| Glaucoma | Diabetic Eye Disease | Low Vision | Healthy Eyes |
Common vision problems
The most common vision problems are refractive errors, more commonly known as nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism and presbyopia. Refractive errors occur when the shape of the eye prevents light from focusing directly on the retina. The length of the eyeball (either longer or shorter), changes in the shape of the cornea, or aging of the lens can cause refractive errors. Most people have one or more of these conditions.
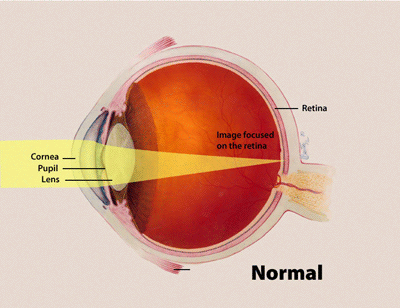
The cornea and lens bend (refract) incoming light rays so they focus precisely on the retina at the back of the eye.
What is refraction?
Refraction is the bending of light as it passes through one object to another. Vision occurs when light rays are bent (refracted) as they pass through the cornea and the lens. The light is then focused on the retina. The retina converts the light-rays into messages that are sent through the optic nerve to the brain. The brain interprets these messages into the images we see.
What are the different types of refractive errors?
The most common types of refractive errors are nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism and presbyopia.
Nearsightedness (also called myopia) is a condition where objects up close appear clearly, while objects far away appear blurry. With nearsightedness, light comes to focus in front of the retina instead of on the retina. Learn more about nearsightedness.
Farsightedness (also called hyperopia) is a common type of refractive error where distant objects may be seen more clearly than objects that are near. However, people experience farsightedness differently. Some people may not notice any problems with their vision, especially when they are young. For people with significant farsightedness, vision can be blurry for objects at any distance, near or far. Learn more about farsightedness.
Astigmatism is a condition in which the eye does not focus light evenly onto the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. This can cause images to appear blurry and stretched out. Learn more about astigmatism.
Presbyopia is an age-related condition in which the ability to focus up close becomes more difficult. As the eye ages, the lens can no longer change shape enough to allow the eye to focus close objects clearly. Learn more about presbyopia.
Who is at risk for refractive errors?
Presbyopia affects most adults over age 35. Other refractive errors can affect both children and adults. Individuals that have parents with certain refractive errors may be more likely to get one or more refractive errors.
What are the signs and symptoms of refractive errors?
Blurred vision is the most common symptom of refractive errors. Other symptoms may include:
- Double vision
- Haziness
- Glare or halos around bright lights
- Squinting
- Headaches
- Eye strain
How are refractive errors diagnosed?
An eye care professional can diagnose refractive errors during a comprehensive dilated eye examination. People with a refractive error often visit their eye care professional with complaints of visual discomfort or blurred vision. However, some people don't know they aren't seeing as clearly as they could.
How are refractive errors corrected?
Refractive errors can be corrected with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or surgery.