NIH Research Matters
March 2009 Archive
March 30, 2009
Neighborhood Food Options Linked to Obesity in New York City
Access to stores that sell healthy foods may be a crucial factor in fighting obesity, according to a new study.
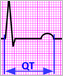
Gene Variants Tied to Abnormal Heart Rhythm Risk
Two international research teams, working independently, have linked variations in 10 gene regions with potentially harmful modifications in the heart's electrical rhythm. The discoveries may lead to new approaches for treating and preventing irregular heart rhythms and sudden cardiac death.
Spinal Cord Stimulation May Ease Parkinson's Symptoms
Electrical stimulation of the spinal cord improves mobility in rodents that have the symptoms of Parkinson's disease, according to a new study. The technique, if effective in people, could provide a less invasive alternative to deep brain stimulation, which involves surgically implanting tiny electrodes into brain regions that control movement.
March 23, 2009
Results Question Annual Prostate Cancer Screening
The prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test can spot prostate cancer early. Surprisingly, annual tests might not lead to fewer prostate cancer deaths, according to a new report.
Heart Failure Before Age 50 More Common in Black People
According to a new study, about 1 in 100 black men and women could develop heart failure before age 50—a strikingly higher rate than for white people. But heart failure is often preceded years earlier by risk factors that can be prevented or treated, like high blood pressure and obesity. These findings highlight the importance of targeting these risk factors in young black people.
DNA Terrain Affects Function in Human Genome
Researchers have developed a novel method for detecting functionalregions of the human genome: examining its three-dimensional(3D) structure. The new approach will help researchers use genomicinformation to improve human health.
March 16, 2009
Vitamin C May Reduce Risk of Gout
A new study has linked higher vitamin C intake with a lower risk of gout. Vitamin C supplements, the results imply, may help to prevent gout.
Thwarting Fungal Defenses
Researchers have devised a way to stymie fungi's ability to become resistant to antifungal drugs. The advance paves the way for future therapies to treat fungal infections, a leading cause of death for people with weakened immune systems.
Understanding How Mosquitoes Fight Malaria
Scientists have discovered how the mosquito immune system detects and kills the deadly malaria parasite. The discovery could help researchers develop innovative methods to block transmission of the disease from mosquitoes to humans.
March 9, 2009
Low Vitamin D Levels Associated with Colds and Flu
A new study has found that vitamin D may play a role in helping the immune system ward off respiratory diseases like the common cold.
Drug Combination Defeats Deadliest Form of Tuberculosis
A new study has identified a potential treatment for extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis, the most deadly form of the disease. The treatment involves a combination of 2 drugs that have already been approved for fighting bacterial infections
Non-Infectious Prion Protein Linked to Alzheimer's Disease
The prion protein, notorious for causing fatal neurodegenerative disorders such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and mad cow disease, may also be an accomplice in Alzheimer's disease, according to a new study. In this case, it's not the infectious misfolded prion protein causing the problem but the cellular form, whose function is relatively unknown.
March 2, 2009
Genetic Tests Help Optimize Doses of Blood-Thinning Drug
Genetic tests can help doctors fine-tune the dosing of the widely prescribed blood-thinner warfarin for individual patients, according to a new study. The research may ultimately help patients avoid the life-threatening dangers of too-high or too-low doses of the drug.
Weight Loss Depends on Less Calories, Not Nutrient Mix
Heart-healthy diets that reduce calorie intake—regardless of differing proportions of fat, protein or carbohydrate—can help overweight and obese adults achieve and maintain weight loss, according to a new study.
Antibodies Neutralize Multiple Flu Strains
Two separate scientific teams have discovered antibodies that attach to a vulnerable region in a broad range of influenza A viruses, including the H5N1 avian virus, the 1918 pandemic influenza virus and seasonal H1N1 flu viruses. The finding could potentially help scientists develop tools to prevent or treat the flu during an outbreak or pandemic.
Editor’s Picks
Contact Us
Phone: 301-435-7489
E-mail: nihresearchmatters@od.nih.gov
Mailing Address:
NIH Research Matters
Bldg. 31, Rm. 5B64A, MSC 2094
Bethesda, MD 20892-2094
About NIH Research Matters
Harrison Wein, Ph.D., Editor
Vicki Contie, Assistant Editor
NIH Research Matters is a weekly update of NIH research highlights from the Office of Communications and Public Liaison, Office of the Director, National Institutes of Health.










Social Media Links