General Information About Breast Cancer
Key Points for This Section
Breast cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the breast.
The breast is made up of lobes and ducts. Each breast has 15 to 20 sections called lobes, which have many smaller sections called lobules. Lobules end in dozens of tiny bulbs that can produce milk. The lobes, lobules, and bulbs are linked by thin tubes called ducts.
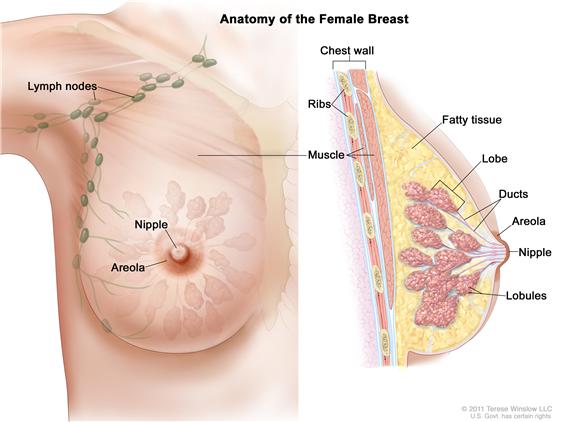
Each breast also has blood vessels and lymph vessels. The lymph vessels carry an almost colorless fluid called lymph. Lymph vessels lead to organs called lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are small bean-shaped structures that are found throughout the body. They filter lymph and store white blood cells that help fight infection and disease. Clusters of lymph nodes are found near the breast in the axilla (under the arm), above the collarbone, and in the chest.
See the following PDQ summaries for more information about breast cancer:
Breast cancer is the second most common type of cancer in American women.
Women in the United States get breast cancer more than any other type of cancer except skin cancer. The number of new cases of breast cancer has stayed about the same since 2003. Breast cancer is second to lung cancer as a cause of cancer death in American women. However, deaths from breast cancer have decreased a little bit every year for the past several years. Breast cancer also occurs in men, but the number of new cases is small.


 Back to Top
Back to Top