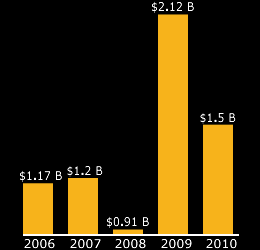
Establishing a safe and healthful working environment requires every employer -- large and small -- and every worker to make safety and health a top priority. The entire work force -- from the CEO to the most recent hire -- must recognize that worker safety and health is central to the mission and key to the profitability of the American company.
Establishing a safe and healthful working environment requires every employer -- large and small -- and every worker to make safety and health a top priority. The entire work force -- from the CEO to the most recent hire -- must recognize that worker safety and health is central to the mission and key to the profitability of the American company.
Occupational Safety and Health Administration's (OSHA) job is to provide leadership and encouragement to workers and employers to take that responsibility seriously. We continue to help employers and employees focus on reducing injuries, illnesses, and fatalities and to increase their commitment to improved safety and health.
OSHA can help small businesses and others through a variety of tools, including partnership, consultation, compliance assistance, education and training, outreach, and plain language regulations.
Why is safety and health important for a small business owner like me?
Safety is good business. An effective safety and health program can save $4 to $6 for every $1 invested. It's the right thing to do, and doing it right pays off in lower costs, increased productivity, and higher employee morale.
As an employer, you have a duty to protect your workers from injury and illness on the job. Protecting workers also makes good business sense. Accidents and injuries are more expensive than many realize. Costs mount up quickly. But substantial savings in workers' compensation and lost workdays are possible when injuries and illnesses decline. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) can help you.









 Establishing a safe and healthful working environment requires every employer -- large and small -- and every worker to make safety and health a top priority. The entire work force -- from the CEO to the most recent hire -- must recognize that worker safety and health is central to the mission and key to the profitability of the American company.
Establishing a safe and healthful working environment requires every employer -- large and small -- and every worker to make safety and health a top priority. The entire work force -- from the CEO to the most recent hire -- must recognize that worker safety and health is central to the mission and key to the profitability of the American company.
 Form W-2 Reporting of Employer-Sponsored Health Coverage
Form W-2 Reporting of Employer-Sponsored Health Coverage If you hire employees there is information that you need to secure for your records and forms that you must complete.
If you hire employees there is information that you need to secure for your records and forms that you must complete.