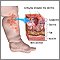
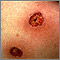
Ecthyma
Ecthyma is a skin infection similar to impetigo. It is often called "deep impetigo" because it occurs deep inside the skin.
Causes
Ecthyma is most often caused by the bacteria streptococcus. Sometimes, staphylococcus bacteria causes this skin infection.
The infection may start in skin that has been injured due to a scratch or insect bite. It often develops on the legs.
Symptoms
The main symptom of ecthyma is a small blister with a red border that may be filled with pus. The blister is similar to that seen in persons with impetigo, but the infection spreads much deeper into the skin.
After the blister goes away, a crusty ulcer appears.
Exams and Tests
Your doctor can usually diagnose this condition simply by looking at your skin. In rare cases, the fluid inside the blister may be sent to a lab for closer examination or a skin biopsy may be done.
Treatment
Your doctor will usually prescribe antibiotics by mouth (oral antibiotics). Very early cases may be treated with topical medications. More advanced forms may need antibiotics given through a vein (intravenous antibiotics).
Placing a warm wet cloth over the area can help remove ulcer crusts. Your doctor may recommend antiseptic soap or peroxide washes to speed recovery.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Unlike impetigo, ecthyma can sometimes result in scarring.
Possible Complications
- Spread of infection to other parts of the body
- Permanent skin damage with scarring
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Make an appointment with your health care provider if you have symptoms of ecthyma.
Prevention
Carefully clean the skin after an injury (such as a bite or scratch). Avoid scratching or digging at scabs and sores.
References
Habif TP. Clinical Dermatology. 4th ed. St. Louis, Mo: Mosby; 2004.
Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R. Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 6th ed. London: Churchill Livingstone; 2005.
Rakel RE. Textbook of Family Practice. 6th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: WB Saunders; 2002.
Update Date: 5/13/2011
Updated by: Kevin Berman, MD, PhD, Atlanta Center for Dermatologic Disease, Atlanta, GA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
MedlinePlus Topics
Images
Read More

A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, also known as the American Accreditation HealthCare Commission (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics and subscribes to the principles of the Health on the Net Foundation (www.hon.ch).
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Duplication for commercial use must be authorized in writing by ADAM Health Solutions.