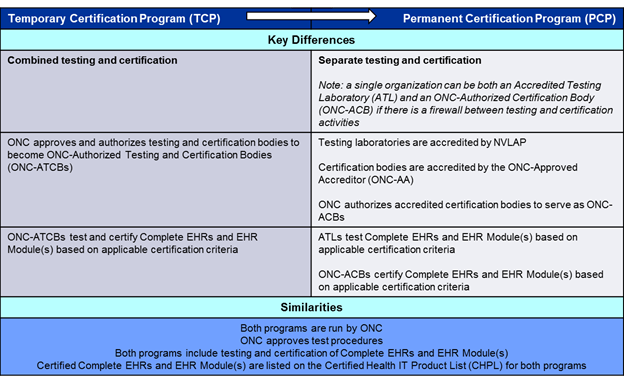
In the PCP, testing and certification will be performed by separate entities. The graphic below further explains the differences and similarities between the Permanent and Temporary Certification Programs.
The major differences and similarities between the Permanent Certification Program and Temporary Certification Program
Program Structure
The graphic below shows the organizational structure of the PCP. As illustrated, ONC manages the overall program.
Permanent Certification Program Overview