 |
||
| http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/ A service of the U.S. National Library of Medicine® | ||
The official name of this gene is “protein phosphatase 1, regulatory subunit 12A.”
PPP1R12A is the gene's official symbol. The PPP1R12A gene is also known by other names, listed below.
The PPP1R12A gene provides instructions for making a protein called myosin phosphatase target subunit 1. This protein functions as part of a larger enzyme called myosin phosphatase, which regulates the interaction of two important muscle proteins, actin and myosin. In muscle cells, actin and myosin work together to generate the force needed for the normal tensing (contraction) of muscles. Myosin phosphatase attaches to myosin and removes clusters of oxygen and phosphorus atoms (phosphate groups) as part of a complex pathway that allows muscles to contract and relax properly. Myosin phosphatase may also play a role in nonmuscle cells, particularly during cell division.
Myosin phosphatase target subunit 1 is responsible for recognizing the myosin protein and allowing myosin phosphatase to bind to it. The subunit is turned on and off in response to signals within the cell. For example, researchers have found that myosin phosphatase target subunit 1 interacts with the protein produced from the DMPK gene. The DMPK protein turns off (inhibits) the subunit by adding phosphate groups to it. When myosin phosphatase target subunit 1 is turned off, it cannot bind to myosin and the muscle does not contract.
The PPP1R12A gene belongs to a family of genes called serine/threonine phosphatases (serine/threonine phosphatases).
A gene family is a group of genes that share important characteristics. Classifying individual genes into families helps researchers describe how genes are related to each other. For more information, see What are gene families? (http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/handbook/howgeneswork/genefamilies) in the Handbook.
Cytogenetic Location: 12q15-q21
Molecular Location on chromosome 12: base pairs 80,167,342 to 80,329,234
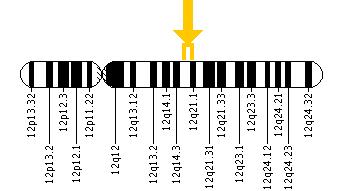
The PPP1R12A gene is located on the long (q) arm of chromosome 12 between positions 15 and 21.
More precisely, the PPP1R12A gene is located from base pair 80,167,342 to base pair 80,329,234 on chromosome 12.
See How do geneticists indicate the location of a gene? (http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/handbook/howgeneswork/genelocation) in the Handbook.
You and your healthcare professional may find the following resources about PPP1R12A helpful.
You may also be interested in these resources, which are designed for genetics professionals and researchers.
See How are genetic conditions and genes named? (http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/handbook/mutationsanddisorders/naming) in the Handbook.
actin ; atom ; cell ; cell division ; contraction ; enzyme ; gene ; myosin ; oxygen ; phosphatase ; phosphate ; phosphorus ; protein ; subunit
You may find definitions for these and many other terms in the Genetics Home Reference Glossary (http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/glossary).
The resources on this site should not be used as a substitute for professional medical care or advice. Users seeking information about a personal genetic disease, syndrome, or condition should consult with a qualified healthcare professional. See How can I find a genetics professional in my area? (http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/handbook/consult/findingprofessional) in the Handbook.