Prototype for Adult and Pediatric Medical Orders During a Radiation Incident
 View/Print as PDF (PDF - 565 KB) View/Print as PDF (PDF - 565 KB)
Table of contents
- Administrative information
- Admit to
- Diagnoses
- Precautions
- Urgent consultations
- Condition
- Vital signs
- Allergies
- Activity
- Diet
- Height, weight
- Age
- IV fluid management
- Foley catheter management
- Monitor I/O
- Deep vein thrombosis prophylaxis
- Respiratory therapy
- Wound care
- Orthopedic care
- Admission studies: labs, imaging
- Standing labs
- Electrocardiogram
- Radiation dose assessment
- Blood bank
- General medications
- Radioisotope decorporation or blocking agents
- Neutropenia therapy and antimicrobials
- Notes
- Body chart for recording results of radiation survey
top of page
1. Administrative information
Name: __________________________________
Unique Identifier: ____________
Address: _________________________________
Phone: _______________
Spoken language: __________
Unaccompanied minor: _________
Next of kin contact information: _________________________________
Special needs: _________________________________________________
top of page
2. Admit to:
__ Hospital ward ______________ Area_______________
__ Team: _______________ ICU_______________
__ Physician: _________________ Other _______________
top of page
3. Diagnoses
Acute Non-radiation Related Admission Diagnoses:
a. ______________________________
b. ______________________________
c. ______________________________
d. ______________________________
e. ______________________________
f. ______________________________
Acute Radiation-related Admission Diagnoses
a. Radiation contamination? Yes_____ No_____
See REMM Body Chart (page 18) to record whole body radiation survey.
__ External contamination with Isotope (Specify or unknown) ____________
__ Internal contamination with Isotope (Specify or unknown) ____________
__ Contamination suspected, Isotope uncertain
b. Radiation Exposure / Acute Radiation Syndrome (ARS)?
Yes_____ No_____
Other potential complicating factors
__ Mass casualty incident
__ Other, Specify __________________
Specific populations potentially requiring more customized management?
Yes____ No_____
__ Infant (< 1 y)
__ Child (1-16 y) __ Age > 65 y
__ Pregnant/Possibly pregnant __ Immunosuppressed
__ Other, Specify ___________________________________
top of page
4. Precautions
Infectious
__ Contact
__ Droplet
__ Airborne
__ Reverse Isolation/Neutropenic
Radiation precautions
__ Precautions: Single room, gown, mask, cap, boots, and gloves
__ Use medical facility procedures for discarding all biological/physical/radioactive waste, including linens/towels/trash/personal protective equipment.
__ Contact Radiation Safety Officer for additional instructions.
Phone: ______________ Page: ____________
__ Place Radiation Safety Sign on door if patient has internal or external radioactive contamination
__ Notify pregnant staff that entry to room is prohibited if patient is/may be contaminated.
__ Everyone entering room/area of contaminated patient must wear personal radiation dosimeter assigned by Radiation Safety.
__ Use medical facility procedures for disposal of radiation waste, including linens/towels/trash/personal protective equipment.
See guidance
top of page
5. Urgent consultations: specify
__ Pediatric Hematology/Oncology
__ Adult Hematology / Oncology__ Transfusion Medicine
__ Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation __ Radiation Oncology
__ Mental Health / Psychiatry __ Endocrinology
__ Ophthalmology __ Pain Service
__ Dermatology / Plastic Surgery __ Gastroenterology
__ Radiation Safety __ Burn Therapy
__Other _______________
top of page
6. Condition
__ Good __ Fair __ Stable __ Guarded __ Critical
top of page
7. Vital Signs
__ q 2 hours X 4 __ Ward routine
__ q 4 hours X 4
Notify physician for:
Temperature ____>38 °C ____ Other: ___________
SBP: _____>180, <100 ____ Other: ___________
DBP: _____ >100, <50 ____ Other: ___________
HR: _____>100, <50 ____ Other: ___________
RR: ______ >30, <8 ____ Other: ___________
O2 saturation: _____<92% ____ Other: ___________
top of page
8. Allergies
__ No Known Drug Allergies (NKDA)
__ Allergies (drugs, foods)
If yes, specify: ________________________________________
top of page
9. Activity
__ Bed rest __ Bathroom privileges
__ Out of bed every ___ hrs. __ Ambulate as tolerated
__ Confine to room
top of page
10. Diet
__ Regular Diet __ Liquids (full, clear) __ NPO
__ Advance as tolerated
__ Neutropenic diet
__ Special dietary needs/requests: _______________________
top of page
11. Height, weight
Height: ____ feet ____ inches or ____ cm
Weight: ____ lbs. ____ oz. or ____ Kg
Repeat body weight:
q ____ hours q ____ days
top of page
12. Age
Months (if <3 years) _____ Years _____
top of page
13. IV fluid management
__ IV Fluids: ______ @ _____ cc/hr, with additive ______
__ IV Fluids: ______ @ _____ cc/hr, with additive ______
top of page
14. __ Foley catheter management (specify) _____________
__ Use radiation precautions for urine and feces for patients with internal radiation contamination.
top of page
15. __ Monitor I / O
Frequency ____________
__ Use radiation precautions for urine and feces for patients with internal radiation contamination.
top of page
16. Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) prophylaxis1
__ TED hose to Bilateral Lower-Extremities
__ Sequential Compression Devices (SCD)
__ Anticoagulation regimen _____________________________________
__ Other
Note: The potential benefit of anticoagulation (e.g. heparin1, 2) should be balanced against the risk of excessive bleeding in patients with severe thrombocytopenia or significant gastrointestinal toxicity.
top of page
17. Respiratory Therapy
__ Use radiation precautions for personnel, equipment, and waste if
patient has internal radiation contamination.
__ Room air __ Chest tube care (Specify)___________
__ Titrate oxygen supplementation for Oxygen saturation > ____%
__ Nebulizer treatment (Specify) ____________________________________
top of page
18. Wound care1 (see also item 25)
__ Decontaminate external wounds if there is external contamination.
See REMM contaminated wound care recommendations.
__ Sterile dressing to wounds daily
__ Monitor waste
__ Use medical facility procedures for discarding
biological/radioactive/physical waste
and linens/towels/trash/personal protective equipment.
__ Radiation precautions (needed if patient has radiation contamination)
__ Silvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)2 cream topically to burns
__ Bacitracin topically to burns
__ Other wound management per Burn team/Dermatology/Surgery:
Pager ____________ Phone ________________________
top of page
19. Orthopedic care
__ Splint/brace/cast
__ Other orthopedic management procedure per orthopedics:
Pager ___________ Phone ________________________
top of page
20. Admission studies: Labs, Imaging
Labs
__ CBC w/differential
__ Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP) / Chem 14
__ Cardiac enzymes
__ PT / PTT
__ Urinalysis
__ Urine culture
__ Blood culture
__ Urine HCG
__ Serum HCG
__ Thyroid Function Tests (Specify) _____________
Serologies:
__ Herpes Simplex Virus type 1 (HSV-1)
__ Herpes Simplex Virus type 2 (HSV-2)
__ Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
__ Varicella-zoster virus (VZV)
Imaging
__ Chest x-ray ______ PA/Lateral _________ Portable
__ Other imaging studies Specify: _________________
top of page
21. Standing labs / studies
__ CBC w/diff q ___ hours, x ___ days,
Followed by q ___ until further orders
__ Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP) / Chem 14
Followed by q ____ hours, x ____ days
Followed by q ____ until further orders
top of page
22. Electrocardiogram
__ Electrocardiogram
__ STAT Electrocardiogram for chest pain, notify physician
top of page
23. Radiation Dose Assessment
A. Biodosimetry and Bioassay assays
B. Biodosimetry assays for radiation exposure
-
See REMM information on
-
Estimated whole body dose from exposure: _____ (Gray)
-
Using which tool(s) ______________________
e.g., vomiting, lymphocyte depletion kinetics, dicentric chromosome assay
Note: if different assays give different results
-
METREPOL Scores: Heme___ GI___ Neuro____Cutaneous____
-
Response Category (RC score) __________
Explain METREPOL
-
Date of exposure: ____________
-
Time of exposure: ____________
-
Location of patient at time of exposure:____________
-
Estimated whole body/partial body dose, specify ________ (dose)
-
Dose unknown: _______
Dicentric Chromosome Assay Instructions:
-
Draw extra green top tube and provide: date ________ time _______
-
See REMM for location of approved US laboratories that perform this test.
-
Send this tube ON ICE for outside lab study
-
To the attention of: _____________________________________
-
Name of lab:_____________________________________
-
Address of lab:____________________________________
C. Radiation bioassay for evaluating/managing internal decontamination
top of page
24. Blood bank
__ Type and cross match
__ Type and screen
For ____ units of packed red blood cells
For ____ units of platelets
Note:
-
Use only leukoreduced AND irradiated products, if available, unless it is known with certainty that the patient was exposed to alow dose of radiation, e.g. less than 100 cGy.
-
If radiation whole body dose is not known with certainty, leukoreduced AND irradiated products are preferred, if available.
-
See REMM blood use page for additional information.
top of page
25. General Medications1:
-
Suggested dose ranges for pediatric patients (PEDS) are included for some but not all drugs.
-
Drug names are generally listed as follows Generic (Brand) names
-
Some drugs with bold blue font have DailyMed hyperlinks with additional information.
For gastric acid suppression:
__ Lansoprazole (Prevacid)2 15-30 mg PO daily
PEDS: 1 mg/kg, max 30 mg/dose.
Dose: ______
For radiation-induced nausea & vomiting:
__ Ondansetron (Zofran)2 4 mg IV q 8h PRN nausea/emesis
PEDS: 0.15 mg/kg, max 8 mg, IV/PO Q 8hrs PRN.
Dose: _____
__ Lorazepam (Ativan)2 0.5 mg - 1 mg PO q 6-8h PRN
anxiety/insomnia/breakthrough nausea
PEDS: 0.03 mg/kg IV/PO q 6 hrs PRN.
Dose: ______
__ Prochlorperazine2 10 mg PO/IM/IV q 6-8h PRN
anxiety/insomnia/breakthrough nausea
See ASCO antiemetic guidelines for adults3:
See New England Journal of Medicine June 5, 2008 article:
Chemotherapy induced nausea and vomiting3
See National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) Antiemetic Guideline for Adults:
NCCN Guideline Version 1.20123
For fever:
__ Acetaminophen (Tylenol)2 650 mg PO q 6 - 8h PRN temperature> 38 °C
PEDS: 15 mg/kg, max 650 mg PO Q 6 hrs PRN.
Dose: _______
For diarrhea:
__ Loperamide hydrochloride (Imodium)2:
For rash:
__ Topical sterile dressing
__ Diphenhydramine hydrochloride (Benadryl)2 25-50 mg PO q 4-6 hours
for pruritis, not to exceed 300 mg/24 hours
PEDS: 1 mg/kg, max 50 mg IV/PO Q 6 hrs PRN.
Dose _______
For pain:
___ Morphine sulphate2 ____ mg ____ route ____ frequency
PEDS: 0.05-0.1 mg/kg IV Q 2 hrs PRN; 0.2-0.5 mg/kg PO Q 4 hrs PRN.
Dose _____
For skin burns: (see also item 18: wound care)
Burn topical regimen __________________________________________
Replace body fluid ___________________________________________
Other burn therapy __________________________________________
For oral mucositis:
Mouth care regimen __________________________________________
top of page
26. Radioisotope decorporation or blocking agents:
|
Medical Countermeasure
|
Administered for
|
Route of
Administration
|
Dosage
|
Duration
|
|
Ca-DTPA2,4
Zn-DTPA2,4
See REMM's DTPA information.
See FDA's Zn-DTPA drug label.
See FDA's Ca-DTPA drug label.
|
Americium
(Am-241)2
Californium
(Cf-252)3
Cobalt
(Co-60)3
Curium
(Cm-244)2
Plutonium
(Pu-238 and
Pu-239)2
Yttrium
(Y-90)3
|
IV2:
Give once daily as a bolus or as a single infusion, i.e., do not fractionate the dose.
DTPA is FDA-approved for intravenous Rx of known or suspected internal contamination with Am, Cm, and Pu only.
Nebulized inhalation2:
DTPA is FDA-approved for nebulized inhalation in adults only, and if the route of contamination is through inhalation.
|
IV:
1 g in 5 cc 5% dextrose in water (D5W) or 0.9% sodium chloride (normal saline, NS) slow IV push over 3-4 minutes
OR
1 g in 100-250 cc D5W or NS as an infusion over 30 minutes
PEDS:
<12 years old:
14mg/kg IV qd, no more than 1g/day
Nebulized inhalation:
1 g in 1:1 dilution with sterile water or NS over 15-20 min
PEDS: nebulized dosing same as adults
|
-
Ca-DTPA for the first dose
-
Give Zn-DTPA for any follow-up doses (i.e., maintenance as indicated)
-
Duration of therapy depends on total body burden and response to treatment
|
|
Potassium iodide2
See REMM's KI summary information.
See FDA's KI information.
|
Iodine
(I-131)
|
PO
|
Adults >40 years:
130 mg/day (for projected thyroid dose ≥500 cGy)
Adults 18-40 years:
130 mg/day (for projected thyroid dose
≥ 10 cGy)
Pregnant or lactating women of any age: 130 mg/day (for projected thyroid dose
≥ 5 cGy)
PEDS:
3-18 yrs:
65 mg/d
1 month - 3 yrs:
32.5 mg/d
Birth-1 month:
16 mg/d
|
-
Some incident will require only a single dose of KI.
-
Incident managers may recommend additional doses if ongoing radioactive iodine ingestion or inhalation represents a continuing threat.
-
See also: Potassium Iodide (KI): Duration of Therapy.
|
|
Prussian blue, insoluble2
See REMM's Prussian Blue summary information.
See FDA's Prussian Blue drug label.
|
Cesium
(Cs-137)
Thallium
(Tl-201)
|
PO
|
Adults:
3 g PO tid (see FDA package insert)
OR
1 - 3 g PO tid with 100-200 mL water, up to 10-12 g/day (based on Goiânia accident data)
PEDS:
>12 yrs:
1 - 3 g po TID;
2-12 yrs:
1 gm TID
|
-
Minimum 30 days course per FDA
-
Obtain bioassay and whole body counting to assess treatment of efficacy
-
Duration of therapy depends on total body burden and response to treatment
|
top of page
27. Neutropenia therapy, if indicated1, 5:
Neutropenia definition:
a total count of neutrophils + bands in the peripheral blood <1,000 /µL
-
Although the 3 drugs listed below are FDA-approved for the treatment of chemotherapy induced neutropenia, none is approved either for radiation-induced neutropenia or as prophylactic treatment prior to the onset of neutropenia.
-
See additional REMM information on white cell growth factors/cytokines.
-
In a mass casualty radiation event, use of these drugs would be off-label or require a formal Emergency Use Authorization.
Myeloid cytokines
|
Cytokine3
|
Adult dose
|
Pregnant Women6
|
|
G-CSF or filgrastim3 (Neupogen)
|
-
Subcutaneous administration
-
5 μg/kg/day via single daily injection
-
Continue until absolute neutrophil count
> 1.0 x 109 cells/L
-
PEDS: 5 μg/kg/day via single daily injection3
|
Class C6
(Same as adults)
|
|
Pegylated
G-CSF or pegfilgrastim3 (Neulasta)
|
-
1 subcutaneous dose, 6 mg
-
Consider second 6 mg dose 7 or more days after initial dose, if significant neutropenia persists
|
Class C6
(Same as adults)
|
|
GM-CSF or sargramostim3(Leukine)
|
|
Class C6
(Same as adults)
|
See Practice Guidelines for myeloid growth factors
For Antimicrobial prophylaxis with neutropenia1:
-
For patients with neutropenia who have NOT HAD NEUTROPENIC FEVER.
-
Use as appropriate for each patient.
-
Drugs listed are examples only.
Anti-bacterial prophylaxis:
__ Levofloxacin (Levaquin)2 500 mg PO/IV daily
PEDS: 16 mg/kg/day divided q12H NOT TO EXCEED ADULT DOSE
Dose: __________
Anti-viral prophylaxis (neutropenia without fever)
__ Acyclovir (Zovirax)2 400 mg PO q12h, or
__ Acyclovir (Zovirax)2 250 mg/m2 IV q12h
PEDS: 250 mg/m2 IV bid or 10 mg/kg IV bid
Dose: _________
Anti-fungal prophylaxis (neutropenia without fever)
__ Fluconazole (Diflucan)2 400 mg PO/IV daily - beginning when
absolute neutrophil Count (ANC) becomes < 1000
PEDS: 5 mg/kg PO/IV daily, max 400 mg daily
Dose: _________
or
__ Posaconazole (Noxafil)2 200 mg PO tid with food - beginning when absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) becomes < 1000
For treatment of neutropenia AND fever (defined as T>38 °C while neutropenic)1
Anti-microbial work-up and therapy
__ Blood cultures __ Urinalysis w/culture
__ Sputum culture + sensitivity __ Chest x-ray
__ Cefepime (Maxipime)2 2gm IV q 8h
PEDS: 50 mg/kg, max 2000 mg IV Q8h
Dose: ________
__ Vancomycin (Vancocin)3 1gm IV q 12h –
Consider if: suspected catheter-related infection, skin or soft tissue infection,
pneumonia or hemodynamic instability.
Consider trough level before 4th dose
PEDS: 15 mg/kg IV Q8h
Dose: _____
Antifungal therapy
Consider one of the following1 if: fever >72 hours on antibacterial therapy, evidence of fungal infection or hemodynamic instability.
__ Voriconazole (Vfend)3 6mg/kg IV q12h for two doses, then 4 mg/kg IV q12h
PEDS: 15 mg/kg IV Q8h
Dose: ______
__ Caspofungin (Cancidas)2 70 mg IV once then 50 mg IV daily
PEDS: 70 mg/m2 IV once, then 50 mg/m2 IV daily
(max dose 70 mg once then 50 mg daily)
Dose: ___
__ Liposomal amphotericin B (Ambisome)2 3 mg/kg/day IV over 1-4h
PEDS: same dose
Dose: ___
__ Amphotericin B lipid complex (Abelcet)2 3 mg/kg/day IV over 1-4h
PEDS: same dose
Dose: ___
See Fever and Neutropenia Guidelines with cancer:
top of page
NOTES
1. Suggested drugs are listed as representatives of a functional class, and no specific medication endorsement is implied. Dosages are based on a 70 kg adult with normal baseline renal and hepatic function. Appropriate dosage adjustments should be made based on age, weight, drug-drug interactions, nutritional status, renal and hepatic function, and any other patient-specific characteristics that may apply.
2. FDA approved for this indication
3. This drug is not approved by the FDA for this indication. If used, this would be an “off label use�, and physician discretion is strongly advised.
4. Ca-DTPA and Zn-DTPA have not been approved by FDA for treating internal contamination with californium, thorium, and yttrium. For initial treatment, Ca-DTPA is recommended, if available, within the first 24 hours after internal contamination.
Zn-DTPA is preferred for maintenance after the first 24 hours, if available, due to safety concerns associated with prolonged use of Ca-DTPA.
5. When to initiate treatment with cytokines
-
Initiation of treatment should be strongly considered for victims who develop an absolute neutrophil count of < 0.500 x 109 cells/L and are not already receiving colony-stimulating factor.
-
Evidence from animal studies indicates that outcomes may be improved if colony stimulating factors are administered as soon as possible after radiation exposure, and prior to the onset of neutropenia.
-
Although most therapy for ARS is directed at actual clinical signs and symptoms, some clinical effects of ARS can be anticipated and potentially mitigated, as with the use of prophylactic white cell cytokines. This prophylactic use is also off label.
-
Emergency Use Authorization will be required for use of cytokines for radiation induced neutropenia in a mass casualty setting.
-
See published guidelines links in section 24.
6. For pregnant women:
-
Experts in biodosimetry must be consulted.
-
Any pregnant patient with exposure to radiation should be evaluated by a health physicist and maternal-fetal specialist for an assessment of risk to the fetus.
-
Class C refers to U.S. Food and Drug Administration Pregnancy Category C, which indicates that studies have shown animal, teratogenic, or embryocidal effects, but there are no adequate controlled studies in women; or no studies are available in animals or pregnant women.
Body Chart for Recording Results of Radiation Survey
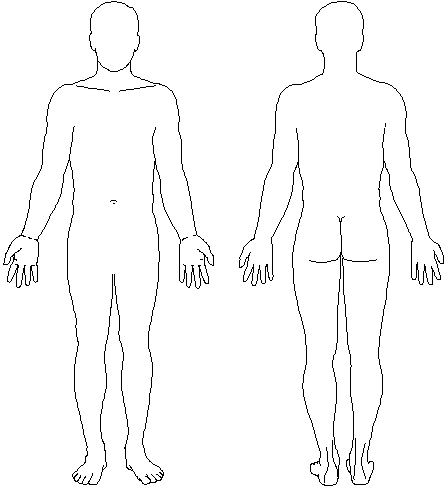
top of page
|


