 |
About Site Map Contact Us
|
|
| A service of the U.S. National Library of Medicine® | ||
|
MT-TV
|
MT-TVOn this page:
Reviewed November 2006
What is the official name of the MT-TV gene?The official name of this gene is “mitochondrially encoded tRNA valine.” MT-TV is the gene's official symbol. The MT-TV gene is also known by other names, listed below. Read more about gene names and symbols on the About page. What is the normal function of the MT-TV gene?The MT-TV gene provides instructions for making a particular type of RNA, a molecule that is a chemical cousin of DNA. This type of RNA, called transfer RNA (tRNA), helps assemble protein building blocks known as amino acids into full-length, functioning proteins. The MT-TV gene provides instructions for a specific form of transfer RNA that is designated as tRNAVal. This molecule attaches to a particular amino acid, valine (Val), and inserts it into the appropriate locations in many different proteins. The tRNAVal molecule is present only in cellular structures called mitochondria. These structures convert energy from food into a form that cells can use. Through a process called oxidative phosphorylation, mitochondria use oxygen and simple sugars to create adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell's main energy source. The tRNAVal molecule is involved in the assembly of proteins that carry out oxidative phosphorylation. Does the MT-TV gene share characteristics with other genes?The MT-TV gene belongs to a family of genes called TRNA (transfer RNAs). A gene family is a group of genes that share important characteristics. Classifying individual genes into families helps researchers describe how genes are related to each other. For more information, see What are gene families? in the Handbook. How are changes in the MT-TV gene related to health conditions?
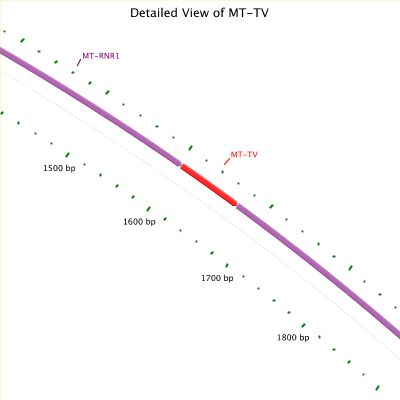
Genetics Home Reference provides information about Leigh syndrome, which is also associated with changes in the MT-TV gene. Where is the MT-TV gene located?The MT-TV gene is located in mitochondrial DNA. Molecular Location in mitochondrial DNA: base pairs 1,601 to 1,669 
 Where can I find additional information about MT-TV?You and your healthcare professional may find the following resources about MT-TV helpful.
You may also be interested in these resources, which are designed for genetics professionals and researchers.
What other names do people use for the MT-TV gene or gene products?
See How are genetic conditions and genes named? in the Handbook. Where can I find general information about genes?The Handbook provides basic information about genetics in clear language.
These links provide additional genetics resources that may be useful. What glossary definitions help with understanding MT-TV?acidosis ; acids ; adenine ; adenosine triphosphate ; amino acid ; ATP ; cardiomyopathy ; cell ; dementia ; DNA ; gene ; guanine ; kidney ; lactic acidosis ; learning disability ; migraine ; mitochondria ; molecule ; mutation ; nervous system ; nucleotide ; oxidative phosphorylation ; oxygen ; phosphorylation ; protein ; RNA ; seizure ; sign ; simple sugar ; symptom ; syndrome ; transfer RNA ; tRNA You may find definitions for these and many other terms in the Genetics Home Reference Glossary. See also Understanding Medical Terminology.
References (7 links)
The resources on this site should not be used as a substitute for professional medical care or advice. Users seeking information about a personal genetic disease, syndrome, or condition should consult with a qualified healthcare professional. See How can I find a genetics professional in my area? in the Handbook. |