Cellulite
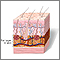
Cellulite is fat that is deposited in pockets just below the surface of the skin. It occurs around the hips, thighs, and buttocks. Because it is very close to the surface of the skin, cellulite leads to a dimpled appearance.
Information
Cellulite may be more visible than fat deeper in the body. Even thin people can have cellulite, because we all have layers of fat just below the surface of the skin. Collagen fibers that connect fat to the skin may stretch, break down, or pull tight, allowing the fat cells to bulge out. This creates the rippled look of cellulite.
Your genes may play a part in whether or not you have cellulite. A poor diet, "fad" dieting, a slow metabolism, hormone changes, and even dehydration may play a role. A great deal of money is spent by people who want to rid themselves of cellulite, but no amount of weight loss, exercise, massages, wraps, creams, supplements, or surgery has proven to effectively eliminate it once you have it. Liposuction, for instance, is not recommended for cellulite, and may even make it look worse.
Although many dermatologists and cosmetic surgeons recognize cellulite as a legitimate problem that patients seek to have them "cure," most of the medical community doesn't view cellulite as a disorder. Instead, it is considered a normal condition of many women and some men.
Tips for avoiding cellulite include:
- Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and fiber
- Staying hydrated with plenty of fluids
- Exercising regularly to keep muscles toned and bones strong
- Maintaining a healthy weight (no yo-yo dieting)
- Not smoking
References
Khan MH, Victor F, Rao B, Sadick NS. Treatment of cellulite: Part I. Pathophysiology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010 Mar;62(3):361-70.
Khan MH, Victor F, Rao B, Sadick NS. Treatment of cellulite: Part II. Advances and controversies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010 Mar;62(3):373-84.
Burns JL, Blackwell SJ. Plastic surgery. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 18th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders Elsevier; 2007:chap 73.
Update Date: 10/10/2010
Updated by: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Medical Director, MEDEX Northwest Division of Physician Assistant Studies, University of Washington, School of Medicine. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.

A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, also known as the American Accreditation HealthCare Commission (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics and subscribes to the principles of the Health on the Net Foundation (www.hon.ch).
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Duplication for commercial use must be authorized in writing by ADAM Health Solutions.