What Is COPD?
COPD, or chronic obstructive pulmonary (PULL-mun-ary) disease, is a progressive disease that makes it hard to breathe. "Progressive" means the disease gets worse over time.
COPD can cause coughing that produces large amounts of mucus (a slimy substance), wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and other symptoms.
Cigarette smoking is the leading cause of COPD. Most people who have COPD smoke or used to smoke. Long-term exposure to other lung irritants—such as air pollution, chemical fumes, or dust—also may contribute to COPD.
Overview
To understand COPD, it helps to understand how the lungs work. The air that you breathe goes down your windpipe into tubes in your lungs called bronchial (BRONG-ke-al) tubes or airways.
Within the lungs, your bronchial tubes branch into thousands of smaller, thinner tubes called bronchioles (BRONG-ke-ols). These tubes end in bunches of tiny round air sacs called alveoli (al-VEE-uhl-eye).
Small blood vessels called capillaries (KAP-ih-lare-ees) run through the walls of the air sacs. When air reaches the air sacs, oxygen passes through the air sac walls into the blood in the capillaries. At the same time, carbon dioxide (a waste gas) moves from the capillaries into the air sacs. This process is called gas exchange.
The airways and air sacs are elastic (stretchy). When you breathe in, each air sac fills up with air like a small balloon. When you breathe out, the air sacs deflate and the air goes out.
In COPD, less air flows in and out of the airways because of one or more of the following:
- The airways and air sacs lose their elastic quality.
- The walls between many of the air sacs are destroyed.
- The walls of the airways become thick and inflamed.
- The airways make more mucus than usual, which can clog them.
Normal Lungs and Lungs With COPD
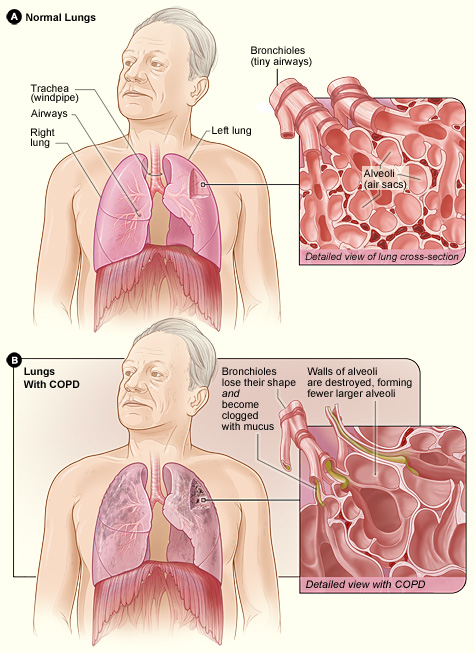
Figure A shows the location of the lungs and airways in the body. The inset image shows a detailed cross-section of the bronchioles and alveoli. Figure B shows lungs damaged by COPD. The inset image shows a detailed cross-section of the damaged bronchioles and alveolar walls.
In the United States, the term "COPD" includes two main conditions—emphysema (em-fih-SE-ma) and chronic bronchitis (bron-KI-tis). (Note: The Health Topics article about bronchitis discusses both acute and chronic bronchitis.)
In emphysema, the walls between many of the air sacs are damaged. As a result, the air sacs lose their shape and become floppy. This damage also can destroy the walls of the air sacs, leading to fewer and larger air sacs instead of many tiny ones. If this happens, the amount of gas exchange in the lungs is reduced.
In chronic bronchitis, the lining of the airways is constantly irritated and inflamed. This causes the lining to thicken. Lots of thick mucus forms in the airways, making it hard to breathe.
Most people who have COPD have both emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Thus, the general term "COPD" is more accurate.
Outlook
COPD is a major cause of disability, and it's the third leading cause of death in the United States. Currently, millions of people are diagnosed with COPD. Many more people may have the disease and not even know it.
COPD develops slowly. Symptoms often worsen over time and can limit your ability to do routine activities. Severe COPD may prevent you from doing even basic activities like walking, cooking, or taking care of yourself.
Most of the time, COPD is diagnosed in middle-aged or older adults. The disease isn't passed from person to person—you can't catch it from someone else.
COPD has no cure yet, and doctors don't know how to reverse the damage to the airways and lungs. However, treatments and lifestyle changes can help you feel better, stay more active, and slow the progress of the disease.
Featured Video
The NHLBI "Grand Opportunity" Exome Sequencing Project

If you have COPD or think you might be at risk, you can take steps to make breathing easier and live a longer and more active life. Get a simple breathing test and talk with your doctor or health care provider about treatment options.
The NHLBI developed the national COPD Learn More Breathe Better® campaign to increase awareness of COPD. The campaign aims to help people with COPD and those at risk get diagnosed early, understand their treatment options, and live better with the disease.
Learn more about key campaign events, activities, and resources.
Clinical trials are research studies that explore whether a medical strategy, treatment, or device is safe and effective for humans. To find clinical trials that are currently underway for COPD, visit www.clinicaltrials.gov.
November 21, 2011
COPD awareness continues to rise, new NIH survey finds
Awareness of COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), the nation’s third leading killer, continues to rise in the United States, according to the results of a Web-based survey released today by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) of the National Institutes of Health.
More than 10,000 volunteers are taking part in an NHLBI-sponsored clinical study to learn more about the role of genetics in COPD. NHLBI grantee Dr. Edwin Silverman discusses this research and the vital role that volunteers play in advancing medical knowledge in this video.
The NHLBI updates Health Topics articles on a biennial cycle based on a thorough review of research findings and new literature. The articles also are updated as needed if important new research is published. The date on each Health Topics article reflects when the content was originally posted or last revised.














 The NHLBI "Grand Opportunity" Exome Sequencing Project
The NHLBI "Grand Opportunity" Exome Sequencing Project COPDGene—Research on the Role of Genetics in COPD
COPDGene—Research on the Role of Genetics in COPD