| |
 linicalTrials.gov provides patients, family members, health care professionals, and members of the public easy access to information on clinical trials for a wide range of diseases and conditions. The U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), through the National Library of Medicine (NLM), developed this site in close and ongoing collaboration with all NIH Institutes and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
linicalTrials.gov provides patients, family members, health care professionals, and members of the public easy access to information on clinical trials for a wide range of diseases and conditions. The U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), through the National Library of Medicine (NLM), developed this site in close and ongoing collaboration with all NIH Institutes and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
The site was developed as a result of the FDA Modernization Act, which was passed into law in November 1997. Section 113 of this Act requires the Department of Health and Human Services, through the NIH, to establish a registry of clinical trials for both federally and privately funded trials of experimental treatments for serious or life-threatening diseases or conditions. At present, the database contains over 5,000 protocol abstracts from clinical studies sponsored primarily by the NIH. During the coming year additional studies from other Federal agencies and the pharmaceutical industry will be included.
Accessing ClinicalTrials.gov
The Web site can be accessed at http://clinicaltrials.gov/. The Home Page is shown in Figure 1.
All three mechanisms for finding clinical study protocol abstracts are available from the Home Page: Basic Search (query box), Focused Search (link), and Browse (link). Direct access to consumer health-oriented resources is also provided under Resources (link). The same menu bar (directly below the logo) appears on all pages on the site to facilitate navigation.
Basic Search Features
Basic Search (or Search) is provided on the Home Page and on the Search page (also linked to the navigation bar), as shown in Figure 2. It allows users to search broadly.
- Context Specific Help
The Tips link next to the search button provides brief explanatory text and examples for using basic search. More information can be found in the Help, accessible from the menu bar.
- Entering a Search
Search terms are entered in the query box. Use commas to separate words and phrases representing different concepts. Boolean operators are not necessary.
The system automatically includes words or phrases that are synonymous with the search terms. For
example, a search for "heart attack" will also include a search for "myocardial infarction".
- Search Operators
Boolean queries can be constructed in the ClinicalTrials.gov system. The following Boolean operators may be used:
Although the operators may be upper-, lower-, or mixed-case, angle brackets (< >) must be used.
Examples:
- asthma <AND> pregnancy
- (coronary <Or> heart) <and> disease
Boolean searches can be done in the Basic Search box, or in any of the text fields in Focused Search: Disease or Condition, Experimental Treatment, Trial Location, and Additional Terms.
Commas may be used to separate words and phrases. If you search with commas, but no results are found, ClinicalTrials.gov automatically expands your search so as to broaden the search strategy with the goal of retrieving search results. For example, searching "nearsightedness, farsightedness" in the Basic Search results in 3 studies and the message shown in Figure 3.
- Performing the Search
After you have entered terms in the query box, click on the "Search" button or hit "Enter."
- Spell Checking
If a word you entered is not recognized by the system, alternative words found in the database may be offered. For example, for the query "glacoma," two alternatives are presented underneath the search box, as shown in Figure 4.
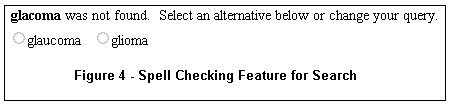
A single click on the circle to the left of the correct word automatically reruns the search with the word substitution.
- Viewing the Results
After users click the "Search" button, retrieved trials are displayed in a brief format on the Search Results page (Figure 5). At the top of the page, the query that was used to obtain these results is shown.
Use the "Examine search details by pressing" button to view the actual query that was formulated by the system. For example, in the case of the phrase "heart attack" (with automatic synonyms), the complete query conducted by the system is:
((myocardial infarctions <TERM>) <OR> (myocardial infarction <TERM>) <OR> (heart attacks <TERM>) <OR> (heart attack <TERM>) <OR> (myocardial infarct <TERM>))
The "Display Selected Studies" button at the bottom of the page allows the viewing of multiple studies. To view a particular set of studies, click on the boxes to the left of the relevant studies. Once they have all been selected, press the "Display Selected Studies" button.
Three important data fields are shown on the "Search Results" page: Status, Title, and Conditions. Status indicates whether a trial is recruiting patients or not. "Not yet recruiting" and "Recruiting" are shown in green; "No longer recruiting," "Completed," "Suspended," and "Terminated," are displayed in red. Trials with these red status indicators are not automatically retrieved when searching. To include these in your retrieval, click on the check box "Show all trials, including those no longer recruiting patients" at the top of the page. See the Help for additional information about status. Titles are hotlinks; clicking on them retrieves the complete record for the clinical study. "Conditions" briefly indicates topics of study.
- Viewing a Study Record
Each study record has the same type of data arranged in the same way on the page. The correspondence between data elements (in the box on the left) and the
information seen by the users (to the right) are shown in Figure 6. Please note
this record has been modified and shortened for illustrative
purposes.
Focused Search Features
Focused Search allows you to narrow your search based on specific criteria. It can be accessed through a link under Search by Specific Information header under the Basic Search query box on the Home Page. Search boxes for five different fields, three limit options, and the "Include synonyms in search" feature make up the search form, as shown in Figure 7.
- Context Specific Help
A Tips link next to the search button at the top of the page provides a brief explanation and examples for using Focused Search. Clicking on the labels to the left of each search box also provides information and examples specific to that field (see Figure 8). More information can be found in the Help, which is accessible from the menu bar.

- Entering a Search
Search terms may be entered in any of the query boxes: Disease or Condition; Experimental Treatment; Trial Location; Additional Terms; and Study ID Number. Not all of the query boxes need to be used. For example, you can type in "heart attack" in the Disease or Condition box and "Kentucky" in the Trial Location box (Figure 7).
- Applying Limits
There are three limits to help narrow the search: Age Group; Study Phase; and Supported By. The checkboxes restrict the search results. By default, no limits are applied. For example, a user searching for Phase II trials for Adults (ages 18-65) would check those boxes.
- Synonyms
The "Include synonyms in search" feature allows the search to include synonyms in the query. By default, synonyms are used in searches. If you prefer not to include synonyms, click on this box to remove the check mark.
- Performing the Search
After all desired terms are entered and limits are applied, click on the "Search" button.
- Spell Checking
Just as in Basic Search, if a query term is not recognized by the system, alternative words may be offered.
Browse
Browse allows you to review clinical studies by selecting from successive groupings. Browse can be accessed from the Home Page and the menu bar. At the top level, there are two branches: Condition and Sponsor.
- Browsing by Condition
The Condition categories are arranged alphabetically (Figure 9) or by Disease Headings (Figure 10).

Browse results also default to those studies that are recruiting or not yet recruiting patients. Clicking on any of the letters brings up a page of diseases and conditions listed alphabetically.
The number of studies related to the disease or condition is shown in parentheses to the right. Clicking on the disease or condition results in a display of studies as described in "Viewing the Results" under the Basic Search Section above.
- Browsing by Sponsor
Another way to browse for studies is by Sponsor. There are four categories of sponsors of clinical studies: National Institutes of Health; Other Federal Agencies; Industry; and University/Organization. Clicking on any group brings up a screen with specific organizations, listed alphabetically. Clicking on one of the organization names results in a list of relevant studies as described in "Viewing the Results" under the Basic Search Section above.
Browse not only provides an overview of what is available in the database, it gives users and other Web sites a way to link directly to groups of trials that are of interest. For example, a support group for diabetes patients may wish to link their Web page directly to the Diabetes entry under Browse (not the ClinicalTrials.gov Home Page).
Future Plans
Plans are underway to evaluate whether user needs are being well served. A framework and model for continued usability testing is under development, including methodologies designed to enhance and refine the interface and content of the system. In addition, together with the National Network of Libraries of Medicine, a number of outreach activities are planned, particularly for underserved and minority communities.
Studies from other Federal agencies and the private sector will be added. Currently, NLM is working with other Federal agencies on the policies and procedures for these Federal agencies and private sector additions.
Contact Information
Please send your comments or questions to custserv@nlm.nih.gov.
By Tony Tse
Lister Hill National Center for Biomedical Communications

Tse T. Searching ClinicalTrials.gov. NLM Tech Bull. 2000 Sep-Oct;(316):e1.
| |


 linicalTrials.gov provides patients, family members, health care professionals, and members of the public easy access to information on clinical trials for a wide range of diseases and conditions. The U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), through the National Library of Medicine (NLM), developed this site in close and ongoing collaboration with all NIH Institutes and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
linicalTrials.gov provides patients, family members, health care professionals, and members of the public easy access to information on clinical trials for a wide range of diseases and conditions. The U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), through the National Library of Medicine (NLM), developed this site in close and ongoing collaboration with all NIH Institutes and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).


