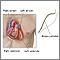
Myocardial biopsy
Myocardial biopsy is the removal of a small piece of heart muscle for examination.
How the Test is Performed
Myocardial biopsy is done during cardiac catheterization or similar procedure.
The procedure will take place in a hospital radiology department, special procedures room, or cardiac diagnostics laboratory. You may be given a sedative prior to the procedure to help you relax, but you will remain awake and able to follow instructions during the test. You will lie flat on a stretcher or table while the test is being done.
The skin is scrubbed and a local numbing medicine (anesthetic) is given.
A surgical cut will be made your arm, neck, or groin. The health care provider inserts a thin tube (catheter) through a vein or artery, depending on whether tissue will be taken from the right or left side of the heart.
If the biopsy is done without another procedure, the catheter is usually placed through a vein in the neck and then carefully threaded into the heart. The doctor uses moving x-ray images (fluoroscopy) to guide the catheter to the correct area. Once in position, a special device with jaws on the tip is used to remove small pieces of tissue from the heart muscle.
The procedure may last 1 or more hours.
How to Prepare for the Test
You will told not to eat or drink anything for 6 - 8 hours before the test. The procedure takes place in the hospital. You will usually be admitted the morning of the procedure, but in some cases, you may need to be admitted the night before.
A health care provider will explain the procedure and its risks. You must sign a consent form.
How the Test Will Feel
You may feel some pressure at the biopsy site. You may have some discomfort due to lying still for a long period of time.
Why the Test is Performed
This procedure is routinely done after heart transplantation to watch for signs of rejection. Your doctor may also order this procedure if you have signs of:
- Alcoholic cardiomyopathy
- Cardiac amyloidosis
- Cardiomyopathy
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Idiopathic cardiomyopathy
- Ischemic cardiomyopathy
- Myocarditis
- Peripartum cardiomyopathy
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy
Normal Results
A normal result means there was no abnormal heart muscle tissue.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An abnormal result means abnormal tissue was found. This test may reveal the cause of cardiomyopathy. Abnormal tissue may also be due to:
- Amyloidosis
- Myocarditis
- Transplant rejection
Risks
Risks are moderate and include:
- Blood clots
- Bleeding from the biopsy site
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Infection
- Injury to the recurrent laryngeal nerve
- Injury to the vein or artery
- Pneumothorax
- Rupture of the heart (very rare)
- Tricuspid regurgitation
Alternative Names
Heart biopsy; Biopsy - heart
Update Date: 6/8/2012
Updated by: Glenn Gandelman, MD, MPH, FACC Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine at New York Medical College, and in private practice specializing in cardiovascular disease in Greenwich, CT. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M. Health Solutions, Ebix, Inc.

A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, also known as the American Accreditation HealthCare Commission (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics and subscribes to the principles of the Health on the Net Foundation (www.hon.ch).
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Duplication for commercial use must be authorized in writing by ADAM Health Solutions.