What Is Geothermal Energy?
The word geothermal comes from the Greek words geo (earth) and therme (heat). So, geothermal energy is heat from within the Earth. We can recover this heat as steam or hot water and use it to heat buildings or generate electricity.
Geothermal energy is a renewable energy source because the heat is continuously produced inside the Earth.
Geothermal Energy Is Generated Deep Inside the Earth
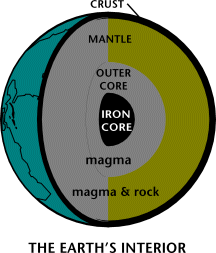
Source: Adapted from a National Energy Education Development Project graphic (Public Domain)
Geothermal energy is generated in the Earth's core. Temperatures hotter than the sun's surface are continuously produced inside the Earth by the slow decay of radioactive particles, a process that happens in all rocks. The Earth has a number of different layers:
- The core itself has two layers: a solid iron core and an outer core made of very hot melted rock, called magma.
- The mantle surrounds the core and is about 1,800 miles thick. It is made up of magma and rock.
- The crust is the outermost layer of the Earth, the land that forms the continents and ocean floors. It can be 3 to 5 miles thick under the oceans and 15 to 35 miles thick on the continents.
The Earth's crust is broken into pieces called plates. Magma comes close to the Earth's surface near the edges of these plates. This is where volcanoes occur. The lava that erupts from volcanoes is partly magma. Deep underground, the rocks and water absorb the heat from this magma. The temperature of the rocks and water gets hotter and hotter as you go deeper underground.
People around the world use geothermal energy to heat their homes and to produce electricity by digging deep wells and pumping the heated underground water or steam to the surface. We can also make use of the stable temperatures near the surface of the Earth to heat and cool buildings.



