By Julia Karow
October 20, 2009
The National Institutes of Health has awarded at least $145 million in funding from the 2009 American Recovery and Reinvestment Act to sequencing-related projects in fiscal year 2009, according to an analysis of award data by In Sequence.
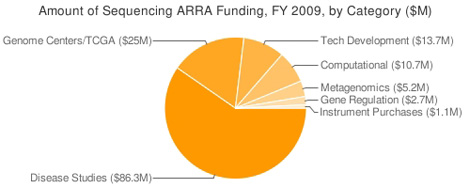
Three-quarters of the funding went to a variety of sequencing projects that are using patient samples to study disease, including sequencing for the Cancer Genome Atlas project, followed by projects for sequencing technology development, computational development, metagenomics, gene regulation and sequencing instrumentation purchases (see charts below).
The analysis was conducted by a survey of project titles for stimulus-funded grants in NIH's RePORTER database, which was frozen as of Sept. 30, the end of the fiscal year. As such, it is likely to be incomplete.
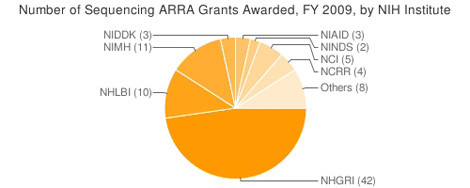
In total, In Sequence identified 89 sequencing-related awards, which received $144.7 million in stimulus funding in fiscal year 2009. Sixty-four of these grants are for new projects, whereas 25 are supplemental awards for existing grants.
The number of awards represents just 0.7 percent of the 12,788 ARRA grants awarded by NIH in fiscal 2009, but around 3 percent of the $4.4 billion in total NIH stimulus funding this year.
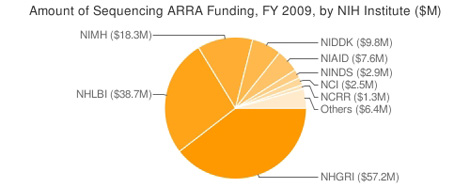
The largest amount of stimulus funding for sequencing came from the National Human Genome Research Institute, which awarded $57.2 million for grants in this area — approximately half its total ARRA budget — in fiscal 2009, followed by $38.7 million from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; $18.3 million from the National Institute of Mental Health; $9.8 million from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; and $7.6 million from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (see charts below).
Focus on Disease
Projects focusing on harnessing sequencing to find genetic factors underlying a variety of diseases reaped the greatest benefit from the reinvestment act: overall, 40 such awards gathered a combined $86.3 million this year, excluding funding for TCGA (see table below).
The largest single award, $12.3 million from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, went to Eric Boerwinkle at the University of Texas Health Science Center for a project titled "Building on GWAS for NHLBI-diseases: the US CHARGE Consortium."
According to the grant abstract, the project aims to identify susceptibility genes, based on findings from genome-wide association studies for heart, lung and blood diseases in the CHARGE consortium. The consortium consists of several large cohort studies, including the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities, or ARIC, study; the Cardiovascular Health Study; the Framingham Heart Study; and the Coronary Artery Risk Developments in Young Adults study.
The researchers plan to first resequence 60 genomic regions that influence 15 phenotypes, sequencing 400 cases and 400 controls for each phenotype. In addition, they want to sequence whole genomes of 230 African-American ARIC participants, selected from the top and bottom 10 percent of the HDL-cholesterol distribution, in order to identify the "the dark matter of unaccounted-for genetic variance" for the HDL cholesterol phenotype. Any sequencing-based discoveries will be validated by genotyping in additional samples.
The infrastructure for the project, according to the abstract, "is already in place," as a result of ongoing collaborations among genomic scientists, physicians, epidemiologists, and population and statistical geneticists.
Two other large NHLBI awards, for exome- and, in some cases, genome-wide sequencing of 10,000 well-phenotyped samples went to David Altshuler and Stacey Gabriel at the Broad Institute, who received $10.2 million in fiscal 2009, and to four researchers at the University of Washington, who received $11 million — $8.5 million from NHLBI and $2.5 million from the Office of the Director.
Both awards, which total $50 million over their lifetime, are part of a $64 million NHLBI project to sequence and analyze the exomes of participants in 12 long-term studies (see In Sequence 10/6/2009). Four related awards, for managing sample cohorts for the study, went to Rebecca Jackson and colleagues at Ohio State University Medical Center, Michael Bamshad and colleagues at the University of Washington, Timothy Graubert and colleagues at Washington University in St. Louis, and Stephen Rich at the University of Virginia Health System.
Altshuler and Michael Boehnke, of the University of Michigan, won another large-scale award for a separate project, from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, that totals $8.9 million in fiscal 2009. Entitled "Low-Pass Sequencing and High-Density SNP Genotyping for Type 2 Diabetes," the project proposes to use next-generation sequencing to study low-frequency variants in type-2 diabetes case-control samples.
According to the grant abstract, the study will compare three strategies for discovering genes involved in type-2 diabetes and other diseases: imputation and in silico association analysis using existing GWA data and data from the 1000 Genomes Project, employing next-generation high-density SNP arrays, and low-pass whole-genome sequencing. Each strategy will be used in 3,000 case-control samples from three GWA studies and will be evaluated "with regard to completeness of variant discovery, genotype accuracy and cost-effectiveness, providing guidance to other researchers in the field."
Several grants went to projects that seek to use sequencing to study neurological diseases, including autism, bipolar disorder and schizophrenia, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, and epilepsy.
Among them are five related awards, totaling almost $8 million in fiscal 2009, for a project to elucidate "the genetic architecture of autism by deep genomic sequencing," to groups at Vanderbilt University, the Broad Institute, Baylor College of Medicine, Mount Sinai School of Medicine and the University of Pennsylvania (see In Sequence 10/6/2009).
Other funded projects in the disease-focused category study Mendelian diseases, gout, myotonic dystrophy, myelodysplastic syndromes, human respiratory chain disease, SCID, B-cell lymphoma, HIV/AIDS, pancreatic cancer, hepatitis C and hyperplastic vasculomyopathy.
Sequencing for TCGA
Another large chunk of stimulus funding — $25 million in fiscal 2009 — went to the three genome centers that are funded by the National Human Genome Research Institute, in the form of supplements to their existing grants.
An NHGRI program officer confirmed this week that this funding will go toward sequencing and analysis for the Cancer Genome Atlas, a project that is jointly sponsored by the National Cancer Institute and the NHGRI.
Earlier this month, NCI said that TCGA had received $275 million in new funding, of which $175 million comes from the recovery act. Approximately $125 million of the total is allocated for sequencing, according to the program director (see In Sequence 10/6/2009).
For now, the Genome Center at Washington University School of Medicine received $10 million, the Broad Institute obtained $9 million, and the Baylor College of Medicine Human Genome Sequencing Center was awarded $6 million for sequencing and analysis under TCGA.
Sequencing Technology Development & Computational Tools
Projects seeking to develop new sequencing technology won a total of $13.7 million in fiscal 2009 stimulus funding, all awarded by NHGRI.
The awards are a mixture of newly funded projects and supplements to existing awards under NHGRI's "$1,000 Genome" grant program (see In Sequence 10/13/2009).
Another $10.7 million in fiscal 2009 stimulus funding went to about a dozen projects aiming to develop computational tools to handle as well as analyze high-throughput sequence data.
The largest such award is $4.8 million in supplemental funding to Mark Daly at the Broad Institute for SNP and CNV calling in sequence data from the 1000 Genomes Project.
Another award, for $1.1 million, went to researchers led by Gabor Marth at Boston College to build a data processing pipeline for the National Center for Biotechnology Information that can also be used "by scientists wishing to process and analyze large of amounts of next-generation sequence data."
Metagenomics & Gene Regulation
Eight projects in the areas of metagenomics as well as gene regulation analysis received a total of $7.9 million in fiscal 2009 stimulus funding.
Among them is a $4.6-million award that went to Bob Strausberg at the J. Craig Venter Institute to sequence 110 reference genome, of which 15 will be finished, for the Human Microbiome Project.
Another award, $900,000 to Kevin White at the University of Chicago, proposed to "systematically epitope-tag transcription and chromatin-associated factors for ChIP-seq" in order to "speed current large-scale mapping projects," such as the ENCODE project.
Sequencing Instrumentation
Three awards, totaling $1.1 million, were made under the National Center for Research Resources' Shared Instrumentation Program for the purchase of DNA sequencers (see In Sequence 7/28/2009).

Disease-Related Sequencing Projects Awarded by NIH in FY2009 Using Stimulus Funding
| FY2009 Funding |
Organization |
Project Title |
Principal Investigators |
Admin IC |
| $12,281,613 |
University of Texas Health Science Center |
Building on GWAS for NHLBI-Disease: The CHARGE Consortium |
Eric Boerwinkle |
NHLBI |
| $10,157,633 |
Broad Institute |
Comprehensive Sequencing and Analysis of Variation in NHLBI Cohorts |
David Altshuler, Stacey Gabriel |
NHLBI |
| $8,951,229 |
University of Michigan |
Low-Pass Sequencing and High-Density SNP Genotyping for Type 2 Diabetes |
David Altshuler, Michael Boehnke |
NIDDK |
| $8,508,061 |
University of Washington |
Northwest Genomics Center |
Phillip Green, Deborah Nickerson, Mark Rieder, Jay Shendure |
NHLBI |
| $3,075,000 |
Broad Institute |
Whole Genome Sequencing of Bipolar Disorder and Schizophrenia |
Shaun Purcell, Pamela Sklar |
NIMH |
| $2,727,684 |
Network Biosystems |
Rapid Biothreat Identification in Clinical Samples by Multilocus Sequencing |
Richard Selden |
NIAID |
| $2,594,102 |
University of Washington |
ARRA - NHLBI Lung Cohorts Sequencing Project |
Michael Bamshad |
NHLBI |
| $2,500,000 |
University of Washington |
Northwest Genomics Center |
Phillip Green, Deborah Nickerson, Mark Rieder, Jay Shendure |
OD |
| $2,478,799 |
Vanderbilt University |
5/5 - Elucidating the Genetic Architecture of Autism by Deep Genomic Sequencing |
James Sutcliffe |
NIMH |
| $2,474,114 |
Children's Hospital, Boston |
Human Autism Genetics and Activity - Dependent Gene Activation |
Christopher Walsh |
NIMH, OD |
| $2,442,659 |
Broad Institute |
2/5 - Elucidating the Genetic Architecture of Autism by Deep Genomic Sequencing |
Mark Daly |
NIMH |
| $2,113,954 |
Ohio State University |
WHI Sequencing Project (WHISP) |
Christopher Carlson, Rebecca Jackson, Kari North, Ulrike Peters |
NHLBI |
| $2,000,000 |
Baylor College of Medicine |
1/5 - Elucidating the Genetic Architecture of Autism by Deep Genomic Sequencing |
Richard Gibbs |
NIMH |
| $1,976,527 |
University of Washington |
Genetics of Lipid Levels: Draft Sequencing of 1000 Genomes |
Goncalo Rocha Abecasis |
NHGRI |
| $1,960,613 |
University of Washington |
Next Generation Mendelian Genetics |
Michael Bamshad, Deborah Nickerson, Wendy Raskind, Jay Shendure |
NHGRI |
| $1,804,409 |
University of Massachusetts Medical School |
Full Human Genome Sequencing in ALS |
Robert Brown |
NINDS |
| $1,671,247 |
Duke University |
Whole-Genome Sequencing for Rare Highly Penetrant Gene Variants in Schizophrenia |
David Goldstein |
NIMH |
| $1,483,107 |
Massachusetts Institute of Technology |
Deep Sequencing Analysis of mRNA Isoform Expression Changes in Myotonic Dystrophy |
Christopher Burge, Thomase Cooper, David Housman |
NHGRI |
| $1,384,503 |
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory |
Deep Sequencing of Autism Candidate Genes in 2000 Families from the Simons Sample |
Richard McCombie, Michael Wigler |
NIMH |
| $1,317,671 |
University of Texas Health Science Center |
Next-Generation Medical Resequencing of Gout Disease Genes in the Aric Cohort |
James Hixon |
NHGRI |
| $1,224,842 |
Washington University |
Whole Genome Sequencing of Myelodysplastic Syndromes |
Timothy Graubert |
NHLBI |
| $1,183,908 |
Yale University |
Genomic Profiling and Functional Mutation Analysis in Autism Spectrum Disorders |
Matthew State |
NIMH |
| $1,099,524 |
Duke University |
Whole-Genome Sequencing in Multiplex Epilepsy Families |
David Goldstein, Ruth Ottman |
NINDS |
| $993,317 |
Massachusetts Institute of Technology |
Defining the Genetic Basis of Human Respiratory Chain Disease |
Vamsi Krishna Mootha |
NHGRI |
| $850,000 |
University of Washington |
Application of Ribotag-seq to Exploration of Tumor Microenvironments |
David Morris |
NCI |
| $817,287 |
University of Virginia Charlottesville |
Human Exome Sequencing in Six Well-Phenotyped NHLBI Cohorts |
Stephen Rich |
NHLBI |
| $810,738 |
University of Texas Austin |
Next-Gen Sequencing: Searching for Mechanisms of Alcohol and Nicotine Dependence |
Roy Mayfield |
NIAAA |
| $758,511 |
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute |
An Infrastructure for Cancer Virus Discovery for Next-Generation Sequencing Data |
Matthew Meyerson |
NCI |
| $571,568 |
Mount Sinai School of Medicine |
3/5-Elucidating the Genetic Architecture of Autism by Deep Genome Sequencing |
Joseph Buxbaum |
NIMH |
| $564,301 |
California Institute of Technology |
RNA-seq Studies of Gene Expression in Cells and Networks in FI and ACC in Autism |
John Allman, Barbara Wold |
NIMH |
| $500,000 |
Duke University |
Identification of Disease-Causing Mutations in SCID Using Exome-Wide Sequencing |
Joseph Roberts |
NHLBI |
| $500,000 |
Scripps Research Institute |
Deep Sequencing of Small Regulatory RNAs in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma |
Changchun Xiao |
NCI |
| $500,000 |
University of California Riverside |
Virus Discovery by Deep Sequencing and Assembly of Virus-Derived siRNAs |
Shou-Wei Ding |
NIGMS |
| $500,000 |
University of Chicago |
Genome-Wide Association and Exon Sequencing Study in IPF |
Naftali Kaminski, Dan Nicolae, Imre Noth |
NHLBI |
| $490,729 |
University of Michigan |
Exon Capture and Large-Scale Sequencing for Disease-Cause Identification, Early Detection |
Friedhelm Hildebrandt |
NIDDK |
| $482,846 |
University of Pennsylvania |
4/5-Elucidating the Genetic Architecture of Autism by Deep Genome Sequencing |
Gerard David Schellenberg |
NIMH |
| $266,000 |
Brigham and Women's Hospital |
V3 Loop Characterization by Ultradeep Sequencing During CCR5 Antagonist Therapy |
Daniel Kuritzkes |
NIAID |
| $255,225 |
Johns Hopkins University |
High-Throughput Analysis of Pancreatic Cancer Mutations |
Scott Ken |
NCI |
| $12,537 |
Saint Louis University |
Role of HCV Sequence Variation in Pathology |
John Tavis |
NIDDK |
| $7,223 |
University of Texas Health Science Center |
Sequencing Candidate Genes for Hyperplastic Vasculomyopathy |
Diana Milewicz |
NHLBI |
This article originally appeared on the GenomeWeb website. Reposted with permission.