Panel Slides
Jump to Slides:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44
Slide 1

New Approaches to Pediatric Obesity: Helping Families Help Kids
Web Seminar
November 18, 2010
Back to top
Slide 2

What Is the Health Care Innovations Exchange?
Searchable database of service innovations
- Includes successes and attempts
- Wide variety of sources, including unpublished materials
- Vetted for effectiveness and applicability to patient care delivery
- Categorized for ease of use—extensive browse and search functions
- Includes innovators’ stories and lessons learned
- Features expert commentaries
Learning opportunities
- Learning networks offering a chance to work with others shared concerns
- Educational content
- Web Events featuring innovators, experts, and adopters
Back to top
Slide 3

Innovations Exchange Web Event Series
How to find archived materials
Next Event
- Web event in January-look for the announcement
Evaluation
- At the end of this Web event, please complete the evaluation.
Back to top
Slide 4

Healthy Weight Initiative
- Led by the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA).
- Aims to provide and promote family-centered, coordinated, community-based care for overweight and obese children and their families
- Integrates public and community health and primary care.
Back to top
Slide 5

Housekeeping
- No phone is necessary for this event
- You may just stream the audio over the Web through the speakers on your computer.
- For help, notify the Vcall team through the question window at the bottom of the screen.
- To refresh your screen, hit f5
- Visit www.innovations.ahrq.gov for a transcript of this Web seminar and the PowerPoint slides.
Back to top
Slide 6

Submitting Questions
- When: Any time during the presentation
- How: Send a written question through the question window
Arrow pointing to the question window during a Web event.
Back to top
Slide 7

Today's Event Moderator
Sarah Hampl, MD
Picture of Sarah Hampl
Medical Director, Weight Management Program
Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics
Associate Professor of Pediatrics
University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine
Back to top
Slide 8

Topics in Today’s Web Event
- LAUNCH (Learning about Activity and Understanding Nutrition for Child Health): Preschooler obesity treatment in clinic and home settings
- Brenner FIT (Families in Training): School-aged/adolescent obesity treatment in clinic and group settings
- Common elements
- Treatment for kids and parents
- Rigorous interventions
- Involve primary care and other providers
Back to top
Slide 9
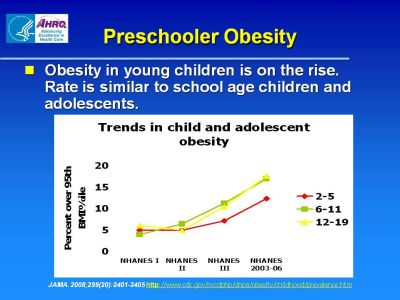
Preschooler Obesity
Obesity in young children is on the rise. Rate is similar to school age children and adolescents.
Figure shows that the percent of children between the ages of 2 and 5 and 6 and 11 and adolescents between the ages of 12 and 19 that are over the 95th BMI percentile has grown in recent years as indicated by results from NHANES I, NHANES II, NHANES III, and NHANES 2003-06.
References:
JAMA. 2008;299(20):2401-2405 http://www.cdc.gov/nccdphp/dnpa/obesity/childhood/prevalence.htm
Back to top
Slide 10

Health Risks for Obese Preschoolers
- More likely to remain overweight at age 12 years than preschoolers who remain <50th percentile body mass index (BMI)
- Medical co-morbidities
References:
Pediatrics 2006 Sep;118(3):e594-601
Pediatrics 2008 Aug;122:267-272
Clin Pediatr 2010 July;49(7):648-655
Back to top
Slide 11

Parent-related Issues
- Influence on eating and physical activity behaviors
- Beliefs about child’s weight status
- Difficulty understanding growth charts
- Perceived barriers to healthy lifestyles
- TV time/location
- Physical activity
- Walking to school
- Less fast food
- Healthier family diet
References:
Pediatrics. 2006 Mar;117(3):681-90
Pediatrics. 2009 Oct;124(4):1100-9
BMC Pediatrics 2009,9:81
Back to top
Slide 12
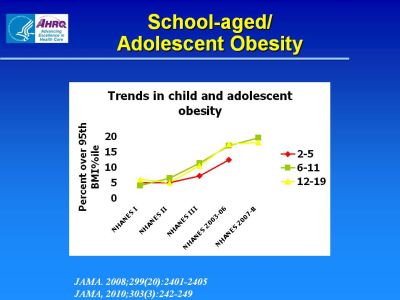
School-aged/Adolescent Obesity
Figure shows that the percent of children between the ages of 2 and 5 and 6 and 11 and adolescents between the ages of 12 and 19 that are over the 95th BMI percentile has grown in recent years as indicated by results from NHANES I, NHANES II, NHANES III, NHANES 2003-06, and NHAMES 2007-8. Growth has been greatest for children ages 6 to 11, followed by children 2 to 5.
References:
JAMA. 2008;299(20):2401-2405
JAMA. 2010;303(3):242-249
Back to top
Slide 13

Treatment Recommendations
- Expert Committee on Assessment, Prevention and Treatment of Child and Adolescent Overweight and Obesity
- U.S. Preventive Services Task Force
References:
Pediatrics 2007;120;S254-S288
Pediatrics 2010;125;e396-e418
Pediatrics 2010;125:361-367
Back to top
Slide 14

Outcomes Evaluation
- Process measures
- Satisfaction
- Barriers/facilitators
- Attrition
- Quality improvement
- Outcome measures
Back to top
Slide 15

Our Innovators
Joseph Skelton, MD
Picture of Joseph Skelton
Assistant Professor of Pediatrics and Epidemiology and Prevention
Wake Forest University School of Medicine
Director, Brenner FIT Program (Families In Training)
Brenner Children’s Hospital
Back to top
Slide 16

Our Innovators
Lori Stark, PhD, ABPP
Picture of Lori Stark
Director, Division of Behavioral Medicine & Clinical Psychology
Professor, Department of Pediatrics
University of Cincinnati School of Medicine
Back to top
Slide 17

LAUNCH: Learning about Activity and Understanding Nutrition for Child Health
Lori J. Stark, PhD, ABPP
Back to top
Slide 18

Participants
- Inclusion criteria
- Exclusion criteria
- Profile of participating children
- Profile of participating parents
Back to top
Slide 19

Intervention: Standard Care
- One-time visit with a pediatrician trained in weight management interventions
- Reduce sweet drinks
- Increase fruits and vegetables
- Reduce portion sizes
- Recommendations for physical activity
- Reduce screen time
- Provided with age-appropriate handouts
Back to top
Slide 20

Standard Care: Examples
Figure shows healthy serving sizes for 4 to 6 year olds for the following food groups: grain, fruit/vegetable, milk, meat, and fat. Figure also shows recommendations for the twelfth visit for 5-6 year olds, including questions about eating habits, advice on appropriate food, and how to support greater physical activity.
Back to top
Slide 21

LAUNCH
- 6 month behavioral Family Intervention
- Alternating clinic and home visits
- Intensive: 12 weeks of weekly visits
- Maintenance: 12 weeks of biweekly visits
- Clinic session includes weigh-in and a 90-minute group
- Parallel child and parent groups
Back to top
Slide 22

Overview: LAUNCH
- Goal: overall healthy family lifestyle through nutrition and activity
- Stimulus control
- Exposure to vegetables
- Shaping
- Addresses developmental issues:
- Feeding—Neophobia
- Challenging behavior—tantrums
Back to top
Slide 23

Nutrition and Behavior
- Nutrition Education:
- Target two meals each week
- Snack/Beverage, Breakfast/Lunch, Dinner
- Portion sizes
- Decrease eating out
- Behavioral:
- Praise and ignoring
- Stimulus control
- Time out
Back to top
Slide 24

Physical Activity
- Physical Activity
- Reduce screen time ≤2 hours/day
- Achieve 60 minutes of active play
- Stimulus control
- Remove TV from play room, bedroom
- Keep TV off when not watching
- Increase outdoor time
- Set up home for active indoor play
Back to top
Slide 25

Home Visits
- Aim of Home Visits—to help parents implement clinic-based recommendations.
- Examples:
- Home clean out
- Make fruit and veggies easily accessible
- Observe and assist with veggie taste test
- Model and coach parents in dealing with temper tantrums for food
- Set up home for active play
- Do a physical activity
Back to top
Slide 26

Parent Response to Home Visit
- Parents welcome home visit
- Do not find home clean out invasive
- Are surprised by number of foods they have that are not in line with weight goal
- Usually have one food they are not willing to part with at initial clean out
- Welcome hands-on help with tantrums
- Parents afraid to deny food if children say they are hungry, even if they just ate
Back to top
Slide 27

Results
- Summary
- Children in LAUNCH were significantly lower than controls on BMI z-score, BMI percentile, and weight at the end of treatment (month 6) and follow-up (month 12)
- Parents of children in LAUNCH lost significantly more weight at the end of treatment and follow-up
Back to top
Slide 28

Problems Encountered
- Parent ambivalence
- “does not look overweight, weight fluctuates, pediatrician has not mentioned this as a problem, will grow out of it”
- Parents find limit setting around food very hard
- Feel like they are depriving the children: “How can I not buy her an ice cream every day at the pool when other kids are getting one? ”
- Influence of other social systems (fathers, grandparents, friends)
- Fathers often not on board and will bring in unhealthy food
- Grandparents as daycare providers or babysitters challenging
- Example: one mother told us her friend confessed to taking her 4 year old daughter for an ice cream every time she babysat because she felt mom was depriving her
Back to top
Slide 29

Problems (Continued)
- Eating out very difficult to impact
- Parent don’t like to cook or don’t know how
- Belief that dinner needs to be an elaborate meal
- Parent desire for fast food
- See eating out as the only “treat” parent gets or only social time
- Difficulties with time management and organization
- Parents feel they have no time to do their own exercise or for child to play
- Parents feel they have no time to cook
- Parent job demands & school and child activity demands
- Parent food preferences and dislikes
- Not unusual for parent to have limited vegetable and fruit likes
- Parents eating in response to stress
Back to top
Slide 30

Conclusions
- Large overall differential effects for a small sample
- Continued drop in BMI for most LAUNCH participants 6 months after treatment ended
- Influencing growth trajectories, but not getting below the 95th percentile
Back to top
Slide 31

Brenner FIT Program
Joseph A. Skelton, MD
Brenner Children’s Hospital logo
Back to top
Slide 32
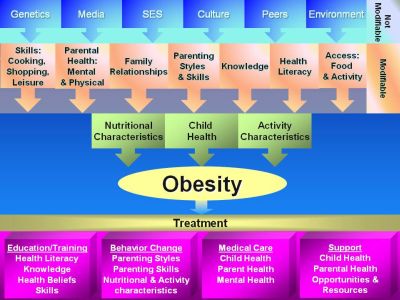
Obesity chart
This chart captures all of the factors that affect obesity, including those not modifiable such as individual genetics and socio-economic background as well as those that are modifiable, such as family relationships, health literacy, and child health. It also captures the major dimensions of treatment for obesity, such as education/training, behavior change, medical care, and support.
Back to top
Slide 33

Overview: Brenner FIT Program
- Mission statement:
Improving the health of obese children through comprehensive, family-focused, & evidence-based treatment
- Tertiary Care Program:
- Multidisciplinary
- High intensity, low volume
- Family-focused and family-centered
- Pilot programs
- Quality Improvement & Outcomes
Back to top
Slide 34

Overview: Brenner FIT Program
- Outcome Measures:
- Reducing Weight
- Reaching high-risk, severely affected children and families (health disparities)
- Reducing drop-out rates
- Increasing satisfaction with treatment
- Philosophy:
- We have evidenced-based treatment approaches
- We need better ways to apply them
Back to top
Slide 35

Brenner FIT Program
- Multidisciplinary team
- Behavioral approach
- Motivational interviewing*
- Family-focused and family-centered
- Physician: assessing and managing co-morbidities
- One year duration, 4 month intervals
Back to top
Slide 36

Brenner FIT: Funding
- MD billing and reimbursement
- Family Counselor and Dietician
- Physical Therapist
- Fundraising a priority
Back to top
Slide 37
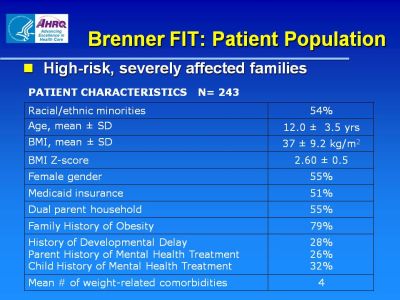
Brenner FIT: Patient Population
- High-risk, severely affected families
Patient Characteristics N=243
| Racial/ethnic minorities |
54% |
| Age, mean ± SD |
12.0 ± 3.5 yrs |
| BMI, mean ± SD |
37 ± 9.2 kg/m2 |
| BMI Z-score |
2.60 ± 0.5 |
| Female gender |
55% |
| Medicaid insurance |
51% |
| Dual parent household |
55% |
| Family History of Obesity |
79% |
History of Developmental Delay
Parent History of Mental Health Treatment
Child History of Mental Health Treatment |
25%
26%
32% |
| Mean # of weight-related comorbidities |
4 |
Back to top
Slide 38

Case Study: "Lisa"
- 14 year old female
- BMI=36, Polycystic Ovaries, insulin resistance
- Single mom employed in law office, Dad minimally involved
- Previous dieter with some binging
- Lost 15lbs last year, but gained back quickly
- Phone coaching
- Delayed starting program until soccer season over
- Motivational Interviewing
- Mom and Lisa chose goals together, cooperatively
- Program halted temporarily
- Participated in community-based programs
- Restarted 9 months later
*Ross et al, MANUSCRIPT IN PREPARATION
Back to top
Slide 39

Brenner FIT: Outcomes
- Outcomes in Brenner FIT
- 84% improved BMI z-score: -0.05 overall
- Factors associated with increased BMI z-score:
- Previous weight management attempt, # of co-morbidities, hours of sedentary activity, age
- No differences by gender, race/ethnicity, distance from clinic, insurance status
Back to top
Slide 40
Brenner FIT: Drop-out Rates
- High drop-out rates from clinical programs: 27-73%*
- Brenner FIT (N=133)**
- 32% drop out in first 4 months—steady rate across 8 visits
- Factors associated with dropout: Older age, poor school performance, lower BMI z-score, presence of major weight-related co-morbidity
- Parent-reported reasons for dropout: child not ready, child’s weight not improving, child wanted to stop, program not meeting expectations (parent and child)
- Instituted satisfaction survey
*Skelton and Beech, Obesity Reviews, 2010 IN PRESS
**Skelton et al UNDER REVIEW
Back to top
Slide 41

Brenner FIT: Quality & Process Improvement
- Pilot programs: geared to reach underserved and improve outcomes
- TOTS: Tele-Obesity Treatment Study
- Spanish Language Program: Case manager model
- FIT Meals: cooking, shopping, meal planning class
- Buddy FIT: modeled on Big Brother/Big Sister
Back to top
Slide 42

Brenner FIT Program: Summary
- High Intensity, comprehensive approach
- Funding always a challenge
- Outcome metrics
- Quality improvement
- Build into culture of program
- Engage team in process
- Pilot programs
Back to top
Slide 43

Get in Touch...
Back to top
Slide 44

Read the Featured Profiles
Back to top
