Brief Description
In collaboration with NIA, HPCIO develops and enhances tools for the archival, retrieval, and mining of genetic association study data. The Genetic Association Database (GAD) is an archive of human genetic association studies of complex diseases and disorders. GAD enables scientists to query association data in a systematic manner and to integrate association data with other molecular databases. Study data are recorded in the context of official human gene nomenclature with additional molecular reference numbers and links. The goal of this project is to collect all published genetic association study data and allow the user to rapidly identify medically relevant polymorphism from the large volume of polymorphism and mutational data, in the context of standardized nomenclature.
Another tool, namely PubMatrix SE , is a Web-based text-mining tool on MEDLINE citations. It applies natural language processing and statistical methods on biomedical literature text to provide an estimation of the strength of associations among various entities, including genes and diseases. The results are represented in a matrix format, facilitating more efficient interpretation of large amount of text data to assist in microarray studies.
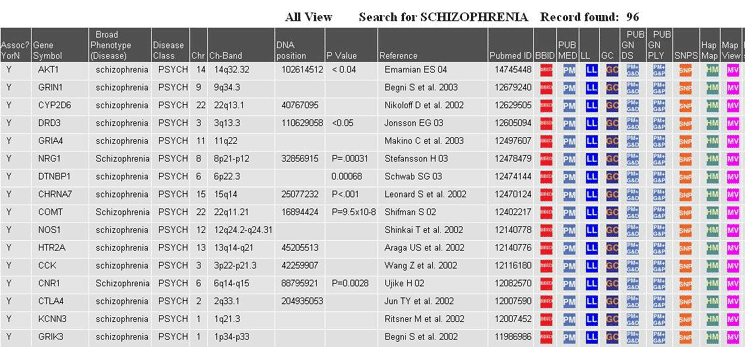
A simple search of positive associations for the disease schizophrenia. Fields in this view include Official Gene Symbol, Disease Phenotype, Disease Class, Chromosome, Chromosome Band, Genomic DNA Position, P Value, Reference, PubMed ID and Links to other gene related resources

Search results for “Candidate Genes for ALZHEIMER DISEASE” from SNPs3D web site. GAD data have been integrated in the search results. Each “Y” represents one positive association record and each “N” represents one negative association record in GAD
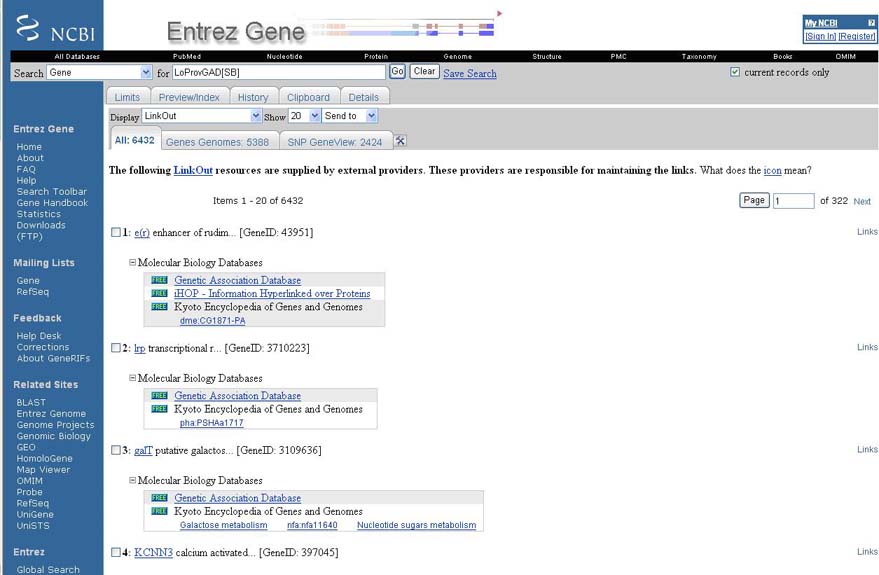
GAD links were provided by multiple NCBI applications including Entrez. User can access GAD data by following the LinkOut resources for each gene.
Recent Accomplishments
GAD has undergone a major upgrade in FY 2006, including an increase in data content, quality, and integration with external genomic data sources. The number of database records has increased 3.5 fold from 8,000 records to over 28,000 records. We have added a Gene-Gene interaction-Environmental Factors (GI-EF) view. The GI-EF view shows specific genes and alleles that are believed to be involved in gene-gene interactions and whether that interaction is dependent upon an environmental factor. We have expanded the disease class categories to include pharmacogenomics, hematological, neurological, mitochondrial, renal, and vision. In addition to official HUGO gene symbols, the batch search function now supports high-throughput searching with human Unigene numbers and human Entrez gene numbers. In FY 2006, GAD had over one million hits and spawned the development of many third-party tools and databases that incorporated either GAD data or GAD web services. A group of researchers including an investigator at NIAMS utilized GAD data in their study of putative candidate-gene associations with rheumatoid arthritis and found novel associations of the genes PTPN22, CTLA4 and PADI4 with clinically relevant subsets of rheumatoid arthritis.
PubMatrix SE is a new area of collaboration with NIA. The goal of this endeavor has been to improve the functionalities and usability of the original system. In FY 2006, we incorporated statistical analysis of the genetic associations. A gene recognition algorithm was developed to improve the accuracy of citation retrieval. The processing time for result assembly has decreased from one day to minutes by building a local copy of the MEDLINE data. Moreover, we have implemented concept identification via NLM's Unified Medical Language System, the ability to customize and navigate a search term hierarchy, and data export function. A prototype Website has been developed.
Current and Future Work
In collaboration with the University of California Santa Cruz, we will place the entire GAD database on the UCSC browser system. This allows integration of large-scale genetic disease data with molecular annotation such as SNPs and RNA splicing; and facilitates the integration with the genomes of other model organisms. A working prototype has been developed.
In FY 2007, a complete copy of the MEDLINE citations will be imported to a local database. Before the PubMatrix SE Website is released to the public, we will continue to improve the gene recognition algorithm and will run it against all the citations. Other features that we plan to implement in FY 2007 include gene clustering using Gene Ontology and association ranking based on citation impact factors, z-scores, and number of citations received.
Collaborators
-
Kevin G. Becker, Ph.D. (Chief, DNA Array Unit Research Resource Branch, NIA )
-
Kathleen C Barnes, Ph.D. (Associate Professor, Department of Epidemiology, Bloomberg School of Public Health, Johns Hopkins University )
-
Narmada Shenoy (Fellow, Research Resource Branch, NIA )
-
Alan B. Zonderma, Ph.D. (Chief, Research Resources Branch, NIA and Physical Disabilities Branch, CC-NICHD, NIH )
Recent Publications
Becker, K.G., Barnes, K.C., Bright, T.J. & Wang, S.A.
“The Genetic Association Database” Nature Genetics 36: 431-432 (2004)
[Full article (PDF, 116kb)] [PubMed]
Other Publications
Sun G, Lau W, Wang A, Shenoy N, Becker K, Cheung H “Ranking and Presenting Gene-Disease Associations from Biomedical Literature.” Poster. 2006 Summer Research Program Student Poster Day. [Full Article (PDF, 144kb)]
Citations in Scientific Literature
Bonci1 A. and Hopf1 F.W., “The Dopamine D2 Receptor: New Surprises from an Old Friend,” Neuron, vol. 47, no. 3, (2005), pp. 335-338
Holloway J. and Yang I., “Adrenergic receptor polymorphism and asthma: True or false?,” Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, vol. 115, no. 5, pp. 960-962
Karopka T., Fluck J., Mevissen H.-T., and Glass A., “The Autoimmune Disease Database: a dynamically compiled literature-derived database,” BMC Bioinformatics, vol. 7 (2006), pp. 325.
Masseroli M., Kilicoglu H., Lang F.-M., and Rindflesch T.C., “Argument-predicate distance as a filter for enhancing precision in extracting predications on the genetic etiology of disease,” BMC Bioinformatics , vol. 7 (2006), pp. 291.
McCarthy M.I., Groop P.-H., Hansen T., “Making the right associations,” Diabetologia , vol. 48, no. 7 (2005), pp. 1241-1243
Rebaï M., Kharrat N., Ayadi I., Rebaï A., “Haplotype structure of five SNPs within the ACE gene in the Tunisian population,” Annals of Human Biology, vol. 33, no. 3 (2006), pp. 319-329
Yi M., Horton J.D., Cohen J.C., Hobbs H.H,, and Stephens R., “WholePathwayScope: a comprehensive pathway-based analysis tool for high-throughput data,” BMC Bioinformatics, vol. 7 (2006), pp. 30.
Yue P., Melamud E., and Moult J., “SNPs3D: Candidate gene and SNP selection for association studies,” BMC Bioinformatics, vol. 7 (2006), pp. 166.
Editorial, “Embracing risk,” Nature Genetics 38, 1 (2006)
Performance Metrics
|
Genetic Association Database
|
|
- Number of records in the database:
|
28,462
|
|
|
964,273
|
- Number of unique visitors:
|
30,788
|
- Number of whole database downloads:
|
463
|
|
|
20,200
|
|
PubMatrix SE
|
|
- Gene Recognition Accuracy:
|
74.5%
|
- Number of processed citations in the database:
|
22,806
|