What is Clinger-Cohen?
Clinger-Cohen Act (CCA) of 1996 provides that the government information technology shop be operated exactly as an efficient and profitable business would be operated. Acquisition, planning and management of technology must be treated as a "capital investment." While the law is complex, all consumers of hardware and software in the Department should be aware of the Chief Information Officer's leadership in implementing this statute.
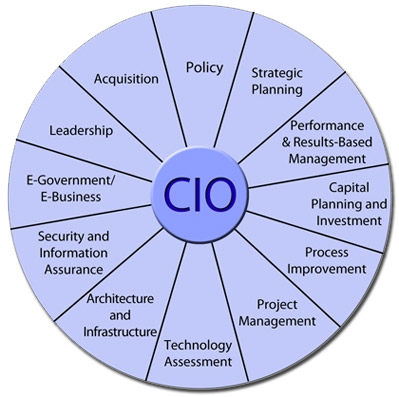
1.0 Policy and Organizational
1.1 Department/Agency missions, organization, functions, policies, procedures
1.2 Governing laws and regulations (e.g., the Clinger-Cohen Act E-Government Act, GPRA, PRA, GPEA, OMB Circulars A-11 and A-130, PDD 63)
1.3 Federal government decision-making, policy making process and budget formulation and execution process
1.4 Linkages and interrelationships among Agency Heads, COO, CIO, and CFO functions
1.5 Intergovernmental programs, policies, and processes
1.6 Privacy and security
1.7 Information management
2.0 Leadership/Managerial
2.1 Defining roles, skill sets, and responsibilities of Senior Officials, CIO staff and stakeholders
2.2 Methods for building federal IT management and technical staff expertise
2.3 Competency testing - standards, certification, and performance assessment
2.4 Partnership/team-building techniques
2.5 Personnel performance management techniques
2.6 Principles and practices of knowledge management
2.7 Practices which attract and retain qualified IT personnel
3.0 Process/Change Management
3.1 Techniques/models of organizational development and change
3.2 Techniques and models of process management and control
3.3 Modeling and simulation tools and methods
3.4 Quality improvement models and methods
3.5 Business process redesign/reengineering models and methods
4.0 Information Resources Strategy and Planning
4.1 IT baseline assessment analysis
4.2 Interdepartmental, inter-agency IT functional analysis
4.3 IT planning methodologies
4.4 Contingency planning
4.5 Monitoring and evaluation methods and techniques
5.0 IT Performance Assessment: Models and Methods
5.1 GPRA and IT: Measuring the business value of IT, and customer satisfaction
5.2 Monitoring and measuring new system development: When and how to "pull the plug" on systems
5.3 Measuring IT success: practical and impractical approaches
5.4 Processes and tools for creating, administering, and analyzing survey questionnaires
5.5 Techniques for defining and selecting effective performance measures
5.6 Examples of and criteria for performance evaluation
5.7 Managing IT reviews and oversight processes
6.0 Project/Program Management
6.1 Project scope/requirements management
6.2 Project integration management
6.3 Project time/cost/performance management
6.4 Project quality management
6.5 Project risk management
6.6 Project procurement management
6.7 System life cycle management
6.8 Software development
7.0 Capital Planning and Investment Assessment
7.1 Best practices
7.2 Cost benefit, economic, and risk analysis
7.3 Risk management- models and methods
7.4 Weighing benefits of alternative IT investments
7.5 Capital investment analysis- models and methods
7.6 Business case analysis
7.7 Integrating performance with mission and budget process
7.8 Investment review process
7.9 Intergovernmental, Federal, State, and Local Projects
8.0 Acquisition
8.1 Alternative functional approaches (necessity, government, IT) analysis 8.2 Alternative acquisition models
8.3 Streamlined acquisition methodologies
8.4 Post-award IT contract management models and methods, including past performance evaluation
8.5 IT acquisition best practices
9.0 E-Government/Electronic Business/Electronic Commerce
9.1 Strategic business issues & changes w/advent of E-Gov/EB/EC
9.2 Web development strategies
9.3 Industry standards and practices for communications
9.4 Channel issues (supply chains)
9.5 Dynamic pricing
9.6 Consumer/citizen information services
9.7 Social issues
10. IT Security/Information Assurance
10.1 Fundamental principles and best practices in IA
10.2 Threats and vulnerabilities to IT systems
10.3 Legal and policy issues for management and end users
10.4 Sources for IT security assistance
10.5 Standard operating procedures for reacting to intrusions/misuse of federal IT systems
11.0 Enterprise Architecture
11.1 Enterprise architecture functions and governance
11.2 Key enterprise architecture concepts
11.3 Enterprise architecture development and maintenance
11.4 Use of enterprise architecture in IT investment decision making
11.5 Interpretation of enterprise architecture models and artifacts
11.6 Data management
11.7 Performance measurement for enterprise architecture
12.0 Technical
12.1 Emerging/developing technologies
12.2 Information delivery technology (internet, intranet, kiosks, etc.)
12.3 Desk Top Technology Tools