This page is for historical and reference purposes only. Updates to content and links will not be maintained. Current information about NIDDK's Kidney, Urological and Hematology programs can be found at http://www2.niddk.nih.gov/Research/ScientificAreas/Kidney/, http://www2.niddk.nih.gov/Research/ScientificAreas/Urology/ and http://www2.niddk.nih.gov/Research/ScientificAreas/Hematology/.
The American Society of Nephology will meet in San Diego, CA on October 30 - November 4, 2012.
Meeting Posters (PDF, 183 KB) Due to technical issues, users may have difficulty printing the poster for viewing. We recommend using the text version below to access URLs and information.
Funding History and Research Opportunities
NIDDK Funding History and Opportunities
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) comprises 27 separate Institutes and Centers and is the largest biomedical research center in the world. The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) was established by Congress in 1950. Within the NIDDK, the Division of Kidney, Urology and Hematology (KUH) manages programs in kidney research.
In 2012, NIDDK awarded >$250M for kidney research.
Exploratory Research (R21) Program
NEW! The NIDDK will no longer accept applications in response to the NIH Parent R21 Funding Opportunity Announcement (PA-10-069). NIDDK is accepting applications in response to:
Collaborative Research
Complex biomedical science often requires the expertise of collaborating investigators working together as an investigative team. Collaborative research can be supported by several different types of grant mechanisms:
- R01 with a Principal Investigator and one or more key personnel or collaborators
- Multi-PI R01 with multiple Principal Investigators collaborating and sharing credit and responsibility
- Center Grants (P20/P30/P50) support a focused set of core activities
- Program Project Grant (P01) designed to support a broadly based interrelated research program that has multiple distinct but synergistic research projects built around a unifying central theme
- Resource-Related Research Project Grant (R24) provides flexible support for an interdisciplinary research team focused on answering a single critically important research question
Diabetic Complications Consortium (formerly AMDCC)
Given the strong evidence that diabetic complications are linked via dysregulation of common pathways, there is a strong need to facilitate the sharing of ideas, information, and reagents between research communities investigating similar pathologic mechanisms in different organs. Like the AMDCC, the DCC will continue to promote this communication and collaboration via an annual scientific meeting and funding opportunities. Unlike the AMDCC, the DCC has a broader scientific scope and supports not only animal model development but all types of basic and translational studies. Full details at www.diacomp.org.
Kidney Research National Dialogue (KRND)
The NIDDK recently asked the community to identify research objectives, which if addressed, would improve our understanding of basic kidney function and aid in the prevention, treatment, and reversal of kidney disease. The Kidney Research National Dialogue (KRND) welcomed all interested parties to submit, discuss, and prioritize ideas via an interactive website. Over 1,600 participants posted almost 300 ideas and 500 comments covering all areas of kidney disease on the KRND website (www.krnd.ideascale.com). The website is still open for additional postings.
Responses to the question, “What are the critical questions in kidney research?” were broad ranging and insightful. The postings in each kidney research topic area captured the distinctiveness of each area’s critical questions. Also, cross cutting themes emerged from the postings. In the coming year, more discussions will refine the content to capture the current state of a field and provide high impact recommendations and potential “roadmaps”. NIDDK is now working with the renal research community to develop individual chapters for the Blueprint for Kidney Research. The chapters will be published in cJASN. Meanwhile, we have taken postings for KRND into consideration during the development of current initiatives.
For more details, contact KRND@nih.gov or GOOGLE “KRND”.
Generation of new mouse strains for analysis of the developing urogenital system
The goal of the Genito-Urinary Developmental Anatomy Project (GUDMAP) consortium is to develop a detailed molecular anatomy of the mammalian urogenital
system (UGS), to inform and stimulate research, and to better understand human disease. As part of this multi-center effort, GUDMAP2 members will generate novel transgenic mouse strains of broad interest to the community.
Gene nominations for targeting are NOW being sought from the research community.
GUDMAP2 will give preference to gene targets expressed in critical cell types of the lower UGS, but will consider cell-type specific marking throughout the urinary system. Once generated and transgene activity is confirmed, mice will be made available to nominating investigators and deposited in a Mouse Mutant Repository Center (MMRC) for broader distribution to the community. Full details at www.gudmap.org.
37 Month Time Limit for NIH Re-submission Applications
Kidney and Urology Funding Announcements
Basic Research
Translational Research
Clinical Research
Centers
Upcoming NIDDK Meetings
- NIDDK New Investigators Workshop
DoubleTree Hotel & Executive Meeting Center, Bethesda, MD
(December 2–4, 2012)
- Urological Complications of Diabetes
Lister Hill, NIH Main Campus, Bethesda, MD
(February 14–15, 2013)
- Genetics of Diabetic Nephropathy
TBD
(January/February 2013)
Updates in the Rules for Financial-Conflict-of-interest Disclosure for National Institutes of Health Grantees
Small Business
Small Business Funding Opportunities
Why Seek SBIR/STTR Funds?
- Over $1 billion are available across NIH
- They provide seed money for high-risk projects
- They promote and foster partnerships with collaborators - including academia!
- Intellectual property rights are normally retained by small business
- Funds are NOT A LOAN - no repayment!
- Large corporations look to small companies for initial development
Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR)
The SBIR program supports innovative research conducted by small businesses to develop products for commercialization. The PI must be employed by the small business, but a research institution may be involved.
http://www.zyn.com/sbir
http://grants.nih.gov/grants/oer.htm
Small Business Technology Transfer (STTR)
The STTR program supports innovative research for products that have the potential for commercialization. STTR projects must be conducted cooperatively by a small business and a research institution.
http://www.zyn.com/sbir
http://grants.nih.gov/grants/oer.htm
Select NIDDK-Supported Small Business Projects
- Predicting kidney stones in relatives of stone formers
- Measurement of GFR (See FAST BioMedical in Inventors Row)
- Computerized Clinical Decision Support
- Probiotic Use in CKD
- Commercialization of embryonic kidney stem cell lines, products and kits (See Probetex, Inc. Poster #FR-PO210)
- Bioartifical renal epithelial cell systems
- Prevention-Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy
- Intravital kidney multiphoton microscopy assays of therapeutic agents
- Renal perfusion quantification (See Targeson, Inc. Poster # FR-PO1041)
- Tracking Transplant Centers Performance
- Production Methods for Engineered Tissues (See Humacyte, Inc.; Brave New World: Engineering Vessels and Organs to Order, November 1, 2012, 2:10-2:40 p.m.)
- Improvements of catheters biomaterials
- Technologies to Improve Data Collection in NIDDK Clinical Studies
Training and Career Development
Post-Doctoral Training
Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Awards (NRSA)
- Individual (F32)
These awards provide support for fellows who have received their M.D., Ph.D., or other doctoral-level degree. Fellows need to identify a mentor and plan a research project before applying for 1 to 3 years of funding.
- Institutional (T32)
In place at many major universities, these grants provide pre- and postdoctoral support to fellows at those institutions. To be appointed to a training grant, contact the director of the training program at your institution.
Training & Career Development Timeline
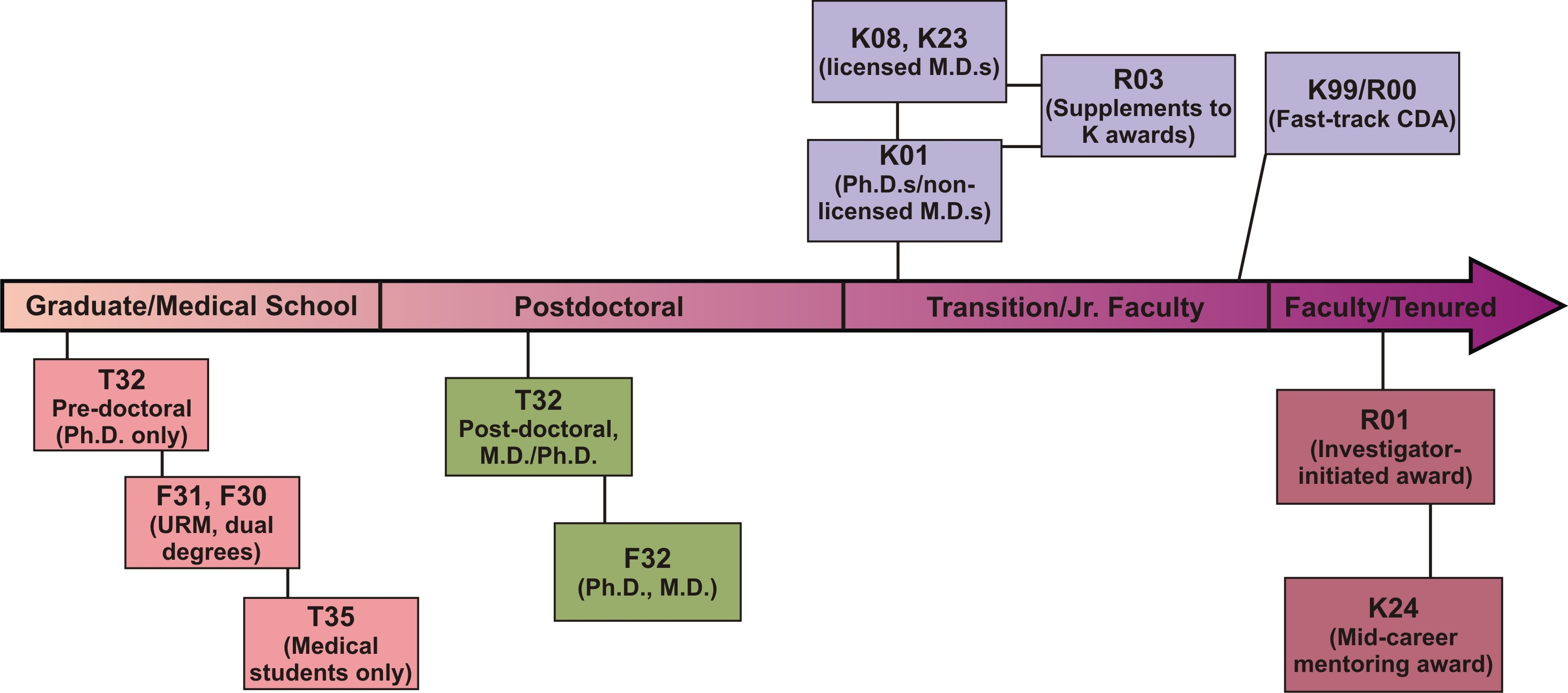
Loan Repayment Program
The goal of the Loan Repayment Program is to ease the debt burden clinical scientists may have incurred while attending medical school and a residency program. The NIDDK has two loan repayment programs: one for clinicians and one for pediatricians. In addition, the National Center on Minority Health and Health Disparities sponsors two other loan repayment programs for clinicians: one for those involved in health disparities research and another for clinical researchers from disadvantaged backgrounds. Competitive applicants must demonstrate their commitment to a research career and have a debt-to-salary ratio of at least 20 percent. The Loan Repayment Program may repay up to $35,000 a year toward each participant’s outstanding eligible educational loan debt, depending on total eligible repayable debt. For more details about eligibility and to apply online, visit http://www.lrp.nih.gov.
Career Development Awards*
Training-Related Program Announcements
Small Grant Program for NIDDK K01/K08/K23 Recipients (R03)
In the final two years of the career development grant, K recipients may apply for small grant funding for additional development support for their research.
NIDDK Education Program Grants (R25)
The R25 program provides support for educational opportunities (E.g., workshops, classes) to engage students from undergraduate to graduate in research areas relevant to NIDDK.
K99/R00 NIH Pathways to Independence
This is intended for talented postdoctoral candidates on the fast-track to a productive research career. Eligible applicants must have five-years or fewer of postdoctoral research experience and may not already have an independent faculty position. The first two years of the award, the K99 phase, is for mentored career-development. At the end of the second year, the applicant must have secured an independent tenure-track position to continue the final three years of the award as an R00. While this award does not require U.S. citizenship or permanent resident status, the applicant must be able to remain in the United States to conduct the full five years of the proposed work. PA-11-197
NEW! Recent revisions to the NIH appeals policy of the initial peer review process (NOT-OD-11-064)
Contacts
Kidney, Urology & Hematology (KUH) Staff
Telephone: (301) 594-7717
Director, KUH
Robert A. Star, M.D.
starr@extra.niddk.nih.gov
Deputy Director, Clinical; Pediatric Neph Program & Renal Centers
Marva Moxey-Mims, M.D.
mimsm@extra.niddk.nih.gov
Deputy Director, Basic; Renal Physiology Program
Christian J. Ketchum, Ph.D.
ketchumc@extra.niddk.nih.gov
Director, Minority Health Program
Lawrence Y. Agodoa, M.D.
agodoal@extra.niddk.nih.gov
Women's Urologic Health Program
Tamara Bavendam, M.D.
bavendamtg@niddk.nih.gov
Epidemiology Program and U.S. Renal Data System
Paul W. Eggers, Ph.D.
eggersp@extra.niddk.nih.gov
Clinical PKD & Inflammatory Renal Diseases Programs
Michael F. Flessner, MD, PhD
flessnermf@niddk.nih.gov
Kidney Development & Repair & Regeneration Programs
Deborah Hoshizaki, Ph.D.
hoshizakid@niddk.nih.gov
Acute Injury and HIV Nephropathy Program
Paul L. Kimmel, M.D.
kimmelp@extra.niddk.nih.gov
Clinical and Translational Urology Programs
Ziya Kirkali, M.D.
ziya.kirkali@nih.gov
Clinical Trials Program
John W. Kusek, Ph.D.
kusekj@extra.niddk.nih.gov
Urology and Kidney Cell Biology Programs
Christopher V. Mullins, Ph.D.
mullinsc@extra.niddk.nih.gov
National Kidney Disease Education Program (NKDEP)
Andrew S. Narva, M.D.
narvaa@extra.niddk.nih.gov
Kidney and Urology Training
Tracy L. Rankin, Ph.D.
rankint@mail.nih.gov
Genetics and Basic PKD Programs
Rebekah Rasooly, Ph.D.
rasoolyr@extra.niddk.nih.gov
Kidney Pathophysiology Program
Krystyna Rys-Sikora, Ph.D.
Krystyna.Rys-Sikora@nih.gov
NIH Center for Scientific Review (CSR)
The Center for Scientific Review (CSR) are organized into Integrated Review Groups (IRGs) representing a general scientific area. Study sections for kidney and urological research within Digestive, Kidney & Urological Sciences (DKUS) are:
- NEW! Kidney Molecular Biology & Genitourinary Organ Development Study Section [KMBD] Replaces Cellular & Molecular Biology of the Kidney (CMBK) study section. KMBD reviews applications involving basic & applied aspects of normal & abnormal renal physiology, cell biology, transport biology, including osmoregulation and osmosensing, hormone action & signal transduction, vascular biology, genetic disorders, cell-matrix interactions, biophysics, bioenergetics, and basic processes underlying upper & lower genitourinary organ development.
- Pathobiology of Kidney Disease [PBKD] Reviews applications involving basic & clinical studies of kidney disease including pathophysiology, diagnosis, consequences & treatment of acute & chronic disorders of the kidney, and consequences of kidney disease & failure, as well as studies of glomerulus normal structure & function.treatment of acute and chronic disorders of the kidney, and consequences of kidney disease and failure, as well as studies of the normal structure and function of the glomerulus.
- NEW! Urologic & Genitourinary Physiology & Pathology Study Section [UGPP] Replaces Urologic & Kidney Development & Genitourinary Diseases (UKGD) and incorporates Urological Sciences Small Business Activities [SBIR/STTR]. UGPP reviews applications involving physiological & pathophysiological processes of the lower urinary tract, male reproductive organs, female pelvic floor including urolithiasis, microbial infection & inflammation in the lower urinary tract.
Scientific Review Officers
KMBD
Ryan Morris, Ph.D.
morrisr@csr.nih.gov
PBKD
Atul Sahai, Ph.D
Atul.Sahai@nih.gov
UGPP
Ryan Morris, Ph.D.
morrisr@csr.nih.gov
More questions about the review process?? Go to http://www.csr.nih.gov.
NIDDK Review Branch
NIDDK Review Branch conducts review of the applications received in response to IC-specific Funding Opportunity Announcements (FOAs: RFAs and PARs):
- Clinical trials to prevent or slow chronic renal disease
- Epidemiology, prevention, and treatment of acute kidney injury
- Epidemiologic and genetic studies of ESRD patients
- Clinical trials to reduce mortality and morbidity in ESRD patients
- Epidemiology of chronic renal insufficiency, including CV disease
Clinical and Translational Research
Clinical Trials and Epidemiological Studies
NIDDK supports a wide range of clinical trials and epidemiological studies on chronic kidney disease. While many of these programs are solicited by NIDDK through initiatives, investigators may also develop their own ideas.
Areas of General Interest
- Clinical trials to prevent or slow chronic renal disease
- Epidemiology, prevention, and treatment of acute kidney injury
- Epidemiologic and genetic studies of ESRD patients
- Clinical trials to reduce mortality and morbidity in ESRD patients
- Epidemiology of chronic renal insufficiency, including CV disease
- Comparative Effectiveness Research (CER)
- Patient-Centered Outcome Research (PCOR)
Mechanisms of Support
If you have patients with Nephrotic Syndrome
NEPTUNE (Nephrotic Syndrome Study Network)
Multi-center collaboration of clinical translational and basic scientists along with the patient support groups NephCure and Halpin Foundations. Study patients with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), Minimal Change Disease (MCD), and Membranous Nephropathy (MN).
Objectives:
- Recruit 450 participants (no upper or lower age limit) for:
- Collaborative, integrated, cost-effective investigational infrastructure for clinical and translational research in FSGS, MCD, and MN
- Longitudinal Observational Cohort Studies of patients with incipient biopsy proven FSGS, MCD or MN
Features:
- Pilot & Ancillary program using unique resources, clinical data, or specimens in NEPTUNE
- Training program for post-doctoral trainees and junior faculty
- Collaborate with the NIH Office of Rare Diseases Data Management Coordinating Center, Halpin and NephCure Foundations
- Contact Registry for Nephrotic SyndromeDiagnosed urinary tract infection (UTI) with either fever or associated symptoms
For more information: See http://NEPTUNE-STUDY.ORG
NEPTUNE Participating Sites:
Harbor UCLA, NYU, University of Toronto, Johns Hopkins, University of Miami, Case Western University, University of North Carolina, Montefiore Medical Center, Mayo Clinic, Cohen Children's Hospital (LIJ Hospital), Children's Hospital Los Angeles, University of Michigan, Temple University, University of Washington, NIDDK Intramural, University of Pennsylvania, Columbia University, Emory University
Ongoing Studies/Currently Recruiting
- ASsessment, Serial Evaluation, and Subsequent Sequelae in Acute Kidney Injury (ASSESS-AKI) Network. An epidemiological study of long-term outcomes following episodes of AKI. Aims are to determine (a) whether AKI leads to a faster progression or greater risk of developing chronic kidney disease, and (b) whether AKI leads to a higher risk of death, cardiovascular events, and other adverse events.
- Prospective Study of Chronic Kidney Disease in Children (CKiD). A large-scale, long-term observational studies of the Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) in children. Aims are (a) to determine risk factors for progression of pediatric chronic kidney disease (CKD) and (b) examine the impact of CKD on neurocognitive development, risk factors for cardiovascular disease and growth.
- Hemodialysis Fistula Maturation Study. A multi-center prospective cohort study of approximately 600 participants (recruitment to be completed in 2013) with a newly created fistula focused on the identification of predictors and underlying mechanisms of fistula maturation and failure utilizing information about vascular anatomy, vascular biology, clinical attributes of patients. and processes of care.
- The Nephrotic Syndrome Study Network (NEPTUNE). An integrated group of academic medical centers, patient support organizations and clinical research resources dedicated to advancing the understanding and treatment of Minimal Change Disease (MCD), Focal and Segmental Glomerulosclerosis(FSGS), and Membranous Nephropathy (MN).
- The Rare Kidney Stone Consortium. An intergrated group of academic medical centers, patient support organizations, and clinical research resources studying primary hyperoxaluria, cystinuria, APRT deficiency, and Dent disease.
- Oral vs. IV Iron Therapy in Chronic Kidney Disease. Single center study (Indiana University) investigating whether IV iron therapy in CKD is associated with more rapid decline in GFR than chronic oral iron therapy.
- Blood Pressure in Dialysis (BID). Pilot clinical trial to test feasibility of randomizing hemodialysis patients to two levels of blood pressure control. Investigators: Drs. Phillip Zager (University of New Mexico Health Sciences Center), Dana Miskulin (Tufts Medical Center), and Jennifer Gassman (Cleveland Clinic Foundation)
Ongoing Studies/NOT Currently Recruiting
- Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study. Cooperative agreementsupported prospective epidemiological study: 7 centers and 1 DCC
- Consortium for Radiologic Imaging Studies in PKD II (CRISP II). Cooperative agreement-supported clinical study; 4 centers and 1 DCC
- HALT-PKD. Cooperative agreement-supported clinical study; 6 sites and 1 DCC
- Randomized Intervention for Vesicoureteral Reflux (RIVUR). Multi-center trial of Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole prophylaxis compared to placebo in children with VUR (13 primary sites and 1 DCC). Age range 2 months – 6 years. Outcome measures will include frequency of UTI, changes in scarring measured by DMSA scan, and development of antimicrobial resistance. (www.ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT00405704)
- Angiotensin II Blockade in Chronic Allograft Nephropathy (ABCAN). Cooperative agreement-supported clinical trial; single center (Un. Minn)
- Assessing Long Term Outcomes of Living Donation (ALTOLD). Multi-center prospective cohort study will address whether kidney donation increases the risk of developing ESRD and/or increases the risk of developing CV disease.
Repository
Central NIDDK Repositories
Data, Biosamples, and DNA for your research
The NIDDK Central Repositories store samples and data from NIDDK-funded clinical studies, which are made available to the community at the end of the study or when an interim phase is completed. Over 150 requesters have received data and 35 have received samples!
DNA and data - Go to the NIDDK Repository for instructions for using the Web-based application system (https://www.niddkrepository.org/niddk/jsp/request/instruction.jsp). Often takes less than 2 weeks to review and deliver data!
Samples - apply using an X01 (no funds; http://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/pa-files/PAR-11-306.html). The next deadline is March 1, 2013.
See https://www.niddkrepository.org/niddk/jsp/public/sampleInstruction.jsp for more details.
Try our new Public Query Tools to find the samples and data you need (https://www.niddkrepository.org/niddk/jsp/pqt/pqtMainPage.jsp)!
Data and/or samples are available from:
- African American Study of Kidney Disease and Hypertension (AASK) AASK compared the effectiveness of various antihypertensive regimens to slow or prevent progressive renal dysfunction in 1,094 African-Americans with a clinical diagnosis of hypertensive renal disease.
- ATN (Acute Renal Failure Trial Network) The ATN study compared two strategies for renal-replacement therapy in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury in prospective multisite randomized trial. The study found no differences between intensive or less intensive renal-replacement therapy in terms of all cause death, recovery of renal function or nonrenal organ failure. Only data is available from ATN.
- CDS (The Comprehensive Dialysis Study) The CDS is a special data collection study designed by the United States Renal System (USRDS) initiated in 2005. The CDS addresses nutrition and rehabilitation/quality of life issues in incident dialysis patients. Only data are available from CDS.
- CRIC (The Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort Study) The Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort Study examines risk factors for progression of chronic renal insufficiency (CRI) and cardiovascular disease (CVD) among 3,939 CRI patients from diverse races and ethnicities. Data and samples from the baseline are available, along with a dataset on atrial fibrillation along with GWAS data.
- CRISP (Consortium for Radiological Imaging Studies of PKD) CRISP compared radiological techniques for measuring increases in renal volume during the progression of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), testing whether magnetic resonance can detect changes in renal volume, cyst volume, or changes in % cystic involvement over a short period of time (1 to 2 years). Data and samples from the first five years of the CRISP study are available.
- Dialysis Access Consortium (DAC) Two clinical trials were conducted (Clopidogrel Prevention of Early AV Fistula Thrombosis and Aggrenox Prevention of Access Stenosis) to identify interventions that improve fistula and graft viability. Data and samples are available.
- EDIC (Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications) EDIC is the continuation of the DCCT (Diabetes Control and Complications Trial), which demonstrated the efficacy of glycemic control for slowing the onset and progression of eye, kidney, and nerve complications and long-term diminution of CV complications. Since 1994, most of the 1,441 DCCT participants have been enrolled in EDIC for regular observational followup. Samples, data, GWAS data, and DNA are available from DCCT, EDIC. and EDIC family study participants.
- FIND (Family Investigation of Nephropathy and Diabetes) The FIND group recruited nearly 7,000 individuals from four ethnic groups to study the genetic determinants of susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy. Linkage data are available and GWAS data are available.
- GoKinD (Genetics of Kidneys in Diabetes) GoKinD created a repository of DNA, biosamples, and clinical information from adults with long-term Type 1 diabetes, with or without kidney disease. GWAS data from a 500K Affymetrix chip are available for all participants.
- HEMO (Hemodialysis Study) The HEMO study showed no apparently major benefit from a higher dialysis dose than that recommended by current U.S. guidelines or from the use of a high-flux membrane in terms of mortality and morbidity. The study randomized 1,846 patients. Data and samples are available.
- MDRD (Modification of Diet in Renal Disease) The multi-center MDRD study found no effect from restriction of dietary protein and phosphorus, and/or reduction of blood pressure below 140/90 on the rate of progression of chronic renal disease. Data and samples are available.
Visit Our NEW NIDDK KUH website!!!!
* Documents in PDF format require the free Adobe Acrobat Reader  application for viewing.
application for viewing.