Tuberculosis
- Topics
- Basic TB Facts
- Treatment
- Testing & Diagnosis
- TB & HIV Coinfection
- Infection Control & Prevention
- Drug-Resistant TB
- TB in Specific Populations
- African-American Community
- Correctional Facilities
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Strengthen TB Information Systems and Program Assessment
- Strengthen TB Environmental Controls and Isolation Practices
- Provide More Comprehensive and Timely Screening and Diagnostic Evaluations
- Develop and Strengthen Contact Investigation Protocols
- Increase HIV Counseling and Testing
- Increase Staff Training
- Strengthen Collaboration Between Health Departments and Jails
- International Travelers
- Pregnancy
- Disaster Responders
- Children
- Vaccines & Immunizations
- Laboratory Information
- Drug Susceptibility Testing
- The Uses of Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests for the Diagnosis of TB
- Rapid Molecular Testing to Detect Drug-Resistant TB in the US
- Executive Summary
- Introduction
- Background on Tests for Molecular Detection of DR
- General Considerations and Principles for a Molecular DR Testing Service�
- Possible Scenarios and Scope of Testing for a Molecular DR Testing Service
- Research Needs
- General Recommendations of the Expert Panel
- Communication Plan for the Report
- Recommendations
- References
- Panel Members and CDC Participants
- Appendix 1
- Appendix 2
- Appendix 3
- Interim Laboratory Biosafety Guidance for XDR Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains
- Molecular Detection of Drug Resistance (MDDR)
- Research
- TB Epidemiologic Studies Consortium
- Background
- Infrastructure
- Research Projects
- Publications
- Meetings
- Directory
- TBESC Committee Members
- Translating Research into Practice (TRIP)
- Contact TBESC
- Prospective Evaluation of Immunogenetic and Immunologic Markers for Susceptibility to Tuberculosis Infection and Progression from M. Tuberculosisinfection to active TB
- Zero Tolerance for Pediatric TB
- Models for Incorporating HIV Counseling, Testing, and Referral into Tuberculosis Contact Investigations
- Prevalence of Latent TB Infection Among High Risk Populations in the United States
- Regional Capacity-Building in Low-Incidence Areas
- Use of Network Analysis Methods to Characterize M. tuberculosis Transmission Patterns Among Women and Other High-Risk Populations
- An Analysis of Molecular Epidemiology of Multi-Drug Resistant M. tuberculosisin the United States
- Missed Opportunities for TB Prevention in Foreign-Born Population in the United States and Canada
- New Model for Assessing TB Surveillance and Action Performance and Cost
- Addressing TB Among African Americans in the Southeast: Identifying and Overcoming Barriers to Treatment Adherence for Latent TB Infection and TB Disease
- Assessing the TB Knowledge, Attitudes, Beliefs, and Practices Among Private Providers Serving Foreign-born Populations at Risk for TB
- Factors Associated with Acceptance of, Adherence to and Toxicity From Treatment for Latent TB Infection and Pilot Study of Treatment for Latent TB Infection Effectiveness
- Culturally Appropriate TB Educational Materials for Leaders and Staff of Hispanic Service Organizations
- Enhancing TB Programs� Capacity for Self-Evaluation: Testing New Tools and Developing an Evaluation Toolkit
- African Refugee Women�s Health Improvement Project
- Evaluation of the TK Medium: A New Rapid Solid Culture System for Tuberculosis
- Evaluation of New Interferon-y Release Assays in the Diagnosis of Latent TB Infection in Health Care Workers
- Request for Proposal
- TB Trials Consortium
- Behavioral & Social Science Research
- TB Epidemiologic Studies Consortium
- Data & Statistics
- Education & Training
- Resources for TB Programs
- Publications & Products
- Fact Sheets
- General
- Fact sheets - Spanish
- TB - General Information
- The Difference Between Latent TB Infection and Active TB Disease
- Diferencia entre la infección de tuberculosis latente y enfermedad de tuberculosis activa
- A Global Perspective on TB
- Tuberculosis Information for Employers in Non-Healthcare Settings
- Bovine Tuberculosis in Humans
- Tuberculosis Information for International Travelers
- TB Can Be Treated
- Exposure to TB
- TB and HIV/AIDS
- You Can Prevent TB
- Testing for TB
- Tuberculosis: informaci�n general
- Diferencia entre la infecci�n de tuberculosis latente y enfermedad de tuberculosis activa
- Informaci�n sobre la tuberculosis para los viajeros internacionales
- Exposición a la tuberculosis
- Usted puede prevenir la tuberculosis
- La tuberculosis puede ser tratada
- Tuberculosis y VIH/SIDA
- Usted puede prevenir la tuberculosis
- Pruebas para detectar la tuberculosis
- Data & Statistics
- A Global Perspective on TB
- Trends in Tuberculosis – United States
- The Revised Report of Verified Case of Tuberculosis
- The National Tuberculosis Indicators Project (NTIP)
- National Tuberculosis Indicators Project (NTIP): Frequently Asked Questions
- TB Genotyping
- TB Genotyping Information Management System (TB GIMS)
- Drug-Resistant TB
- Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis (MDR TB)
- Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis (XDR TB)
- CDC’s Role in Preventing Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis (XDR TB)
- Tuberculosis multirresistente (MDR)
- Tuberculosis extremadamente resistente (XDR)
- El papel de los CDC en la prevenci�n de la tuberculosis extremadamente resistente (XDR)
- Infection Control & Prevention
- TB in Specific Populations
- Tuberculosis Information for Employers in Non-Healthcare Settings
- Tuberculosis in Minorities
- Tuberculosis Information for International Travelers
- TB and HIV/AIDS
- Recommendations for Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Screening in Tuberculosis (TB) Clinics
- Treatment of Drug-Susceptible Tuberculosis Disease in HIV-Infected Persons
- Tuberculosis in Blacks
- Tuberculosis and Pregnancy
- Tuberculosis y embarazo
- Treatment
- TB Can Be Treated
- Treatment of Latent TB Infection
- Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection: Maximizing Adherence
- Treatment Options for Latent Tuberculosis Infection
- Treatment of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis
- Treatment of Drug-Susceptible Tuberculosis Disease in Persons Not Infected with HIV
- Treatment of Drug-Susceptible Tuberculosis Disease in HIV-Infected Persons
- Tratamiento de la infecci�n de tuberculosis latente
- Testing & Diagnosis
- TB Can Be Treated
- Testing for TB
- Recommendations for Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Screening in Tuberculosis (TB) Clinics
- Interferon-Gamma Release Assays (IGRAs)
- Tuberculin Skin Testing
- Diagnosis of Tuberculosis Disease
- Targeted Tuberculin Testing and Interpreting Tuberculin Skin Test Results
- Prueba cutánea de la tuberculina
- Diagnóstico de la tuberculosis activa
- Vaccines & Immunizations
- General
- Guidelines
- Guides & Toolkits
- Core Curriculum
- Self-Study Modules
- Report of Verified Case of Tuberculosis (RVCT)
- Forging Partnerships to Eliminate TB
- Understanding the TB Cohort Review Process
- Latent Tuberculosis Infection: A Guide for Primary Health Care Providers
- Effective TB Interviewing for Contact Investigation
- Mantoux Tuberculin Skin Testing Products
- Ethnographic Guides
- Newsletters
- Pamphlets, Brochures, Booklets
- Posters
- Mantoux Tuberculin Skin Test Wall Chart
- World TB Day
- Afiches
- 2011 Poster (English)
- 2011 Poster (Spanish)
- 2010 Poster (English)
- 2010 Poster (Spanish)
- 2008 Poster (English)
- 2008 Poster (Spanish)
- 2006 Poster (English)
- 2004 Poster (English)
- 2004 Poster (Spanish)
- 2003 Poster (English)
- 2003 Poster (Spanish)
- 2003 Now is the Time Poster (English)
- 2003 Now is the Time Poster (Spanish)
- Think TB
- Stop TB
- Reports & Articles
- Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Reports (MMWRs)
- Contact Investigations
- Control and Elimination
- Data & Statistics
- Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis
- Infection Control & Prevention
- Laboratory
- TB in Specific Populations
- Foreign-Born
- High-Risk Settings
- Homeless
- International
- Occupational Groups
- Travel
- TB & HIV
- Testing & Diagnosis
- Treatment
- LTBI Updates
- Vaccines & Immunizations
- World TB Day
- DTBE Authored Journal Articles
- Tuberculosis Laboratory Aggregate Reports
- Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Reports (MMWRs)
- Slide Sets
- Core Curriculum
- Self-Study Modules
- Prevention and Control of Tuberculosis in Correctional and Detention Facilities
- Guidelines for Preventing the Transmission of M. TB in Health care Settings
- Investigation of Contacts of Persons with Infectious TB
- Text-Only version
- Introduction
- Decisions to Initiate a Contact Investigation
- Investigating the Index Patient and Sites of Transmission
- Assigning Priorities to Contacts
- Diagnostic and Public Health Evaluation of Contacts
- Medical Treatment for Contacts with LTBI
- When to Expand a Contact Investigation
- Communicating Through the News Media
- Data Management and Evaluation of Contact Investigations
- Confidentiality and Consent in Contact Investigations
- Staff Training for Contact Investigations
- Contact Investigations in Special Circumstances
- Source-Case Investigations
- Cultural Competency and Social Network Analysis
- Resources
- Epidemiology of Pediatric Tuberculosis in the United States
- Text-Only version
- Introduction
- Pediatric TB Cases by Age and Race
- Pediatric TB Cases by Origin of Birth
- Pediatric Cases, Percentages and Rates by States
- Pediatric TB Cases by Case Verification Criterion and Site of Disease
- Pediatric TB Cases in Specific Groups
- Pediatric TB Cases Case Completion
- Slide 1
- Slide 2
- Slide 3
- Slide 4
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- Slide 7
- Slide 8
- Slide 9
- Slide 10
- Slide 11
- Slide 12
- Slide 13
- Slide 14
- Slide 15
- Slide 16
- Slide 17
- Slide 18
- Slide 19
- Slide 20
- Slide 21
- Slide 22
- Slide 23
- Slide 24
- Slide 25
- Slide 26
- Slide 27
- Slide 28
- Slide 29
- Slide 30
- Slide 31
- Treatment of TB
- Targeted Tuberculosis Testing and Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection
- CD Roms
- Electronic Tools & Resources
- Web-Based Courses & Webinars
- Fact Sheets
- Global TB
- Events
- Links
- About Us
- Mission Statement and Activities
- Organization Chart
- Advisory Groups
- Federal TB Task Force
- Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Introduction
- Chronology in the Development of This Report
- Strategies for Maintaining Control of TB
- Strategies for Accelerating the Decline of TB
- Activities for Developing New Tools
- Global U.S. Actions
- Assessing the Impact of Actions Taken
- Federal TB Task Force Members and Others Involved in the Development of This Report
- Glossary
- References
- Federal TB Task Force Roster
- Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Introduction
- How to Eliminate TB? – The IOM Report
- Why Eliminate TB? – Rationale for Elimination
- Who Will Lead? – CDC's Response
- Goal I: Maintain control of TB
- Goal II: Accelerate the decline
- Goal III: Create new tools
- Goal IV: Reduce the global burden of TB
- Goal V: Summon and sustain support
- Goal VI: Track progress
- References
- Federal TB Task Force
- Funding
Basic TB Facts
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria usually attack the lungs, but TB bacteria can attack any part of the body such as the kidney, spine, and brain. If not treated properly, TB disease can be fatal.
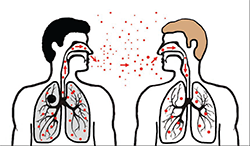 How TB Spreads
How TB Spreads
TB is spread through the air from one person to another. The TB bacteria are put into the air when a person with TB disease of the lungs or throat coughs, sneezes, speaks, or sings. People nearby may breathe in these bacteria and become infected.
TB is NOT spread by
- shaking someone’s hand
- sharing food or drink
- touching bed linens or toilet seats
- sharing toothbrushes
- kissing
Latent TB Infection and TB Disease
Not everyone infected with TB bacteria becomes sick. As a result, two TB-related conditions exist: latent TB infection and TB disease.
Latent TB Infection
TB bacteria can live in the body without making you sick. This is called latent TB infection. In most people who breathe in TB bacteria and become infected, the body is able to fight the bacteria to stop them from growing. People with latent TB infection do not feel sick and do not have any symptoms. People with latent TB infection are not infectious and cannot spread TB bacteria to others. However, if TB bacteria become active in the body and multiply, the person will go from having latent TB infection to being sick with TB disease.
TB Disease
TB bacteria become active if the immune system can't stop them from growing. When TB bacteria are active (multiplying in your body), this is called TB disease. People with TB disease are sick. They may also be able to spread the bacteria to people they spend time with every day.
Many people who have latent TB infection never develop TB disease. Some people develop TB disease soon after becoming infected (within weeks) before their immune system can fight the TB bacteria. Other people may get sick years later when their immune system becomes weak for another reason.
For people whose immune systems are weak, especially those with HIV infection, the risk of developing TB disease is much higher than for people with normal immune systems. Learn more about the difference between LTBI and TB Disease.
TB Risk Factors
Once a person is infected with TB bacteria, the chance of developing TB disease is higher if the person:
- Has HIV infection;
- Has been recently infected with TB bacteria (in the last 2 years);
- Has other health problems, like diabetes, that make it hard for the body to fight bacteria;
- Abuses alcohol or uses illegal drugs; or
- Was not treated correctly for TB infection in the past
Testing for TB Infection
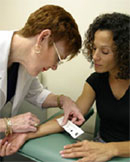 There are two kinds of tests that are used to detect TB bacteria in the body: the TB skin test (TST) and TB blood tests. These tests can be given by a health care provider or local health department. If you have a positive reaction to either of the tests, you will be given other tests to see if you have latent TB infection or TB disease.
There are two kinds of tests that are used to detect TB bacteria in the body: the TB skin test (TST) and TB blood tests. These tests can be given by a health care provider or local health department. If you have a positive reaction to either of the tests, you will be given other tests to see if you have latent TB infection or TB disease.
Treatment for Latent TB Infection and TB Disease
Treatment for Latent TB Infection
 If you have latent TB infection but not TB disease, your health care provider may want you be treated to keep you from developing TB disease. Treatment of latent TB infection reduces the risk that TB infection will progress to TB disease. Treatment of latent TB infection is essential to controlling and eliminating TB in the United States. The decision about taking treatment for latent TB infection will be based on your chances of developing TB disease.
If you have latent TB infection but not TB disease, your health care provider may want you be treated to keep you from developing TB disease. Treatment of latent TB infection reduces the risk that TB infection will progress to TB disease. Treatment of latent TB infection is essential to controlling and eliminating TB in the United States. The decision about taking treatment for latent TB infection will be based on your chances of developing TB disease.
Treatment for TB Disease
TB disease can be treated by taking several drugs, usually for 6 to 9 months. It is very important to finish the medicine, and take the drugs exactly as prescribed. If you stop taking the drugs too soon, you can become sick again. If you do not take the drugs correctly, the germs that are still alive may become resistant to those drugs. TB that is resistant to drugs is harder and more expensive to treat.
Related Links
For Patients
- TB - General Information (Fact sheet)
- Basic Tuberculosis Facts (Audio Podcast)
- Questions and Answers About TB (Booklet)
- The Difference Between Latent TB Infection and TB Disease (Fact sheet)
- Get the Facts About TB Disease (Pamphlet) (PDF - 430k)
- What You Need to Know about TB Infection (Pamphlet) (PDF - 409k)
- Tuberculosis Information for Employers in Non-Healthcare Settings (Fact sheet)
For Health Care Providers
- TB - General Information (Fact sheet)
- TB Guidelines
Contact Us:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Division of Tuberculosis Elimination (DTBE)
1600 Clifton Rd., NE
MS E10
Atlanta, GA 30333 - 800-CDC-INFO
(800-232-4636)
TTY: (888) 232-6348 - New Hours of Operation
8am-8pm ET/Monday-Friday
Closed Holidays - cdcinfo@cdc.gov



