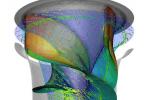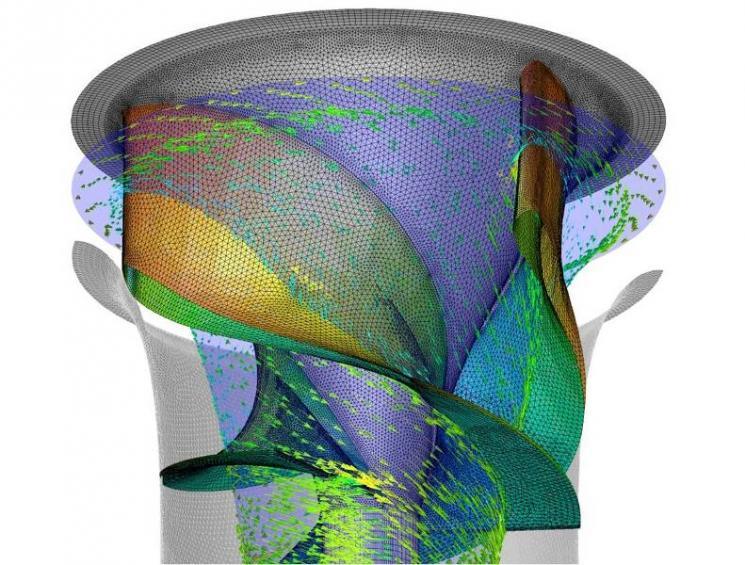
A revolutionary new turbine technology for hydropower plants is one step closer to its first commercial deployment. At peak performance, an Alden turbine should convert about 94 percent of the water’s energy into usable electricity, comparable or superior to the efficiency of traditional turbines; the overall wildlife survival rate should be over 98 percent, up from 80-85 percent for a traditional turbine. Read more.
Aerosols -- tiny particles like soot and dust — in our atmosphere can make a difference in weather, as well as climatic warming and cooling. Studying these tiny particles could lead to improvements in global climate models.
The Energy Department's mobile climate facility makes a stop in the Ganges Valley in India. Find out how studying the relation of aerosols to monsoons will inform our climate studies.
Accurate weather forecasts are critical for making energy sources -- including wind and solar -- dependable and predictable.