How Is an Aneurysm Treated?
Aortic aneurysms are treated with medicines and surgery. Small aneurysms that are found early and aren’t causing symptoms may not need treatment. Other aneurysms need to be treated.
The goals of treatment may include:
- Preventing the aneurysm from growing
- Preventing or reversing damage to other body structures
- Preventing or treating a rupture or dissection
- Allowing you to continue doing your normal daily activities
Treatment for an aortic aneurysm is based on its size. Your doctor may recommend routine testing to make sure an aneurysm isn't getting bigger. This method usually is used for aneurysms that are smaller than 5 centimeters (about 2 inches) across.
How often you need testing (for example, every few months or every year) is based on the size of the aneurysm and how fast it's growing. The larger it is and the faster it's growing, the more often you may need to be checked.
Medicines
If you have an aortic aneurysm, your doctor may prescribe medicines before surgery or instead of surgery. Medicines are used to lower blood pressure, relax blood vessels, and lower the risk that the aneurysm will rupture (burst). Beta blockers and calcium channel blockers are the medicines most commonly used.
Surgery
Your doctor may recommend surgery if your aneurysm is growing quickly or is at risk of rupture or dissection.
The two main types of surgery to repair aortic aneurysms are open abdominal or open chest repair and endovascular repair.
Open Abdominal or Open Chest Repair
The standard and most common type of surgery for aortic aneurysms is open abdominal or open chest repair. This surgery involves a major incision (cut) in the abdomen or chest.
General anesthesia (AN-es-THE-ze-ah) is used during this procedure. The term “anesthesia” refers to a loss of feeling and awareness. General anesthesia temporarily puts you to sleep.
During the surgery, the aneurysm is removed. Then, the section of aorta is replaced with a graft made of material such as Dacron® or Teflon.® The surgery takes 3 to 6 hours; you’ll remain in the hospital for 5 to 8 days.
If needed, repair of the aortic heart valve also may be done during open abdominal or open chest surgery.
It often takes a month to recover from open abdominal or open chest surgery and return to full activity. Most patients make a full recovery.
Endovascular Repair
In endovascular repair, the aneurysm isn't removed. Instead, a graft is inserted into the aorta to strengthen it. Surgeons do this type of surgery using catheters (tubes) inserted into the arteries; it doesn't require surgically opening the chest or abdomen. General anesthesia is used during this procedure.
The surgeon first inserts a catheter into an artery in the groin (upper thigh) and threads it to the aneurysm. Then, using an x ray to see the artery, the surgeon threads the graft (also called a stent graft) into the aorta to the aneurysm.
The graft is then expanded inside the aorta and fastened in place to form a stable channel for blood flow. The graft reinforces the weakened section of the aorta. This helps prevent the aneurysm from rupturing.
Endovascular Repair
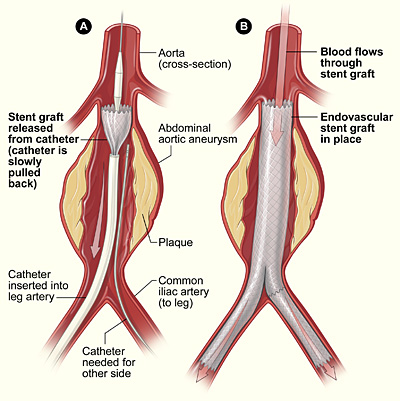
The illustration shows the placement of a stent graft in an aortic aneurysm. In figure A, a catheter is inserted into an artery in the groin (upper thigh). The catheter is threaded to the abdominal aorta, and the stent graft is released from the catheter. In figure B, the stent graft allows blood to flow through the aneurysm.
The recovery time for endovascular repair is less than the recovery time for open abdominal or open chest repair. However, doctors can’t repair all aortic aneurysms with endovascular repair. The location or size of an aneurysm may prevent the use of a stent graft.
Clinical trials are research studies that explore whether a medical strategy, treatment, or device is safe and effective for humans. To find clinical trials that are currently underway for Aneurysm, visit www.clinicaltrials.gov.
The NHLBI supports a national registry that enrolls patients with genetic conditions related to thoracic aortic aneurysms. The data collected through the GenTAC registry will help doctors and researchers better understand how genes, thoracic aortic aneurysms, and heart disease are linked. To learn more about GenTAC, visit https://gentac.rti.org/Home.aspx.
The NHLBI updates Health Topics articles on a biennial cycle based on a thorough review of research findings and new literature. The articles also are updated as needed if important new research is published. The date on each Health Topics article reflects when the content was originally posted or last revised.