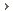Electronic Medical Records and Genomics (eMERGE) Network
- Background
- Network Members
- Sites in Phases I and II
- Additional Sites in Phase II
- External Scientific Panel
- Network Structure
- Phase II Network Biorepositories, EMR Characteristics and Study Samples
- eMERGE Products Dissemination
- Funding Announcements
- Contacts
Background
The Electronic Medical Records and Genomics (eMERGE) Network was announced in September 2007 (RFA HG-07-005). It is a National Institutes of Health (NIH)-organized and funded consortium of U.S. medical research institutions. The Network brings together researchers with a wide range of expertise in genomics, statistics, ethics, informatics, and clinical medicine from leading medical research institutions across the country to achieve its overall goals.
The primary goal of the eMERGE Network is to develop, disseminate, and apply approaches to research that combine DNA biorepositories with electronic medical record (EMR) systems for large-scale, high-throughput genetic research. In eMERGE Phase I (September 2007 - July 2011), each institution participating in the consortium led the studies of the relationship between genetic variation and at least two common human traits among the network participants, using the technique of genome-wide association analysis. Such studies involve testing hundreds of thousands of genetic variants called single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) throughout the genome in people with and without a condition of interest. A fundamental question is whether electronic medical record (EMR) systems can serve as resources for such complex genomic analysis of disease susceptibility and therapeutic outcomes, across diverse patient populations. In addition, the consortium includes a focus on social and ethical issues such as privacy, confidentiality, and interactions with the broader community. During the past four years, the network has established a rich culture of collaboration. During Phase I, the network established a rich culture of collaboration.
Given the success of eMERGE Phase I, the eMERGE Network has transitioned to Phase II (August 2011 - July 2015). A key goal of eMERGE Phase II is to explore the best avenues to incorporate genetic variants into EMR for use in clinical care such as improvement of genetic risk assessment, prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and/or accessibility of genomic medicine (RFA-HG-10-009 and RFA-HG-10-010). Consent, education, regulation and consultation issues related to the use of genomic data in clinical care will also be studied. eMERGE continues to discover genomic variants associated with clinical conditions identified using EMRs and to develop algorithms for electronic phenotyping. To expand the number and diversity of participating eMERGE sites under the currently available budget, two new sites that include racial/ethnic minorities and rural populations were included in the eMERGE Network in 2011. In August 2012, two new sites that include pediatric populations were included in the eMERGE Network.
As eMERGE has become increasingly known in the scientific community, a wide range of institutions are interested in collaboration with eMERGE given that genomic research in biorepositories linked to electronic medical records and application of genomic results to clinical care has been or will be initiated in those institutions. To facilitate collaboration, external institutions may apply for affiliate membership to the eMERGE Network. Information about affiliate membership such as benefits, criteria for participation, and application process can be found at the eMERGE webpage.
Network Members
Sites in Phases I and II
- Group Health Cooperative with the University of Washington [ghc.org]
Principal Investigator (PI): Gail Jarvik, M.D., Ph.D.
Principal Investigator (PI): Eric Larson, M.D., M.P.H.
- Marshfield Clinic [marshfieldclinic.org]
Principal Investigator (PI) Cathy McCarty, Ph.D., M.P.H.
- Mayo Clinic [mayoclinic.com]
Principal Investigator (PI): Chris Chute, M.D., Ph.D.
Principal Investigator (PI): Iftikhar Kullo, M.D.
- Northwestern University [northwestern.edu]
Principal Investigator (PI): Rex Chisholm, Ph.D.
Principal Investigator (PI): Maureen Smith, M.S., C.G.C.
- Vanderbilt University [vanderbilt.edu]
Principal Investigator (PI): Dan Roden, M.D.
Additional Sites in Phase II
- Geisinger [geisinger.org]
Principal Investigator (PI): David Carey, Ph.D.
Principal Investigator (PI): Marc Williams, M.D. - Mount Sinai School of Medicine [mssm.edu]
Principal Investigator (PI): Erwin Böttinger, M.D. - The eMERGE Coordinating Center at Vanderbilt University
Principal Investigator (PI): Jonathan Haines, Ph.D.
Additional Pediatric Sites in Phase II
- Children's Hospital of Philadelphia [chop.edu]
Principal Investigator (PI): Hakon Hakonarson, M.D. - Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center [cincinnatichildrens.org]
Boston Children's Hospital [childrenshospital.org]
Principal Investigator (PI): John Harley, M.D., Ph.D.
Principal Investigator (PI): Isaac Kohane, M.D., Ph.D.
External Scientific Panel
- Howard McLeod (Chair): University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill
- Eta Berner: University of Alabama, Birmingham
- Jeffrey Botkin: University of Utah
- Charis Eng: Cleveland Clinic Foundation
- Gerardo Heiss: University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill
- Stan Huff: Intermountain Healthcare
- Jeff Murray: University of Iowa
- Lisa Parker: University of Pittsburgh
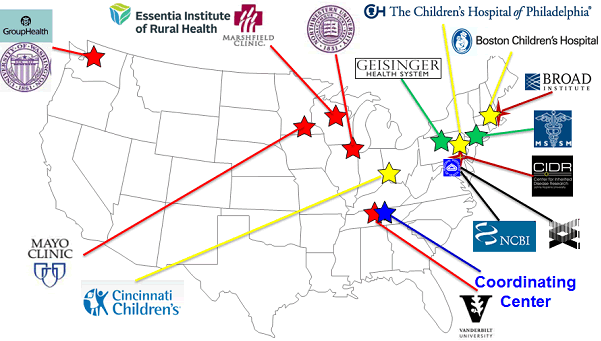
Network Structure
- The Steering Committee is the governing body for the consortium and is composed of the Principal Investigators from each institution and the NIH Project Scientist.
- An External Scientific Panel provides input to the NHGRI Director about the progress and direction of the Network.
- The Coordinating Center provides centralized support and infrastructure for eMERGE Phase II programs.
- The Genotyping Centers provide genotyping service under CLIA certification for clinical actionable genetic variants.
- The Consent, Education, Regulation, and Consultation (CERC) group explores models for informing patients, physicians, and the public about the proper use of genomic data and return of clinically relevant findings.
- The Electronic Health Records (EHR) Integration group focuses on creating standards for representing genomic data and developing clinical-decision support tools for its use.
- The Genomics workgroup reviews site-specific genotyping data, performs quality control procedures, and imputes genotyping data for inclusion in network-wide analyses.
- The Phenotyping workgroup identifies efficient, effective, and transportable phenotyping methods in order to complete Network phenotyping.
- The Return of Results workgroup defines standards for clinical actionability and determines what genetic variants meet these standards.
- The eMERGE-PGx Initiative is a Network collaboration with Pharmacogenomics Research Network (PGRN) that seeks to return pharmacogenomic variants of known significance to EMRs for clinical care and to identify pharmacogenomic variants of unknown significance.
Phase II Network biorespositories, EMR Characteristics, and study samples
| Institution | Repository size and race/ethnic distribution | EMR description | GWA study size (female participation) | Genotyping methods | Primary Phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children's Hospital of Philadelphia |
40,000 51% EA, 38% AA, 4% Asian, 6%HL |
Epic EMR since 2001 |
8,000 (50% female) |
Illumina 550 610Q, 660W, or Affymetrix 6.0, DMET |
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), asthma, atopic dermatitis, attention- deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), lipids |
| Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, Boston Children's Hospital |
Combined:
40,000 83.8% EA, 9.8% AA, 3.3% HL, 2.1% Asian, 3.1% other |
CCHMC: Epic EMR since early 2000s BCH: Cerner since early 1990s |
5,586 (41.9% female) |
Affymetrix 6.0, 550 or Illumina 660W Quad, 1M-Duo, 1M-Quad, OMNI-1, OMNI-5 |
Autism, eosinophilic esophagitis, absence seizures, hypertrophic left heart, juvenile idiopathic arthritis |
| Geisinger Health System |
19,650; 99.4% EA |
Epic EMR since 1996 |
4,191 (47.5% female) |
Illumina OmniExpress or Metabochip |
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA), Extreme Obesity and Related Conditions, and Anti-Psychotic Induced Weight Gain |
| Group Health, University of Washington |
91% EA, 3.7% EA, 3.7%AA 2.8% Asian, 3.5% other |
EpicCare EMR since 2004 |
3,575 (57% female) |
Illumina 660W-Quad or OmniExpress |
Dementia, White Blood Cell Indices, drug response, infectious disease susceptibility, longitudinal traits, and incidental findings of chromosomal abnormalities |
| Marshfield Clinic |
20,000; 99% EA |
Internally developed EMR (CattailsMD) since 1960 | 4,987 (58.4% female) |
Illumina 660W-Quad or Affymetrix 6.0 |
Cataracts, Diabetic Retinopathy, other eye diseases, and drug response |
| Mayo Clinic |
19,000; 93.5% EA |
GE Centricity and Cerner | 6,940 (38% female) |
Illumina 660W-Quad, HumanHap 550, 550/610 |
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD), Red Blood Cell Indices, coronary heart disease (CHD), adverse drug response |
| Mt. Sinai School of Medicine |
21,000; 24.1% EA, 30.6% AA, 43.8% HL, 1.5% Asian or NA |
Epic EMR since 2000 |
16,000 (52.4% female) |
Affymetrix 6.0 or OmniExpress |
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD), Coronary Arterial Disease (CAD), hepatitis C/liver disease |
| Northwestern University |
10,500; 67.7% EA, 19.7% AA, 4.8% Asian, 2.8% NA, 8.5% other |
Epic outpatient and Cerner inpatient EMRs |
4,962 (83% female) |
Illumina 1M-Duo, 660W-Quad, or OmniExpress |
Type 2 Diabetes, Height and Lipids Profile |
| Vanderbilt University | >140,000; 56% EA, 34% AA, 10% other |
Internally developed EMR (StarChart) since 2000 |
33,228 (58.9% female) |
Illumina 660W-Quad, 1M-Duo, or ADME |
QRS Duration, Hypothyroidism, Resistant Hypertension, Twenty-five Diseases for Phenome-wide Association |
Key:
EA: European Americans
AA: African Americans
HL: Hispanic/Latino
NA: Native American
eMERGE Products Dissemination
- Model Consent Language
- Phenotyping Library
- Software Packages
- PheKB: Collaborative environment for building and validating electronic phenotype algorithms
- eleMAP: Data harmonization tool
- DARRT: Re-identification risk and mitigation software
- Phenome-Wide Association Studies (PheWAS): The software and code translation file can be downloaded
- Steering Committee Minutes Coming Soon
- Network Publications
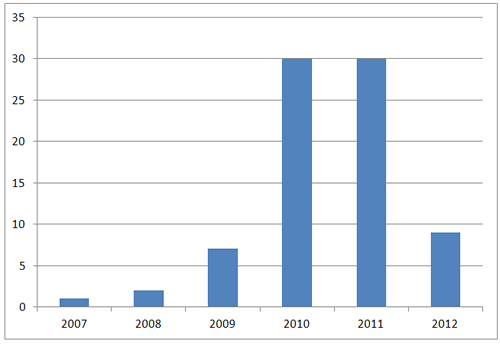
Number of eMERGE Publications by Year (though June 2012)
Funding Announcements
- RFA-HG-11-022: [grants.nih.gov] The Electronic Medical Records and Genomics (eMERGE) Network, Phase II - Pediatric Study Investigators (U01)
- RFA HG-10-010: [grants.nih.gov] The Electronic Medical Records and Genomics (eMERGE) Network, Phase II - Coordinating Center (U01)
- RFA HG-10-009: [grants.nih.gov] The Electronic Medical Records and Genomics (eMERGE) Network, Phase II - Study Investigators (U01)
- RFA-HG-07-005: [grants.nih.gov] Genome-Wide Studies in Biorepositories with Electronic Medical Record Data (U01)
Frequently Asked Questions for RFA - HG-11-022: The Electronic Medical Records and Genomics (eMERGE) Network, Phase II - Pediatric Study Investigators (U01)
Frequently Asked Questions for RFA - HG-10-009: The Electronic Medical Records and Genomics (eMERGE) Network, Phase II - Study Investigators (U01)
Contacts
Last Updated: July 19, 2012