Basic Information About Breast Cancer
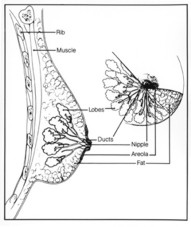
A breast is made up of three main parts: glands, ducts, and connective tissue. The glands produce milk. The ducts are passages that carry milk to the nipple. The connective tissue (which consists of fibrous and fatty tissue) connects and holds everything together.
What Is a Normal Breast?
No breast is typical. What is normal for you may not be normal for another woman. Most women say their breasts feel lumpy or uneven. The way your breasts look and feel can be affected by getting your period, having children, losing or gaining weight, and taking certain medications. Breasts also tend to change as you age.
Lumps in the Breast
Many conditions can cause lumps in the breast, including cancer. But most breast lumps are caused by other medical conditions. The two most common causes of breast lumps are fibrocystic breast condition and cysts. Fibrocystic condition causes noncancerous changes in the breast that can make them lumpy, tender, and sore. Cysts are small fluid-filled sacs that can develop in the breast.
Common Kinds of Breast Cancer
There are different kinds of breast cancer. The kind of breast cancer depends on which cells in the breast turn into cancer. Breast cancer can begin in different parts of the breast, like the ducts or the lobes.
Common kinds of breast cancer are—
- Ductal carcinoma. The most common kind of breast cancer. It begins in the cells that line the milk ducts in the breast, also called the lining of the breast ducts.
- Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). The abnormal cancer cells are only in the lining of the milk ducts, and have not spread to other tissues in the breast.
- Invasive ductal carcinoma. The abnormal cancer cells break through the ducts and spread into other parts of the breast tissue. Invasive cancer cells can also spread to other parts of the body.
- Lobular carcinoma. In this kind of breast cancer, the cancer cells begin in the lobes, or lobules, of the breast. Lobules are the glands that make milk.
- Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS). The cancer cells are found only in the breast lobules. Lobular carcinoma in situ, or LCIS, does not spread to other tissues.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma. Cancer cells spread from the lobules to the breast tissues that are close by. These invasive cancer cells can also spread to other parts of the body.
Uncommon Kinds of Breast Cancer
There are several other less common kinds of breast cancer, such as Paget's disease or inflammatory breast cancer. For more information, visit the National Cancer Institute's Inflammatory Breast Cancer and Paget Disease of the Nipple: Questions and Answers.

Contact Us:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Division of Cancer Prevention and Control
4770 Buford Hwy NE
MS K-64
Atlanta, GA 30341 - 800-CDC-INFO
(800-232-4636)
TTY: (888) 232-6348 - Contact CDC-INFO


