
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES
Albumin (al-BYOO-min) is a protein found in the blood. A healthy kidney does not let albumin pass into the urine. A damaged kidney lets some albumin pass into the urine. The less albumin in your urine, the better.
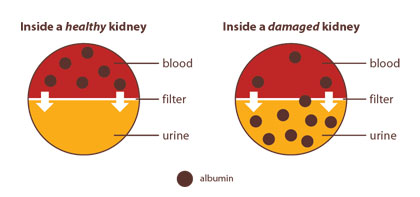
If you are at risk for kidney disease, your provider should check your urine for albumin along with checking your GFR.
Your provider may send your urine sample to the lab to see if albumin, a type of protein, is in your urine.
When your results come back, you may hear terms such as "microalbuminuria," "macroalbuminuria," "urine protein," "proteinuria," "albuminuria," or "urine-to-creatinine ratio," which are all used to describe how much albumin was found.
In addition to your urine albumin test, your provider should also check your GFR.
If you do not understand your lab results, ask your health care provider to explain them to you. Please remember that the information on this website should not take the place of talking with your health care provider.
You should also ask your provider what you can do to keep your kidneys healthy.
Learn more about how to keep your kidneys healthy.
Page last updated: March 1, 2012