
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES
By the end of each session, participants will be able to:
Considering what you have learned so far, which type of treatment do you think may be best for your situation?
What information would help you make a decision?
For group: Label four cups with options. Have participants place a cottonball into the cup that they are considering choosing (their "choice"). Use for discussion.
Have flip chart or white board available to write down group's response to: What are the benefits of making a treatment choice sooner instead of later? Have group discuss whatever benefits they come up with. Examples:
OPTIONAL: Then ask what are the benefits of not making the choice (hopefully no one will have any)
These images are available free of charge to download and include in your patient education materials.
 |
 |
 |
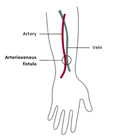
| A schematic of an arteriovenous or AV fistula Download (.jpg/27 K) |
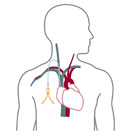
A schematic of the hemodialysis process Download (.jpg/33 K) |
A schematic of a catheter for temporary access Download (.jpg/32 K) |
 |
 |
|
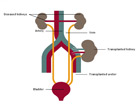
| A schematic showing a transplanted kidney placed in the groin area. Native kidneys usually are not removed. Download (.jpg/86 K) |
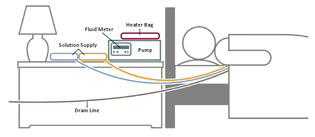
A schematic of a continuous cycler-assisted peritoneal dialysis exchange while person is sleeping Download (.jpg/49 K) |
|
 |
 |
|
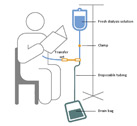
| A schematic of a person receiving continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis exchange while reading Download (.jpg/40 K) |
A schematic showing that the peritoneal membrane is the semipermeable “filter” in peritoneal dialysis Download (.jpg/39 K) |
|
 |
||
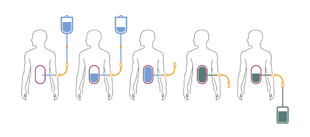
| A schematic showing during a cycle of peritoneal dialysis or exchange Download (.jpg/63 K) |
||
Page last updated: March 1, 2012