National Institutes of Health
- The primary NIH organization for research on Diabetes is the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
 A service of the U.S. National Library of Medicine
A service of the U.S. National Library of Medicine  National Institutes of Health
National Institutes of Health
Diabetes is a disease in which your blood glucose, or sugar, levels are too high. Glucose comes from the foods you eat. Insulin is a hormone that helps the glucose get into your cells to give them energy. With type 1 diabetes, your body does not make insulin. With type 2 diabetes, the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well. Without enough insulin, the glucose stays in your blood.
Over time, having too much glucose in your blood can cause serious problems. It can damage your eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Diabetes can also cause heart disease, stroke and even the need to remove a limb. Pregnant women can also get diabetes, called gestational diabetes.
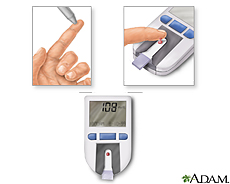
A blood test can show if you have diabetes. Exercise, weight control and sticking to your meal plan can help control your diabetes. You should also monitor your glucose level and take medicine if prescribed.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
 (07/10/2012, HealthDay)
(07/10/2012, HealthDay)
References and abstracts from MEDLINE/PubMed (National Library of Medicine)
 Facts about Diabetes: A Leading Cause of Death in the U.S.
Facts about Diabetes: A Leading Cause of Death in the U.S.