Identification of Survival Motor Neuron Modulators for Potential Spinal Muscular Atrophy Therapeutics
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is an autosomal recessive disorder affecting the selective degeneration of survival motor neuron (SMN) in the spinal cord due to the deletion or mutations of the survival motor neuron gene 1 (SMN1). However, the human genome includes a second nearly identical gene called SMN2 which functionally differs from SMN1 by a critical nucleotide C to T transition residing in exon 7. Although SMN2 is able to produce a small portion of full length SMN protein, the majority of SMN2 RNAs undergo alternative splicing and produce truncated, proteolytically unstable SMN variants that are not able to replace the function of full length SMN protein.
Therefore, increasing overall SMN production through up-regulation of SMN2 expression or through the variation of splicing rate has been postulated to be one of the potential therapeutic strategies for SMA. In the report below, we detail the discovery of a series of arylpiperidines as novel modulators of SMN protein production from a qHTS campaign of the 210,386-compound NIH Molecular Libraries Small Molecule Repository. We anticipate that the probe compound, which has very high potency and a capacity to increase induction of SMN promoter 3 to 7 fold in the reporter assay, may serve as a useful lead for exploring the therapeutic benefits of SMN protein induction in SMA animal models, and ultimately in human clinical trials.
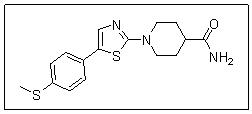
ML200
Key Investigators
National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences
Jingbo Xiao, Ph.D.
Juan J. Marugan, Ph.D.
Wei Zheng, Ph.D.
Steve Titus
Noel Southall, Ph.D.
Christopher P. Austin, M.D.
University of Massachusetts Medical School
Jonathan J. Cherry
Matthew Evans, Ph.D.
Elliot Androphy, M.D.
Public Health Impact
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is caused by insufficient levels of the survival motor neuron (SMN) protein. The probe indentified can be used to study the mechanism of action for the specific upregulation of SMN2, as well as serve as a useful lead for exploring the therapeutic benefits of SMN protein induction in SMA animal models, and ultimately in human clinical trials.
Probe Report
Discovery, SAR and Biological Evaluation of Aryl-thiazol-piperidines as SMN Modulators
Social Media Links