News Release Information
BLS-11-167
Thursday, December 1, 2011
Contacts
- Technical Information: (415) 625-2286
- Media Contact: (415) 625-2270, option 1
- BLSInfoSF@bls.gov
- www.bls.gov/ro9
Women's Earnings in Alaska - 2010
In 2010, Alaska women who were full-time wage and salary workers had median weekly earnings of $705 or 74.4 percent of the $948 median weekly earnings for their male counterparts, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported today. Regional Commissioner Richard J. Holden noted that the women’s to men’s earnings ratio in Alaska in 2010 rose 2.2 percentage points from the previous year. Nationwide, women earned $669 or 81.2 percent of the $824 median for men. (See table 1. Earnings in this report do not control for many factors that can be significant in explaining earnings differences.)
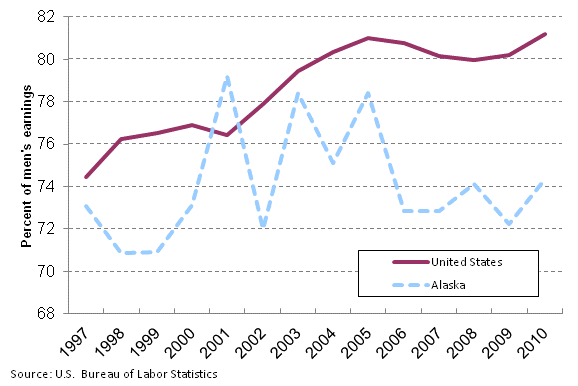
In Alaska, the ratio of women’s to men’s earnings has fluctuated considerably since 1997, ranging from a low of 70.9 percent in both 1998 and 1999 to a high of 79.2 percent just two years later. Since 2006, however, the ratio has never exceeded 75 percent. (See chart 1.)
Among the 50 states, median weekly earnings of women in full-time wage and salary positions in 2010 ranged from $530 in Arkansas to $835 in Connecticut. States with the highest wages for women were located along the Northeastern coastline. In addition to Connecticut, Massachusetts and New Jersey also had wages above $800, and Maryland was close at $798. (See table 1 and See chart 2.)
Across the nation, median weekly earnings for men were lowest in Arkansas at $640 and highest in Connecticut at $1,101, the same pattern that emerged for women. Five of the six states with wages above $950 (Connecticut, Massachusetts, New Jersey, New Hampshire, and Virginia) were located along or close to the east coast. The sole exception was on the west coast—Washington.
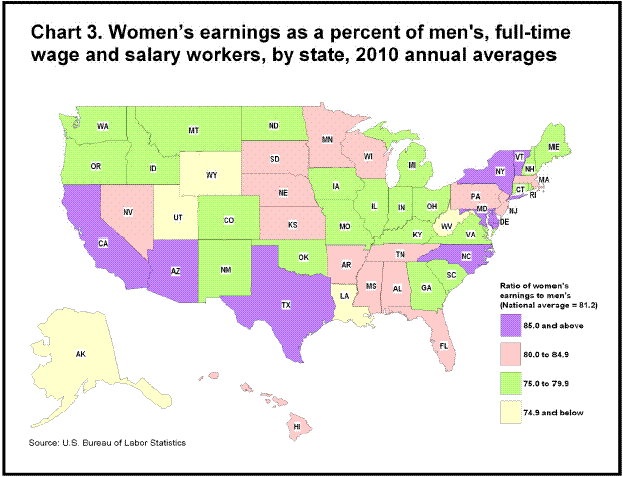
The ratio of female-to-male earnings in 2010 varied across the nation, ranging from 68.8 percent in West Virginia to 91.3 percent in Delaware. Of the eight states with the highest ratios, 85 percent or higher, seven were either in the Northeast or along the border with Mexico, the only exception being North Carolina. (See chart 3.) The differences among the states reflect, in part, variation in the occupations and industries found in each state and in the age composition of each state’s labor force. In addition, comparisons by sex are on a broad level and do not control for factors such as educational attainment, which can be significant in explaining earnings differences.
For more information on the median weekly earnings of women and men, see Bureau of Labor Statistics Report 1031, “Highlights of Women’s Earnings in 2010,” issued July 2011; copies are available on the Internet at www.bls.gov/cps/cpswom2010.pdf or by calling the West Region Information Office at (415) 625-2270. Information in this release is also available to sensory impaired individuals. Voice phone: (202) 691- 5200; Federal Relay Service: 1–800–877–8339.
Technical Note
The estimates in this report were obtained from the Current Population Survey (CPS), which provides a wide range of information on the labor force, employment, and unemployment. This survey is conducted monthly for the Bureau of Labor Statistics by the U.S. Census Bureau, using a national sample of about 60,000 households, with coverage in all 50 states and the District of Columbia. The earnings data are collected from one-fourth of the CPS monthly sample.
Statistics based on the CPS data are subject to both sampling and nonsampling error. The differences among data for the states reflect, in part, variations in the occupation, industry, and age composition of each state’s labor force. In addition, sampling error for the state estimates is considerably larger than it is for the national data.
The principal definitions used in connection with the earnings series in this release are described below.
Usual weekly earnings. Data represent earnings before taxes and other deductions and include any overtime pay, commissions, or tips usually received (at the main job in the case of multiple jobholders).
Median weekly earnings. The median is the amount which divides a given earnings distribution into two equal groups, one having earnings above the median and the other having earnings below the median.
Wage and salary workers. Workers who receive wages, salaries, commissions, tips, payment in kind, or piece rates. The group includes employees in both the private and public sectors but, for the purposes of the earnings series, excludes all self-employed persons, regardless of whether or not their businesses are incorporated.
Full-time worker. Workers who usually work 35 hours or more per week at their sole or principal job.
| State | Both sexes | Women | Men | Women's earnings as percent of men's | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of workers (in thousands) | Median weekly earnings | Standard error of median | Number of workers (in thousands) | Median weekly earnings | Standard error of median | Number of workers (in thousands) | Median weekly earnings | Standard error of median | ||
United States |
99,531 | $747 | $2 | 44,472 | $669 | $3 | 55,059 | $824 | $3 | 81.2 |
Alabama |
1,478 | 661 | 20 | 678 | 597 | 18 | 800 | 709 | 20 | 84.2 |
Alaska |
241 | 827 | 18 | 107 | 705 | 20 | 134 | 948 | 28 | 74.4 |
Arizona |
2,028 | 723 | 11 | 878 | 667 | 17 | 1,150 | 767 | 16 | 87.0 |
Arkansas |
911 | 594 | 9 | 416 | 530 | 14 | 496 | 640 | 18 | 82.8 |
California |
10,999 | 793 | 8 | 4,712 | 747 | 9 | 6,287 | 840 | 13 | 88.9 |
Colorado |
1,727 | 823 | 15 | 728 | 719 | 14 | 998 | 925 | 22 | 77.7 |
Connecticut |
1,195 | 976 | 24 | 524 | 835 | 32 | 672 | 1,101 | 56 | 75.8 |
Delaware |
293 | 760 | 16 | 137 | 735 | 16 | 156 | 805 | 30 | 91.3 |
District of Columbia |
259 | 1,014 | 21 | 131 | 965 | 20 | 128 | 1,103 | 58 | 87.5 |
Florida |
5,804 | 717 | 8 | 2,735 | 647 | 8 | 3,069 | 773 | 11 | 83.7 |
Georgia |
3,198 | 725 | 14 | 1,458 | 637 | 13 | 1,740 | 822 | 27 | 77.5 |
Hawaii |
401 | 732 | 16 | 185 | 658 | 15 | 216 | 797 | 22 | 82.6 |
Idaho |
445 | 666 | 12 | 181 | 585 | 14 | 264 | 754 | 20 | 77.6 |
Illinois |
4,264 | 771 | 10 | 1,865 | 678 | 13 | 2,399 | 872 | 14 | 77.8 |
Indiana |
2,030 | 693 | 15 | 869 | 598 | 13 | 1,160 | 772 | 22 | 77.5 |
Iowa |
1,056 | 700 | 14 | 481 | 622 | 13 | 575 | 786 | 23 | 79.1 |
Kansas |
970 | 689 | 16 | 439 | 611 | 12 | 531 | 763 | 18 | 80.1 |
Kentucky |
1,301 | 650 | 15 | 596 | 581 | 11 | 705 | 743 | 19 | 78.2 |
Louisiana |
1,436 | 682 | 23 | 646 | 582 | 12 | 790 | 834 | 20 | 69.8 |
Maine |
406 | 722 | 15 | 189 | 637 | 19 | 217 | 810 | 30 | 78.6 |
Maryland |
2,148 | 867 | 19 | 1,006 | 798 | 43 | 1,142 | 932 | 32 | 85.6 |
Massachusetts |
2,193 | 946 | 15 | 982 | 832 | 19 | 1,212 | 1,033 | 23 | 80.5 |
Michigan |
2,848 | 768 | 11 | 1,290 | 684 | 14 | 1,558 | 857 | 23 | 79.8 |
Minnesota |
1,856 | 823 | 17 | 819 | 749 | 18 | 1,037 | 903 | 23 | 82.9 |
Mississippi |
854 | 618 | 11 | 406 | 564 | 18 | 449 | 693 | 20 | 81.4 |
Missouri |
1,977 | 725 | 16 | 926 | 616 | 12 | 1,051 | 819 | 22 | 75.2 |
Montana |
280 | 658 | 16 | 128 | 553 | 18 | 152 | 730 | 19 | 75.8 |
Nebraska |
652 | 688 | 13 | 304 | 621 | 14 | 348 | 748 | 18 | 83.0 |
Nevada |
811 | 687 | 12 | 359 | 614 | 8 | 452 | 751 | 14 | 81.8 |
New Hampshire |
486 | 848 | 16 | 213 | 745 | 16 | 273 | 966 | 27 | 77.1 |
New Jersey |
3,074 | 895 | 17 | 1,352 | 824 | 16 | 1,722 | 972 | 19 | 84.8 |
New Mexico |
606 | 688 | 17 | 270 | 605 | 15 | 336 | 780 | 25 | 77.6 |
New York |
6,602 | 798 | 10 | 3,062 | 747 | 7 | 3,540 | 861 | 11 | 86.8 |
North Carolina |
3,049 | 671 | 12 | 1,418 | 622 | 10 | 1,630 | 728 | 17 | 85.4 |
North Dakota |
249 | 689 | 13 | 112 | 603 | 13 | 137 | 764 | 16 | 78.9 |
Ohio |
3,679 | 732 | 8 | 1,668 | 645 | 11 | 2,012 | 817 | 16 | 78.9 |
Oklahoma |
1,202 | 661 | 12 | 542 | 579 | 12 | 660 | 746 | 23 | 77.6 |
Oregon |
1,129 | 754 | 17 | 468 | 659 | 22 | 661 | 828 | 29 | 79.6 |
Pennsylvania |
4,171 | 751 | 7 | 1,835 | 664 | 11 | 2,336 | 822 | 15 | 80.8 |
Rhode Island |
335 | 805 | 22 | 152 | 700 | 26 | 183 | 930 | 30 | 75.3 |
South Carolina |
1,416 | 664 | 10 | 679 | 586 | 16 | 737 | 752 | 19 | 77.9 |
South Dakota |
280 | 651 | 12 | 131 | 598 | 10 | 149 | 716 | 17 | 83.5 |
Tennessee |
2,001 | 639 | 15 | 926 | 589 | 15 | 1,076 | 715 | 26 | 82.4 |
Texas |
8,381 | 665 | 8 | 3,575 | 611 | 7 | 4,806 | 714 | 10 | 85.6 |
Utah |
853 | 717 | 9 | 324 | 620 | 12 | 528 | 841 | 26 | 73.7 |
Vermont |
217 | 754 | 14 | 102 | 696 | 22 | 116 | 807 | 18 | 86.2 |
Virginia |
2,892 | 831 | 18 | 1,351 | 719 | 18 | 1,540 | 956 | 21 | 75.2 |
Washington |
2,193 | 870 | 18 | 938 | 748 | 16 | 1,255 | 978 | 22 | 76.5 |
West Virginia |
566 | 705 | 15 | 244 | 572 | 17 | 321 | 832 | 27 | 68.8 |
Wisconsin |
1,894 | 761 | 12 | 856 | 684 | 17 | 1,037 | 826 | 18 | 82.8 |
Wyoming |
197 | 776 | 15 | 81 | 616 | 14 | 116 | 891 | 17 | 69.1 |
Note: Data refer to persons 16 years and older. |
||||||||||

Last Modified Date: December 1, 2011