

| ||
| May 6, 2005 [posted] June 7, 2005 [note added] | ||
| RSS Feeds Available from PubMed® | ||
|
[Editor's Note: This feature was implemented in PubMed on June 2, 2005.]
You can set up multiple PubMed searches for RSS feeds. PubMed RSS feeds will include citations retrieved by your PubMed searches since the last time you were connected to your RSS reader. To add PubMed searches to your collection of RSS feeds, run a search in PubMed and choose RSS Feed from the Send to pull-down menu (see Figure 1). 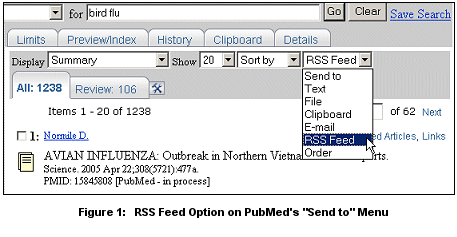
This will take you to the RSS Options Page where you may name the feed and limit the number of items to be displayed by each feed (see Figure 2). If the number of citations retrieved is greater than your "limit" number, you will have the option to link to PubMed to see the entire retrieval. 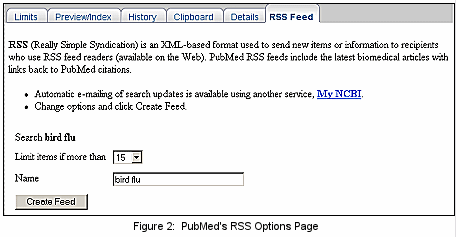
After clicking the Create Feed button, the system will generate an XML icon (see Figure 3). 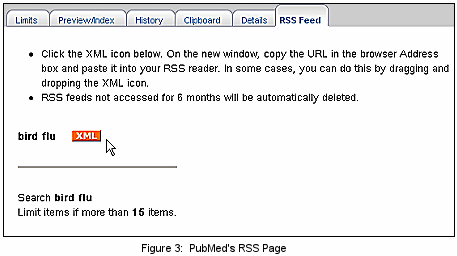
Click the XML icon to display a screen of XML. You don't need the code, just the the URL from the address line (see Figure 4). Copy and paste this into the "subscribe" form located in your RSS reader. Web Browsers and RSS readers may use different options to copy the feed. 
Once you have successfully subscribed to a PubMed RSS feed you will receive daily messages in your RSS reader (see Figure 5). 
RSS Update Strategy Searches for RSS feeds that include Search field tags or some Limits use an abbreviated "What's New" search to ensure that all citations are retrieved. This approach may result in some duplication of citations. Searches that include these search tags or their aliases AU, PS, IP, TA, LA, PG, TI, TIAB, or VI use the following: Query AND T1 : T2 [EDAT]. Searches that include the Search Field tags (may be in addition to other tags) AD, FILTER, SB, RN, MAJR, MESH, PT, SI, SH, NM, or TW, use the strategy: Query AND T1 : T2 [MHDA]
RSS or Automatic E-mailed Updates?
Technical Support for RSS Readers
By Kathi Canese Canese, K. RSS Feeds Available from PubMed®. NLM Tech Bull. 2005 May-Jun;(344):e2. | ||

 ubMed will soon offer RSS 2.0 (Really Simple Syndication) feeds. RSS is a Web standard for the delivery of news and other frequently updated content provided by Web sites. An RSS reader is required to use this service on your computer and retrieve new items from PubMed. There are numerous RSS readers from which to choose and many are available to download free from the Web. Different RSS readers behave and display data differently. The following is an example of the process for setting up an RSS feed. Not all readers will behave the same way.
ubMed will soon offer RSS 2.0 (Really Simple Syndication) feeds. RSS is a Web standard for the delivery of news and other frequently updated content provided by Web sites. An RSS reader is required to use this service on your computer and retrieve new items from PubMed. There are numerous RSS readers from which to choose and many are available to download free from the Web. Different RSS readers behave and display data differently. The following is an example of the process for setting up an RSS feed. Not all readers will behave the same way.