On this Page
The Public Health Approach to Violence Prevention
The focus of public health is on the safety and well-being of entire populations. A unique aspect of the field is that it strives to provide services that benefit the largest number of people.
Public health draws on a science base that is multi-disciplinary. It relies on knowledge from a broad range of disciplines including medicine, epidemiology, sociology, psychology, criminology, education, and economics.1 This broad knowledge base has allowed the field of public health to respond successfully to a range of health conditions across the globe.
 The field also emphasizes input from diverse sectors including health, education, social services, justice, and policy.1 Collective action on the part of these stakeholders can help in addressing problems like violence.
The field also emphasizes input from diverse sectors including health, education, social services, justice, and policy.1 Collective action on the part of these stakeholders can help in addressing problems like violence.
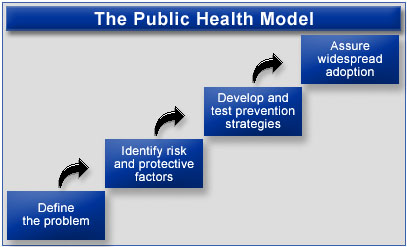
The public health approach is a four-step process that is rooted in the scientific method. It can be applied to violence and other health problems that affect populations.
Step 1: Define and Monitor the Problem
The first step in preventing violence is to understand the "who", "what", "when", "where" and "how" associated with it. Grasping the magnitude of the problem involves analyzing data such as the number of violence-related behaviors, injuries, and deaths. Data can demonstrate how frequently violence occurs, where it is occurs, trends, and who the victims and perpetrators are. These data can be obtained from police reports, medical examiner files, vital records, hospital charts, registries, population-based surveys, and other sources.
Step 2: Identify Risk and Protective Factors
It is not enough to know the magnitude of a public health problem. It is important to understand what factors protect people or put them at risk for experiencing or perpetrating violence. Why are risk and protective factors useful? They help identify where prevention efforts need to be focused.
Risk factors do not cause violence. The presence of a risk factor does not mean that a person will always experience violence. Victims are never responsible for the harm inflicted upon them.
Definitions
- Risk Factor - Characteristic that increases the likelihood of a person becoming a victim or perpetrator of violence.
- Protective Factor - Characteristic that decreases the likelihood of a person becoming a victim or perpetrator of violence because it provides a buffer against risk.
Step 3: Develop and Test Prevention Strategies
Research data and findings from needs assessments, community surveys, stakeholder interviews, and focus groups are useful for designing prevention programs. Using these data and findings is known as an evidence-based approach to program planning. Once programs are implemented, they are evaluated rigorously to determine their effectiveness.
Step 4: Assure Widespread Adoption
Once prevention programs have been proven effective, they must be implemented and adopted more broadly. Communities are encouraged to implement evidence-based programs and to evaluate the program's success. Dissemination techniques to promote widespread adoption include training, networking, technical assistance, and evaluation.
Reference
1. Dahlberg LL, Krug EG. Violence-a global public health problem. In: Krug E, Dahlberg LL, Mercy JA, Zwi AB, Lozano R, eds. World Report on Violence and Health. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2002:1-56.
Contact Us:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
National Center for Injury Prevention and Control (NCIPC)
4770 Buford Hwy, NE
MS F-63
Atlanta, GA 30341-3717 - 800-CDC-INFO
(800-232-4636)
TTY: (888) 232-6348
New Hours of Operation:
8am-8pm ET/
Monday-Friday
Closed Holidays - cdcinfo@cdc.gov



