R&D, Patents are Key Manufacturing Drivers Chief Economist Mark Doms Tells National Association for Business Economics 2012 Conference
This afternoon Chief Economist Mark Doms addressed the 2012 National Association for Business Economics (NABE) Industry Conference, themed “Making it in America: Manufacturing Matters” in Cleveland, OH. Hosted by the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland, this NABE industry conference focused on “the changing dynamics and rebalancing of U.S. manufactures in the global economy, focusing on its rejuvenation and new challenges and opportunities.” He previewed an upcoming ESA report showing that many communities depend critically on manufacturing, and these communities are spread all across the United States. That is because manufacturing provides the basis for many middle class jobs with good benefits.
- Much of our country’s innovation comes from the manufacturing sector: close to 70 percent of our research and development and 90 percent of our patents.
- Since the trough of manufacturing employment, firms have added about a half million new jobs.
- The manufacturing industry has been one of the leading contributors to GDP growth over the last two years, accounting for 38 percent of total economic growthIn 2011, the U.S. exported over $1.26 trillion worth of manufactured goods, more than double the amount in 2002. Also, since the trough in 2009, manufactured goods exports are up 38 percent.
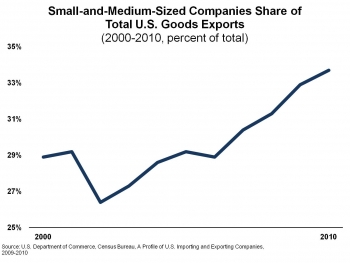
- In particular, small and medium sized companies are increasingly contributing to our export growth, and they now make up over a third of total exports.
That is why the Administration’s focus on manufacturing is so important. Doms highlighted what the Commerce Department is doing to help.