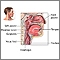
Peritonsillar abscess
Peritonsillar abscess is a collection of infected material in the area around the tonsils.
See also:
Causes
Peritonsillar abscess is a complication of tonsillitis. It is most often caused by a type of bacteria called group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus.
Peritonsillar abscess is usually a disease of older children, adolescents, and young adults. It has become uncommon with the use of antibiotics to treat tonsillitis.
Symptoms
One or both tonsils become infected. The infection may spread over the roof of the mouth (palate), and to the neck and chest, including the lungs. Swollen tissues may block the airway, which is a life-threatening medical emergency.
The abscess can break open (rupture) into the throat, infecting or further blocking the airway.
Symptoms of peritonsillar abscess include:
- Chills
- Difficulty opening the mouth, and pain with opening the mouth
- Difficulty swallowing
- Drooling or inability to swallow saliva
- Facial swelling
- Fever
- Headache
- Muffled voice
- Sore throat (may be severe and is usually on one side)
- Tender glands of the jaw and throat
Exams and Tests
An examination of the throat often shows swelling on one side and on the roof of the mouth.
The uvula in the back of the throat may be shifted away from the swelling. The neck and throat may be red and swollen on one or both sides.
The following tests may be done:
- Aspiration of the abscess
- CT scan
Treatment
If the infection is caught early, you will be given antibiotics. More likely, if an abscess has developed, it will need to be drained with a needle or by cutting it open.
Sometimes, the abscess may be drained and the tonsils removed at the same time. You will be prescribed painkillers.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Peritonsillar abscess usually goes away with treatment, although the infection may return in the future.
Possible Complications
- Airway obstruction
- Cellulitis of the jaw, neck, or chest
- Endocarditis (rare)
- Fluid around the lungs (pleural effusion)
- Inflammation around the heart (pericarditis)
- Pneumonia
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if you have had tonsillitis and you develop symptoms of peritonsillar abscess.
Call your health care provider if you have:
- Difficulty breathing
- Difficulty swallowing
- Pain in the chest
- Persistent fever
- Symptoms that get worse
Prevention
Quickly and completely treating tonsillitis, especially bacterial tonsillitis, may help prevent an abscess.
Alternative Names
Quinsy; Abscess - peritonsillar
References
Shirley WP, Woolley AL, Wiatrak BJ. Pharyngitis and adenotonsillar disease. In: Cummings CW, Flint PW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Otolaryngology: Head & Neck Surgery. 5th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Mosby Elsevier;2010:chap 196.
Melio FR. Upper respiratory tract infections. In: Marx JA, Hockberger RS, Wallis RM, et al, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 7th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Mosby Elsevier;2009:chap 73.
Update Date: 11/23/2010
Updated by: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Medical Director, MEDEX Northwest Division of Physician Assistant Studies, University of Washington, School of Medicine; and Seth Schwartz, MD, MPH, Otolaryngologist, Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, Washington. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.

A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, also known as the American Accreditation HealthCare Commission (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics and subscribes to the principles of the Health on the Net Foundation (www.hon.ch).
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Duplication for commercial use must be authorized in writing by ADAM Health Solutions.