General Information About Colon Cancer
Key Points for This Section
- Colon cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the colon.
- Age and health history can affect the risk of developing colon cancer.
- Possible signs of colon cancer include a change in bowel habits or blood in the stool.
- Tests that examine the colon and rectum are used to detect (find) and diagnose colon cancer.
- Certain factors affect prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options.
Colon cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the colon.
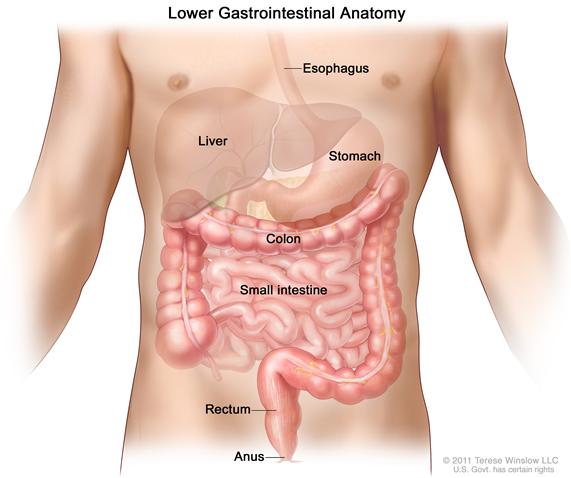
The colon is part of the body’s digestive system. The digestive system removes and processes nutrients (vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and water) from foods and helps pass waste material out of the body. The digestive system is made up of the esophagus, stomach, and the small and large intestines. The first 6 feet of the large intestine are called the large bowel or colon. The last 6 inches are the rectum and the anal canal. The anal canal ends at the anus (the opening of the large intestine to the outside of the body).
See the PDQ summary about Unusual Cancers of Childhood for information about colorectal cancer in children.
Age and health history can affect the risk of developing colon cancer.
Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors doesn’t mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your doctor if you think you may be at risk. Risk factors include the following:
- Age 50 or older.
- A family history of cancer of the colon or rectum.
- A personal history of cancer of the colon, rectum, ovary, endometrium, or breast.
- A history of polyps (small pieces of bulging tissue) in the colon.Enlarge
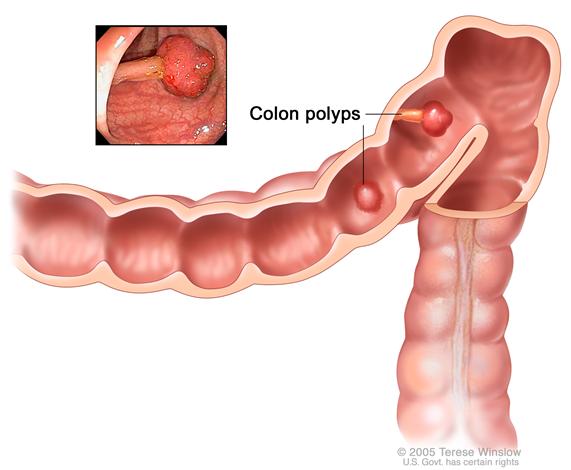 Polyps in the colon. Some polyps have a stalk and others do not. Inset shows a photo of a polyp with a stalk.
Polyps in the colon. Some polyps have a stalk and others do not. Inset shows a photo of a polyp with a stalk. - A history of ulcerative colitis (ulcers in the lining of the large intestine) or Crohn disease.
- Certain hereditary conditions, such as familial adenomatous polyposis and hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer (HNPCC; Lynch Syndrome).
Possible signs of colon cancer include a change in bowel habits or blood in the stool.
These and other symptoms may be caused by colon cancer. Other conditions may cause the same symptoms. Check with your doctor if you have any of the following problems:
- A change in bowel habits.
- Blood (either bright red or very dark) in the stool.
- Diarrhea, constipation, or feeling that the bowel does not empty completely.
- Stools that are narrower than usual.
- Frequent gas pains, bloating, fullness, or cramps.
- Weight loss for no known reason.
- Feeling very tired.
- Vomiting.
Tests that examine the colon and rectum are used to detect (find) and diagnose colon cancer.
The following tests and procedures may be used:
- Physical exam and history: An exam of the body to check general signs of health, including checking for signs of disease, such as lumps or anything else that seems unusual. A history of the patient’s health habits and past illnesses and treatments will also be taken.
- Digital rectal exam: An exam of the rectum. The doctor or nurse inserts a lubricated, gloved finger into the rectum to feel for lumps or anything else that seems unusual.
- Fecal occult blood test: A test to check stool (solid waste) for blood that can only be seen with a microscope. Small samples of stool are placed on special cards and returned to the doctor or laboratory for testing.
- Barium enema: A series of x-rays of the lower gastrointestinal tract. A liquid that contains barium (a silver-white metallic compound) is put into the rectum. The barium coats the lower gastrointestinal tract and x-rays are taken. This procedure is also called a lower GI series.Enlarge
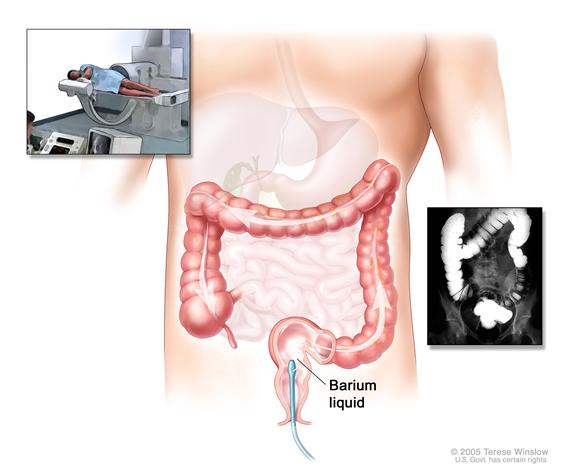 Barium enema procedure. The patient lies on an x-ray table. Barium liquid is put into the rectum and flows through the colon. X-rays are taken to look for abnormal areas.
Barium enema procedure. The patient lies on an x-ray table. Barium liquid is put into the rectum and flows through the colon. X-rays are taken to look for abnormal areas. - Sigmoidoscopy: A procedure to look inside the rectum and sigmoid (lower) colon for polyps (small pieces of bulging tissue), abnormal areas, or cancer. A sigmoidoscope is inserted through the rectum into the sigmoid colon. A sigmoidoscope is a thin, tube-like instrument with a light and a lens for viewing. It may also have a tool to remove polyps or tissue samples, which are checked under a microscope for signs of cancer.Enlarge
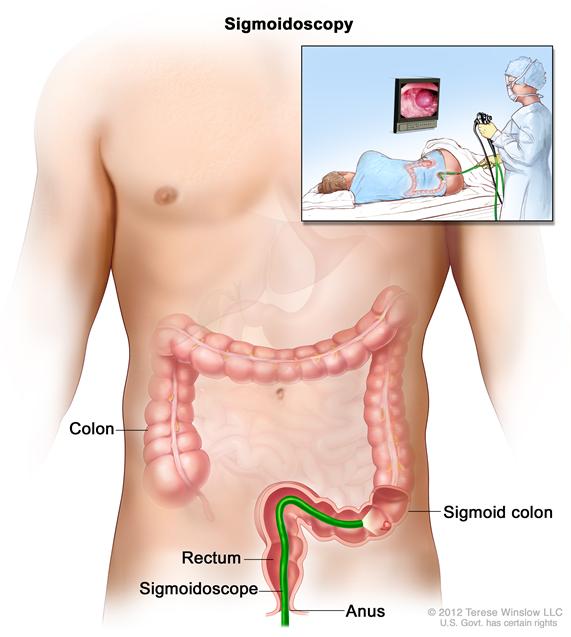 Sigmoidoscopy. A thin, lighted tube is inserted through the anus and rectum and into the lower part of the colon to look for abnormal areas.
Sigmoidoscopy. A thin, lighted tube is inserted through the anus and rectum and into the lower part of the colon to look for abnormal areas. - Colonoscopy: A procedure to look inside the rectum and colon for polyps, abnormal areas, or cancer. A colonoscope is inserted through the rectum into the colon. A colonoscope is a thin, tube-like instrument with a light and a lens for viewing. It may also have a tool to remove polyps or tissue samples, which are checked under a microscope for signs of cancer.Enlarge
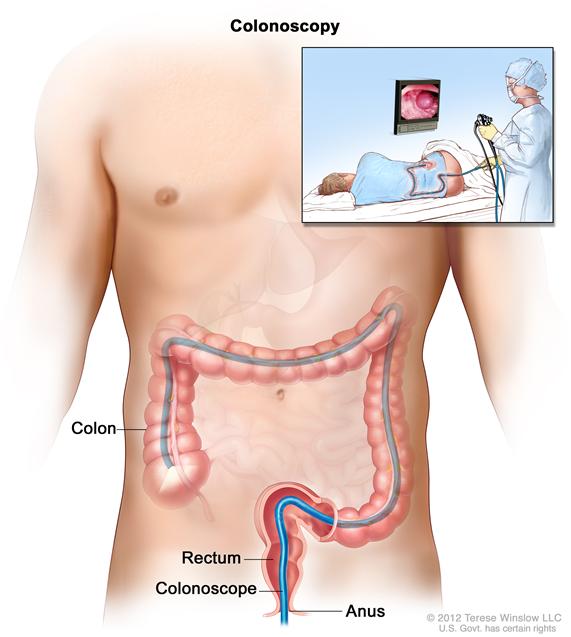 Colonoscopy. A thin, lighted tube is inserted through the anus and rectum and into the colon to look for abnormal areas.
Colonoscopy. A thin, lighted tube is inserted through the anus and rectum and into the colon to look for abnormal areas. - Virtual colonoscopy: A procedure that uses a series of x-rays called computed tomography to make a series of pictures of the colon. A computer puts the pictures together to create detailed images that may show polyps and anything else that seems unusual on the inside surface of the colon. This test is also called colonography or CT colonography.
- Biopsy: The removal of cells or tissues so they can be viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer.
Certain factors affect prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options.
The prognosis (chance of recovery) depends on the following:
- The stage of the cancer (whether the cancer is in the inner lining of the colon only, involves the whole colon, or has spread to other places in the body).
- Whether the cancer has blocked or created a hole in the colon.
- Whether there are any cancer cells left after surgery.
- The blood levels of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA; a substance in the blood that may be increased when cancer is present) before treatment begins.
- Whether the cancer has recurred.
- The patient’s general health.
Treatment options depend on the following:
- The stage of the cancer.
- Whether the cancer has recurred.
- The patient’s general health.



 Back to Top
Back to Top