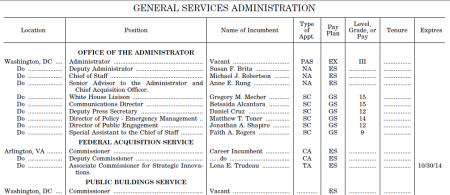
Guest blogger GPO Public Relations Specialist Emma Wojtowicz reviews this new publication asking whether our economic security is a neglected dimension of U.S. national security policy, a timely topic considering the recent national economic recession and yesterday’s news of the GDP drop.
The public generally agrees that the United States’ economic security is a vital component to the country’s overall national security. This is especially true in light of yesterday’s announcement that the U.S. gross domestic product (GDP)—the measure of all goods and services produced by the economy—shrank an unexpected 0.1% annual rate in the fourth quarter of 2012, the first quarterly contraction since the second quarter of 2009 during the recession.
But what exactly does economic security mean in this context? This topic is explored in Economic Security: Neglected Dimension of National Security?, a publication by the Institute for National Strategic Studies of the National Defense University.
 The book’s editor, Sheila R. Ronis, argues that the economy has often been ignored and misunderstood in relation to national security and that economic strength is the foundation of national security. To make this argument, papers from a conference in 2010 that had the same title as the book comprise the publication and focus on the different factors that contribute to economic security.
The book’s editor, Sheila R. Ronis, argues that the economy has often been ignored and misunderstood in relation to national security and that economic strength is the foundation of national security. To make this argument, papers from a conference in 2010 that had the same title as the book comprise the publication and focus on the different factors that contribute to economic security.
Foundation: The first chapter explains how the economy works and provides the reader with a foundation for understanding economic components like budgets, debt, deficits, lenders, interest rates, GDP and so on. This is the best chapter of the book because it gives the reader perspective when considering the country’s economic security.
History: Taking up 50 pages of this 110 page publication, the second chapter focuses on how the U.S. emerged after World War II as an economic and military superpower and how the boom in industrialization and commerce in the previous decades lead to America’s position after World War II. This approach to understanding the United States’ current economy is fascinating but the use of minute historical details to make the point is perhaps too in-depth for the casual reader, but will be of great interest to scholars, specialists and journalists.
Energy: The third and fourth chapters tackle the topic of energy security and how that relates to the country’s economic and national security. If you are not an energy aficionado, then the content may be over your head, but there are some fundamental facts that anyone can absorb. The U.S. spends $500 billion annually on energy and is the world’s largest energy consumer second to China. The United States’ energy consumption grows every year along with its energy imports. These chapters strategize how to reform energy policy, thus strengthening the country’s economic and national security.
Image: Energy security is a common topic in relation to economic and national security. Another professor, Massoud Amin at the University of Minnesota, describes energy security as the overlap between economic security, national security, and environmental security. Source: DialogueEarth.org
Education: Chapter five explores education in the U.S. and the skill set needed for the workforce of today and the future. Science and technology are necessary skills for the country’s current workforce in order for the U.S. to play a role in the global economy. Those skills are also important for engaging the next generation of students who were born into an already technologically advanced society, well-versed in using computers, the Internet and mobile devices. This chapter takes a comprehensive approach to the topic of education and the long-term effect it will have on the country’s economic security.
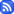
Innovation: The author of the sixth and final chapter takes on the subject of innovation and its contribution to United States’ economic prosperity more so than its economic security. Building upon the previous chapter of education, innovation is the next step to strengthening the economy by creating jobs through new industries and products. The best take-away from this chapter is that while innovation is important and vital to the economy, it alone cannot ensure economic security.
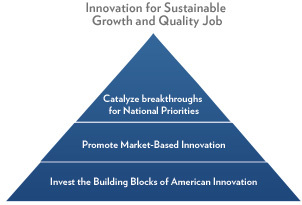 Image: This image represents the President’s “Strategy for American Innovation” which, according to the White House, “seeks to harness the ingenuity of the American people to ensure economic growth that is rapid, broad-based, and sustained. This economic growth will bring greater income, higher quality jobs, and improved quality of life to all Americans.” Source: White House.
Image: This image represents the President’s “Strategy for American Innovation” which, according to the White House, “seeks to harness the ingenuity of the American people to ensure economic growth that is rapid, broad-based, and sustained. This economic growth will bring greater income, higher quality jobs, and improved quality of life to all Americans.” Source: White House.
Economic Security: Neglected Dimension of National Security? does a good job of breaking down the issue of economic security making the reader more thoughtful and aware of this important, relevant topic.
HOW DO I OBTAIN THIS BOOK: “Economic Security: Neglected Dimension of National Security?”
- Buy it online 24/7 at GPO’s Online Bookstore.
- Buy it at GPO’s retail bookstore at 710 North Capitol Street NW, Washington, DC 20401, open Monday-Friday, 9am to 4pm, except Federal holidays, (202) 512-0132.
- Find it in a library.
Related Publications:
- The 2012 Long Term Budget Outlook
- Economic Report of the President, Transmitted to the Congress February 2012 Together With the Annual Report of the Council of Economic Advisers
- Economic Indicators Monthly Subscription
- Budget and Economic Outlook, Fiscal Years 2012 to 2022
- US-China Economic & Security Review Commission Annual Report 2012



 Posted by GPOBookstore
Posted by GPOBookstore