Food
Determining the Regulatory Status of a Food Ingredient
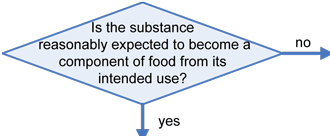
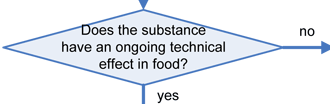
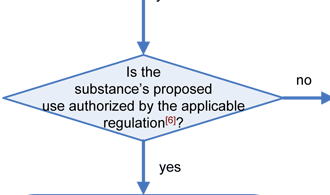
Any substance that is reasonably expected to become a component of food is a food additive that is subject to premarket approval by FDA, unless the substance is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) among experts qualified by scientific training and experience to evaluate its safety under the conditions of its intended use, or meets one of the other exclusions from the food additive definition in section 201(s) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FFDCA). Any food additive that is intended to have a technical effect in the food is deemed unsafe unless it either conforms to the terms of a regulation prescribing its use or to an exemption for investigational use. Otherwise, in accordance with section 409 of the Act, the substance is deemed an unsafe food additive. Any food that contains an unsafe food additive is adulterated under section 402(a)(2)(C) of the FFDCA.
Similarly, any substance that is added to food and imparts color to the food is a color additive (see color additive definition in §201(t) of the FFDCA and 21 CFR 70.3(f)). Any color additive in food is deemed unsafe unless its use is either permitted by regulation or exempt by regulation. Unlike the definition for food additive, there is no GRAS exemption for color additives. Any food that contains an unsafe color additive is adulterated under section 402(c) of the FFDCA.
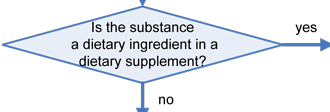
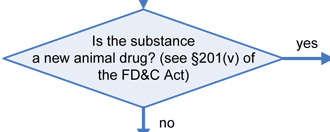
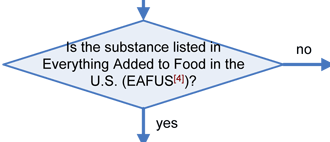
The decision tree below will help in determining the regulatory status of a food ingredient. It is the responsibility of the manufacturer of any food to ensure that all ingredients used are of food-grade purity and comply with specifications and limitations in all applicable authorizations. The overall regulatory status of a food is affected by the regulatory status of each individual food ingredient. To determine compliance, consider each authorization to be composed of three parts:
- the identity of the substance,
- specifications including purity and physical properties, and
- limitations on the conditions of use.
To assure a customer that an ingredient that is being shipped to them is not adulterated or misbranded, the ingredient manufacturer may want to provide a letter of guaranty with the shipment (see 21 CFR 7.13 for suggested forms of guaranty).
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
References:
- Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act)
- Overview of Dietary Supplements
- Determining the Regulatory Status of Components of a Food Contact Material
- Everything Added to Food in the U.S. (EAFUS)
- Codex General Standard for Food Additives (GSFA)
- FDA’s Food and Color Additives Regulations
- Petition Process
- GRAS